Adipose Connective Tissue Drawing
Adipose Connective Tissue Drawing - Also present are various leukocytes (white blood cells) involved in immune response. Based on its location, fat tissue is divided into parietal (under the. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ecm). It is found mainly under the skin but also in deposits between the muscles, in the intestines and in their membrane folds, around the heart, and. Mesenchymal stem cells are pluripotent cells that can transform into various cell types, including fat cells, bone cells, cartilage cells, and muscle cells, among others. Web figure 33.9.1 33.9. There are two types of adipose tissue: Body fat is primarily known for storing and releasing energy and providing. Web adipose tissue, otherwise known as body fat, is a connective tissue that extends throughout your body. Web adipose tissue figure 5.
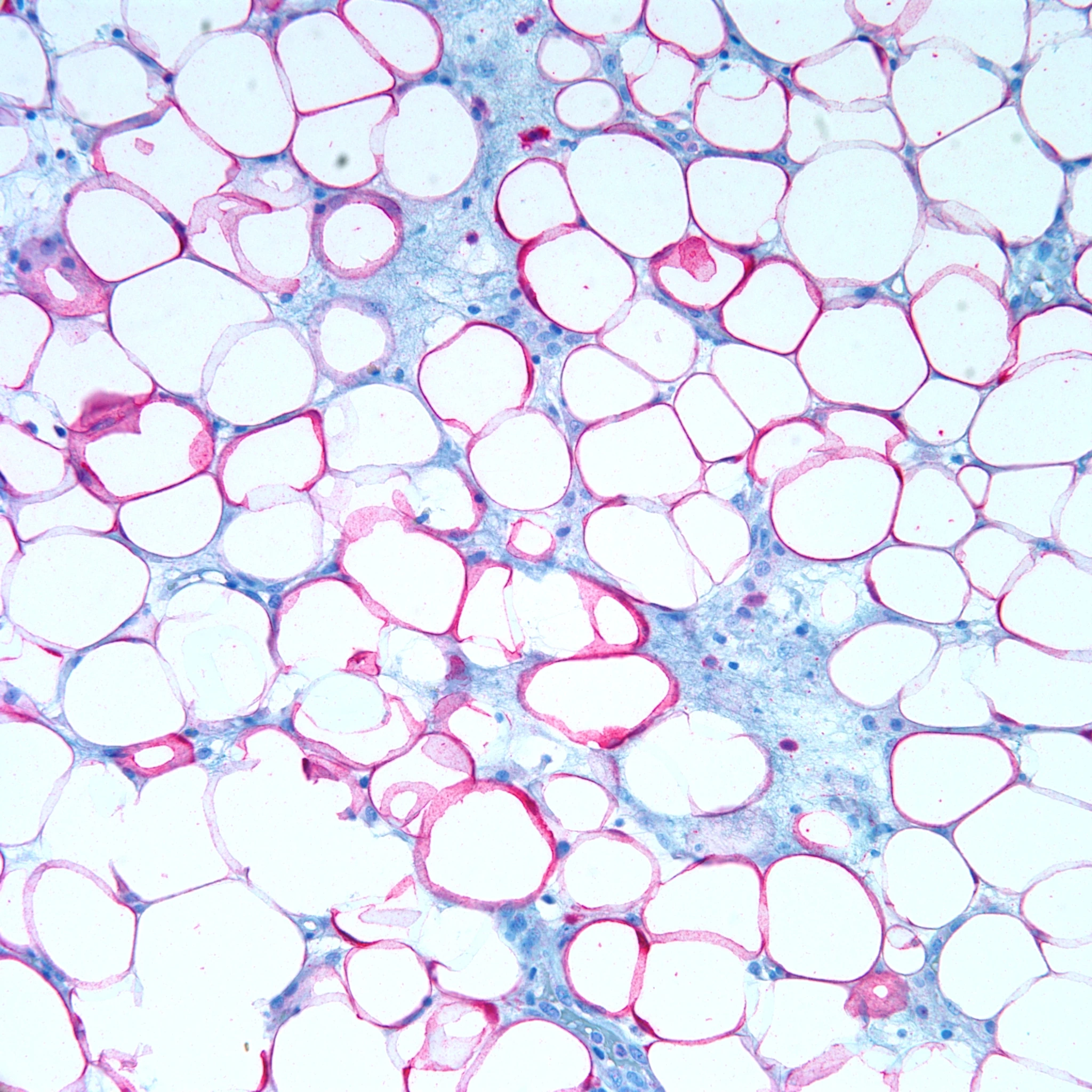
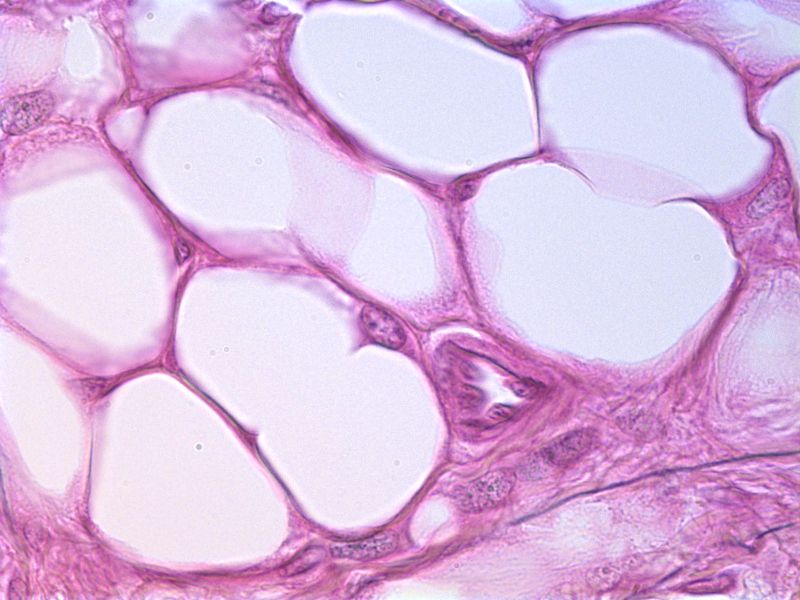
Web white adipose connective tissue is composed of lobules of adipocytes separated by prominent connective tissue septa containing blood and lymphatic vessels. This video is a part of our histology video course (htt. Multiple hormones, growth factors, and cytokines are expressed by adipocytes and their. Adipose is also located between muscles and around. Web adipose tissue, connective tissue consisting mainly of fat cells ( adipose cells, or adipocytes), specialized to synthesize and contain large globules of fat, within a structural network of fibres. The light purple dots you see inside the cells are an artifact of process used to make the images, and do not represent real structures. White fat and brown fat. Web adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that arises from the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes during fetal development. Erythrocytes (red blood cells), the predominant cell type, are involved in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. White adipose tissue also provide a layer of insulation, while brown adipose is found in too small quantities (in children and adults) to do this.
White adipose tissue also provide a layer of insulation, while brown adipose is found in too small quantities (in children and adults) to do this. Web learn to dray adipose connective tissue histology diagram ( for medical students) Web adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that arises from the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes during fetal development. White adipose tissue is found in many organs throughout the body, typically forming about 20% of the body. Web adipose tissue figure 5. Also present are various leukocytes (white blood cells) involved in immune response. There are two types of adipose tissue: (fat cells) are the largest component of loose connective tissue. Adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that has both structural and highly complex metabolic functions, including energy storage, glucose homeostasis, and a multitude of endocrine capabilities. White adipocytes are large, round cells (up to a 100 µm diameter) with a single droplet of lipids.
