Cardiac Muscle Tissue Drawing
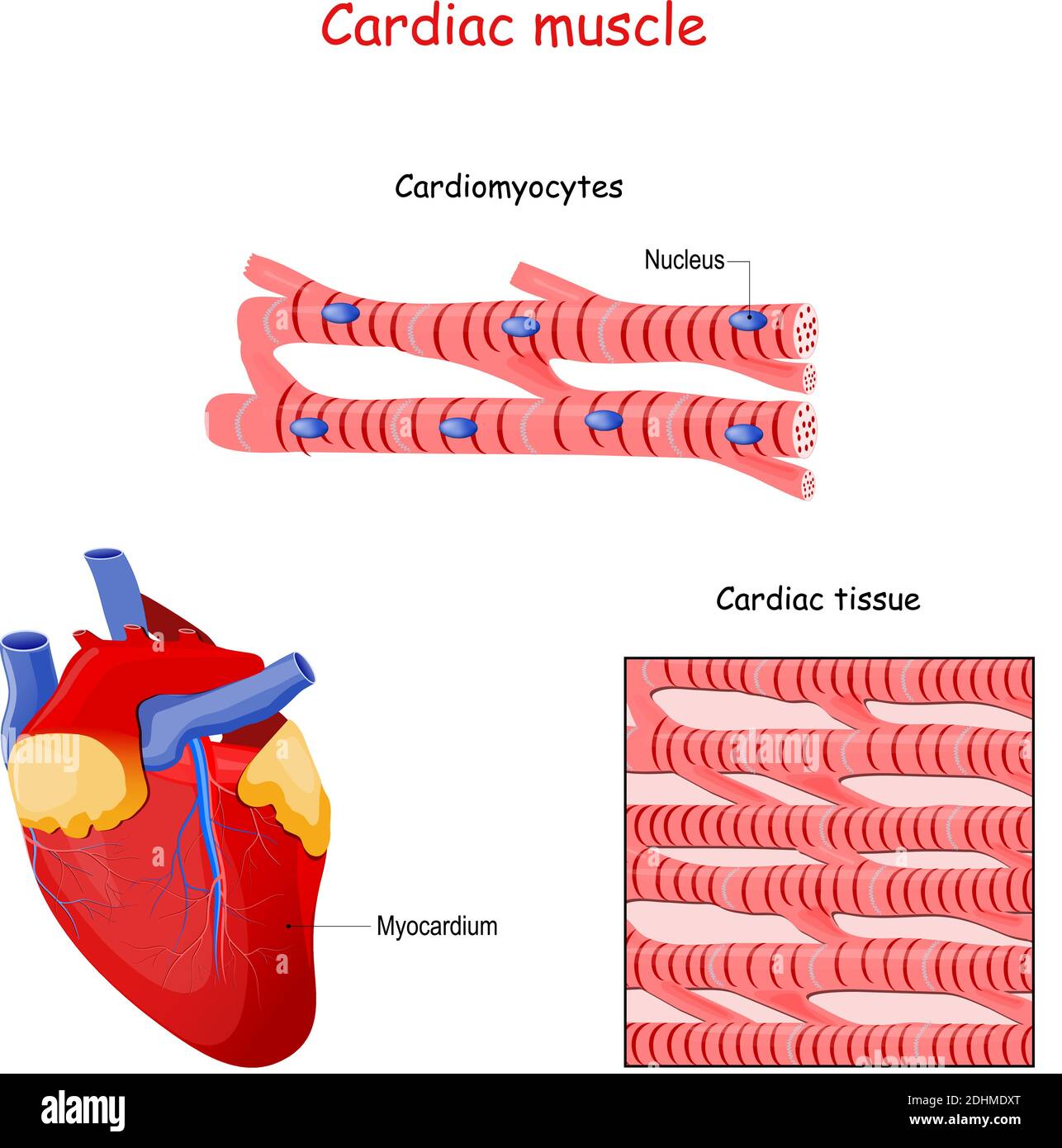
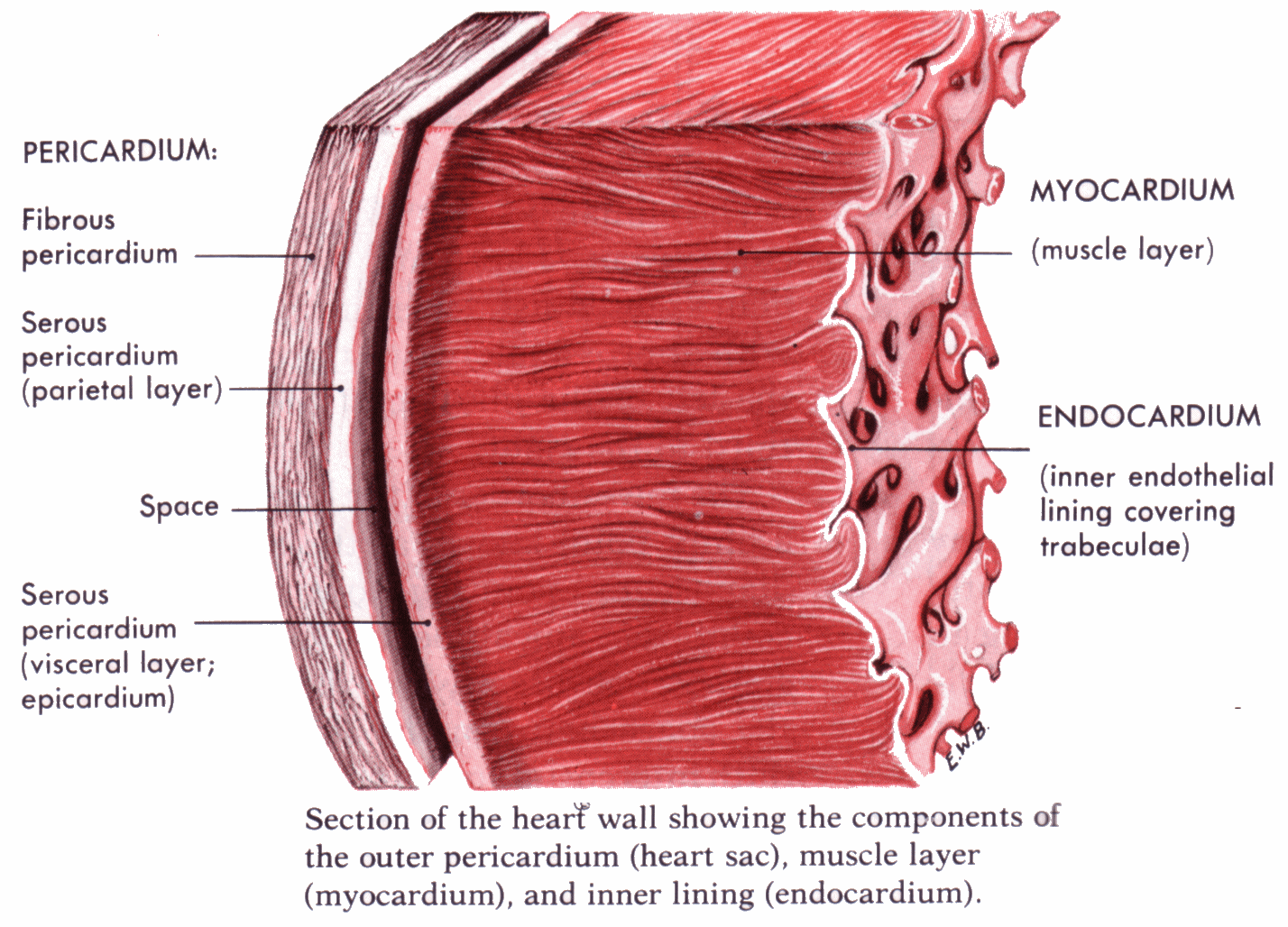
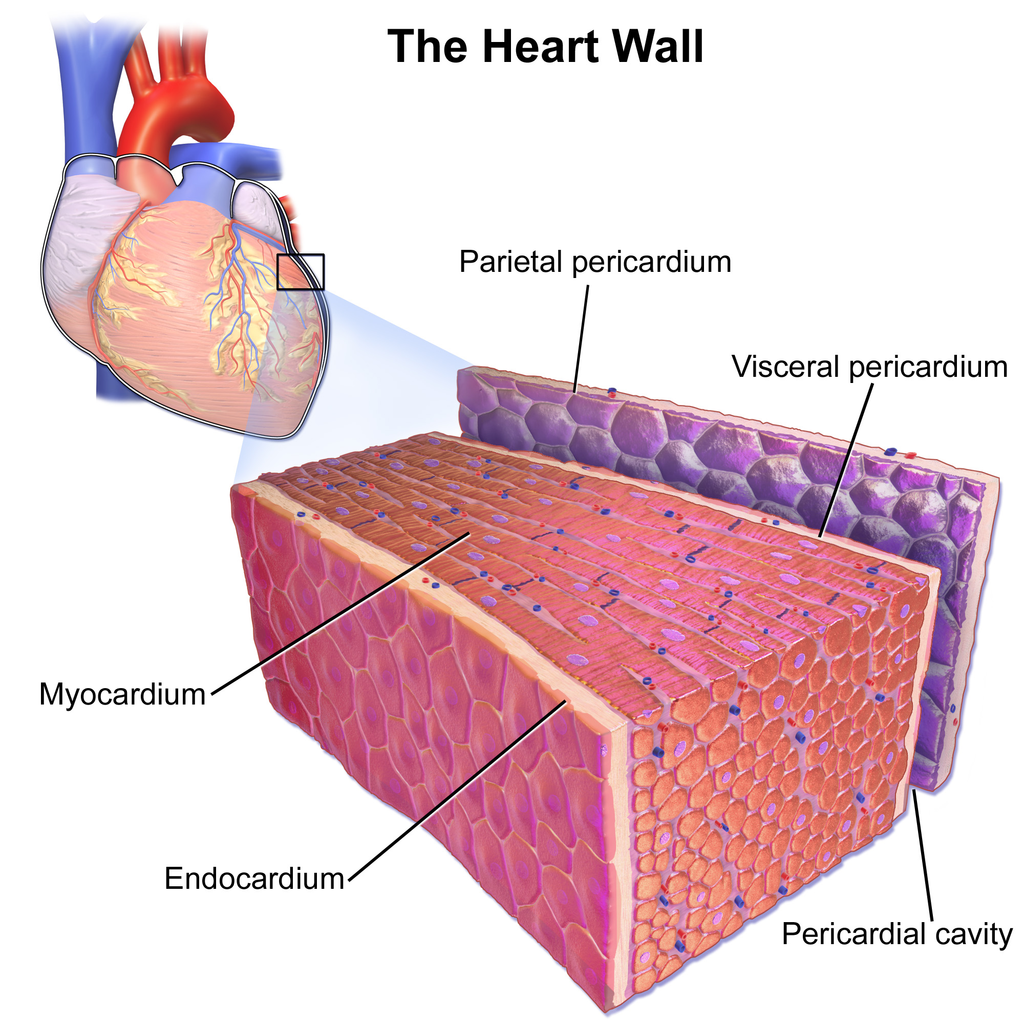
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Drawing - Web cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Two cardiac muscle cell nuclei are indicated in the labelled image. Web the cardiac muscle or the myocardium forms the musculature of the heart. 1 waiting premieres may 2, 2023 #histology #anatomy #lpanatomy. Cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is a type of muscle tissue that forms the heart. 80k views 2 years ago class 9 diagram. Cross section of cardiac muscle fibers. Web cardiac muscle cells are cylindrical cells whose ends branch and form junctions with other cardiac muscle cells. The myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium.