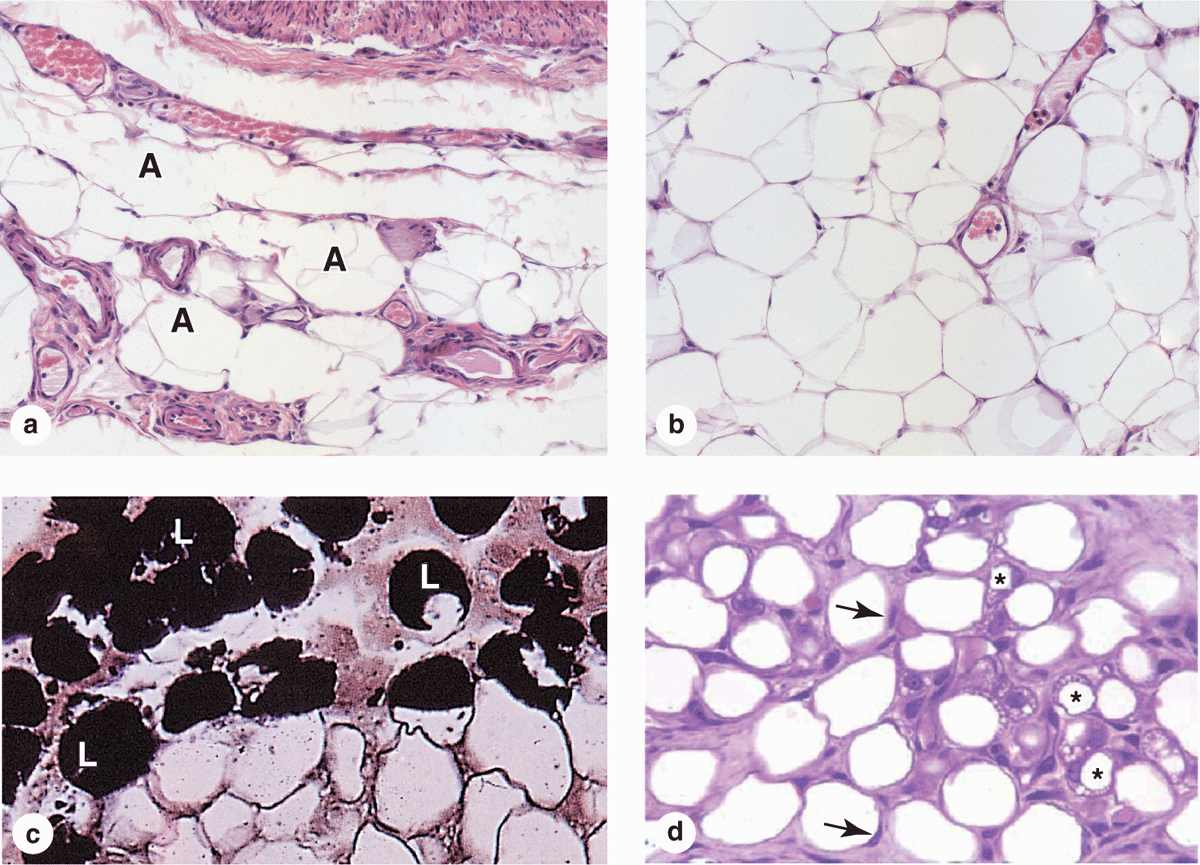
Structure of adipose tissue. AT is composed of a collagenous background
Summary of the properties of the major types of connective tissue proper. Some of the individual fat cells are often broken during tissue preparation, but the overall impression of what the tissue looks like is the important point. The cells appear empty because lipids are extracted during tissue. It comprises a diverse group of cells that can be found in.
Histology Image Connective tissue
While adipose tissue can be found in a number of places in the body, it is found primarily beneath the skin. Body fat is primarily known for storing and releasing energy and providing. Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is considered a connective tissue even though it does not have fibroblasts or a real matrix and only has a few fibers..
How to draw adipose tissue most easy way YouTube
Web adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that arises from the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes during fetal development. Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is considered a connective tissue even though it does not have fibroblasts or a real matrix and only has a few fibers. While adipose tissue can be found in a number.