Web cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues. Cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is a type of muscle tissue that forms the heart. On any slide of cardiac muscle you will see cells that have been sectioned in every possible direction, from transverse to oblique to longitudinal. These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in your heart. Let's learn more about the cardiac muscle with the help of a diagram. Web cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Components of intercalated disc cannot be resolved with the light microscope. By the end of this section, you will be able to:
There are two major types of cardiac muscle cells: Cardiac muscle histology slide identification. Components of intercalated disc cannot be resolved with the light microscope. Cardiac muscle with intercalated discs. Web cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. Describe intercalated discs and gap junctions. You will find some unique features in cardiac muscle that will help you to differentiate it. Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle ( figure 10.21 ). This feature, however, also distinguishes it from smooth muscle, the third muscle type. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
Cardiac Muscle Structure
A cardiac muscle cell typically has one nucleus located near the center. These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and. Myocardial contractile cells and myocardial conducting cells. The myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. Cardiac.
Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity Anatomy and Physiology II
Web cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues. How to draw a muscle. Cardiac muscle, in vertebrates, one of three major muscle types, found only in the heart. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood.
Muscle Cardiac Muscle Cell A hand drawn sketch by Dr. Chr… Flickr
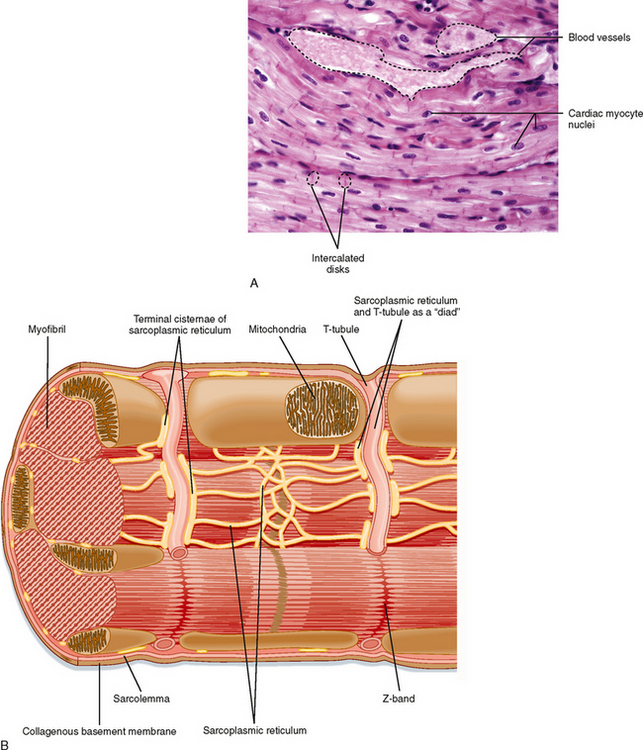
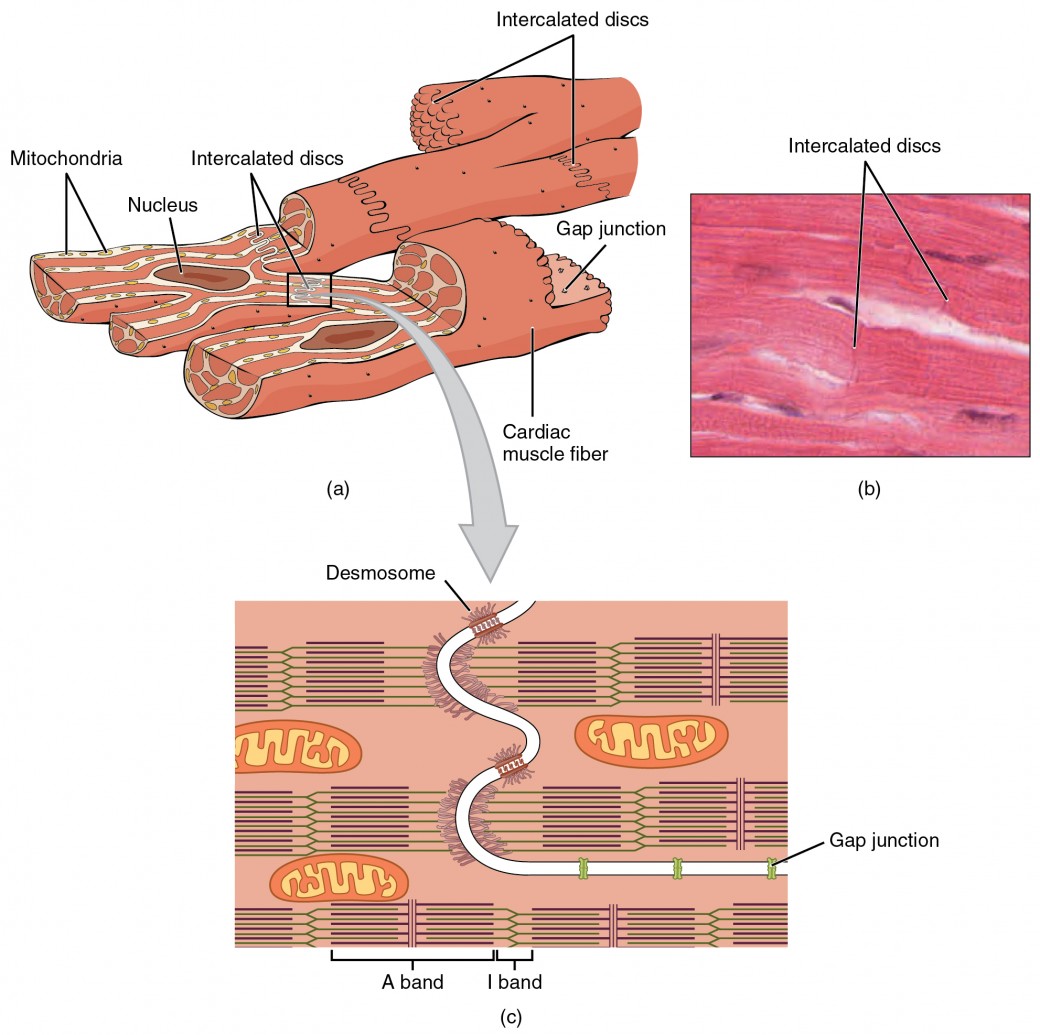
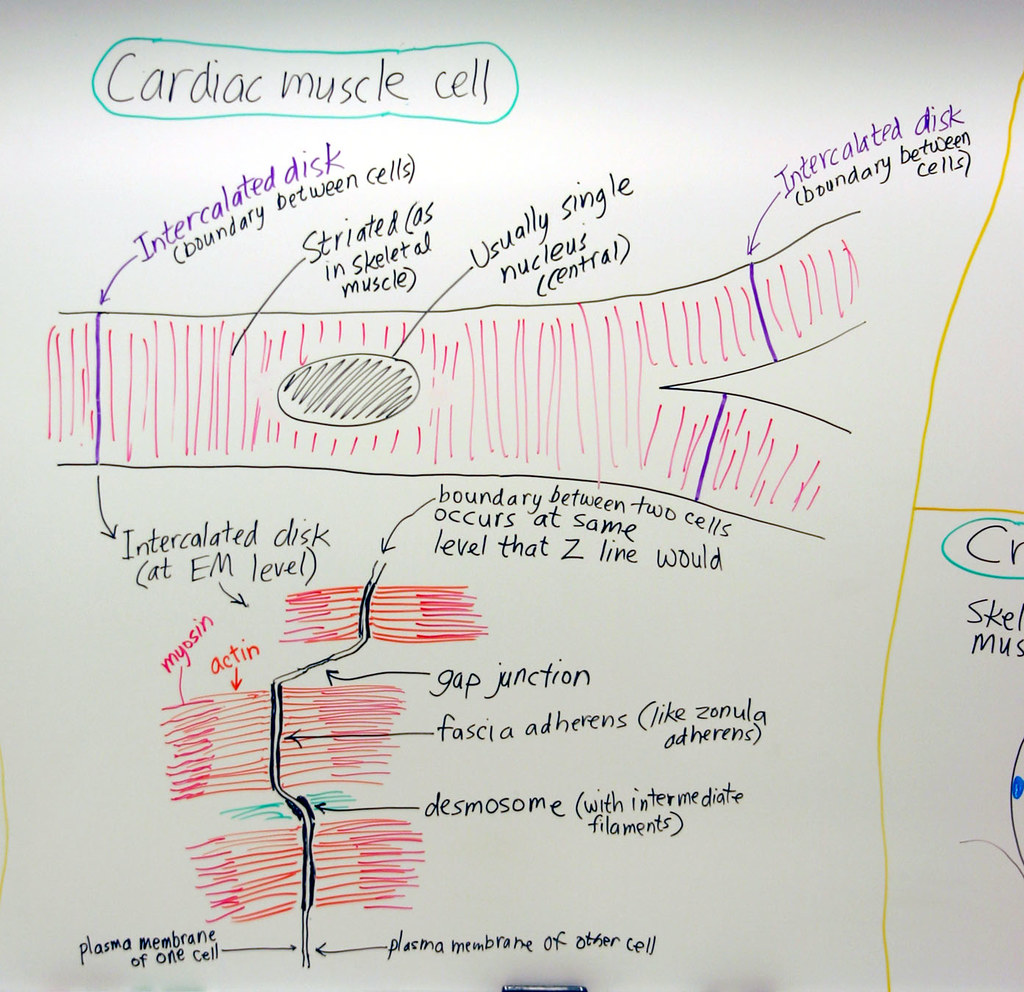
Intercalated discs are complex cell junctions between the ends of adjacent cardiac muscle fibers. Its unique structural and functional characteristics enable the heart to perform its vital role of pumping blood throughout the body continuously and rhythmically. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. On any slide of cardiac muscle you will.
Simple histology diagram of Cardiac Tissue/ Muscle Longitudinal Section
Web cardiac muscle 40x. Web draw cardiac muscle tissue diagram easily with this video. Its unique structural and functional characteristics enable the heart to perform its vital role of pumping blood throughout the body continuously and rhythmically. Web 16/10/2023 17/12/2022 by sonnet poddar. The myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an.
How to draw " Cardiac Muscles" step by step in a very easy way Type
These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and. Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. Its unique structural and functional characteristics enable the heart to perform its vital role of pumping blood throughout the.