Adipose tissue JacquesScience
Adipose is also located between muscles and around. It comprises a diverse group of cells that can be found in different parts of the body. White adipocytes are large, round cells (up to a 100 µm diameter) with a single droplet of lipids. White adipose tissue is found in many organs throughout the body, typically forming about 20% of the.
Adipose Connective Tissue
Web connective tissue is a term used to describe a variety of types of tissues. In drawing images of connective tissue proper preparations seen under the microscope, it is important to simplify the visuals. Brown fat does, however, release energy in the form of heat. This is a loose connective tissue that consists of fat cells with little extracellular matrix..
Adipose tissue or body fat anatomical inner cell structure outline
Brown fat does, however, release energy in the form of heat. Web figure 33.9.1 33.9. White fat and brown fat. Adipose is a connective tissue is made up of cells called adipocytes. However connective tissue differs from other types in that its cells are loosely, rather than tightly, packed.
Adipose Connective Tissue
Web white adipose connective tissue is composed of lobules of adipocytes separated by prominent connective tissue septa containing blood and lymphatic vessels. Summary of the properties of the major types of connective tissue proper. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Brown.
Adipose Connective Tissue Labeled
Erythrocytes (red blood cells), the predominant cell type, are involved in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Web adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that arises from the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes during fetal development. Web connective tissue is the tissue that connects or separates, and supports all the other types of tissues.
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 168 > Hixon > Flashcards > Slides Connective
Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is considered a connective tissue even though it does not have fibroblasts or a real matrix and only has a few fibers. White adipocytes are large, round cells (up to a 100 µm diameter) with a single droplet of lipids. The cells appear empty because lipids are extracted during tissue. Web adipose tissue figure 5..
Adipose Connective Tissue Diagram
Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web we will make it easy for medical students to make histology diagrams in short time during practical exams. (fat cells) are the largest component of loose connective tissue. This video is a part of.
A Thin Rim Of Cytoplasm Encircles The Droplet With The Nucleus Flattened Along The Edge Of The Cell.
This video is a part of our histology video course (htt. It is found mainly under the skin but also in deposits between the muscles, in the intestines and in their membrane folds, around the heart, and. Also called fat tissue, adipose is composed primarily of adipose cells or adipocytes. Erythrocytes (red blood cells), the predominant cell type, are involved in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Adipose Tissue Is A Specialized Type Of Connective Tissue That Has Both Structural And Highly Complex Metabolic Functions, Including Energy Storage, Glucose Homeostasis, And A Multitude Of Endocrine Capabilities.
Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ecm). Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is considered a connective tissue even though it does not have fibroblasts or a real matrix and only has a few fibers. The light purple dots you see inside the cells are an artifact of process used to make the images, and do not represent real structures. Web learn to dray adipose connective tissue histology diagram ( for medical students)
Summary Of The Properties Of The Major Types Of Connective Tissue Proper.
Brown fat does, however, release energy in the form of heat. It is an important structural element that supports and separates spaces between our organs and tissues in the human body.the cells that make this connective tissue are loosely. Web brown adipose tissue is thermogenic, meaning that as it breaks down fats, it releases metabolic heat, rather than producing adenosine triphosphate (atp), a key molecule used in metabolism. Web cells of adipose tissue are supported by reticular fibers, with connective tissue septa dividing the tissue into lobules of various sizes.
Web Adipose Tissue, Connective Tissue Consisting Mainly Of Fat Cells ( Adipose Cells, Or Adipocytes), Specialized To Synthesize And Contain Large Globules Of Fat, Within A Structural Network Of Fibres.
Based on its location, fat tissue is divided into parietal (under the. It’s found under your skin ( subcutaneous fat ), between your internal organs ( visceral fat) and even in the inner cavities of bones ( bone marrow adipose tissue). Adipose is a connective tissue is made up of cells called adipocytes. Web covers the histological structure for adipose tissue and relevant cellular physiology for adipocytes.