17.2 Heart Anatomy Medicine LibreTexts
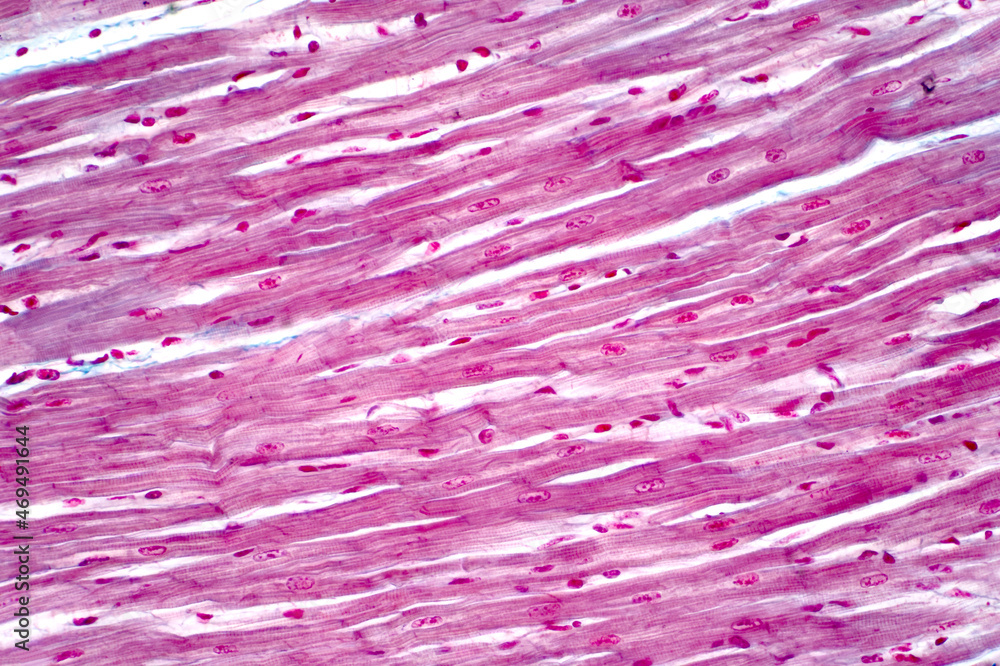
The cardiac muscle under a microscope shows a short cylindrical fiber with a centrally placed oval nucleus. These are striated and involuntary muscles that are supplied by autonomic nerve fibres. This longitudinal section of cardiac muscle fibers demonstrates two of their distinctive features, centrally located nuclei and intercalated discs. Web draw cardiac muscle tissue diagram easily with this video. Highly.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Labeled Diagram
Web in this video i have shown the simplest way of drawing muscle drawing. Intercalated discs are complex cell junctions between the ends of adjacent cardiac muscle fibers. Web 16/10/2023 17/12/2022 by sonnet poddar. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in your heart. 1 waiting premieres may 2, 2023 #histology #anatomy #lpanatomy.
Which is the cardiac muscle layer of the heart? Socratic
It performs involuntary, coordinated contractions that allow your heart to pump blood. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Describe intercalated discs and gap junctions. On any slide of cardiac muscle you will see cells that have been sectioned in every possible direction, from transverse to oblique to longitudinal. Cross section of cardiac muscle fibers.
Histology of human cardiac muscle under light microscope view for
These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and. This feature, however, also distinguishes it from smooth muscle, the third muscle type. Web neither smooth nor skeletal muscle can do this. The cells and their detailed structure is best seen on cells that. Its unique structural and functional.
12.3 Types of Muscle Tissue Human Biology
Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle ( figure 10.21 ). How to draw a muscle. On any slide of cardiac muscle you will see cells that have been sectioned in every possible direction, from transverse to oblique to longitudinal. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in.
It Is The Pen Diagram Of Skeletal, Smooth And Cardiac Muscle For Class 10, 11 And 12.
Web table of contents. Cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is a type of muscle tissue that forms the heart. In the connective tissue between cardiac. Its unique structural and functional characteristics enable the heart to perform its vital role of pumping blood throughout the body continuously and rhythmically.
Web Circulatory System > Heart Anatomy > Cardiac Muscle Tissue:
It performs involuntary, coordinated contractions that allow your heart to pump blood. The myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. Cross section of cardiac muscle fibers. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
These Are Striated And Involuntary Muscles That Are Supplied By Autonomic Nerve Fibres.
By the end of this section, you will be able to: Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Lab 4 muscle and nervous tissue. This longitudinal section of cardiac muscle fibers demonstrates two of their distinctive features, centrally located nuclei and intercalated discs.
You Will Find Some Unique Features In Cardiac Muscle That Will Help You To Differentiate It.
The individual cardiac muscle cells are arranged in bundles that form a spiral pattern in the wall of the heart. Describe intercalated discs and gap junctions. The cells and their detailed structure is best seen on cells that. Web cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.