Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life
Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life - Web the chemistry of life chapter 2 the chemistry of life 2.1 atoms and molecules 2.2 chemical compounds 2.3 mixtures 2.4 chemical reactions 2.5 types of reactions 2.6 organic molecules 2.7 macromolecules needed for life 2.7 macromolecules needed for life. Web start studying chapter 2: Removing energy (cooling) atoms and molecules decreases their motion,. In this chapter, we will explore the chemistry of how atoms are. The chapter describes biochemical compounds and reactions as well as the significance of water to life. Web chapter 2 the chemistry of life study guide terms in this set (85) the main source of energy for living things carbohydrates help carry out chemical reactions proteins contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen,. Web it covers atoms, elements, subatomic particles, chemical bonds, and chemical reactions. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Water and carbon compounds play essential roles in organisms, which carry out chemical reactions in their daily life. Web the subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What are the basic chemical principles that affect living things? Web adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature. Removing energy (cooling) atoms and molecules decreases their motion,. The center of the atom that is formed by protons and neutrons bound together with strong forces. The basic unit of matter. In your textbook, read about the role of carbon. Gas, liquid, solid atoms are the. For each of the following. Web the chemistry of life chapter 2 the chemistry of life 2.1 atoms and molecules 2.2 chemical compounds 2.3 mixtures 2.4 chemical reactions 2.5 types of reactions 2.6 organic molecules 2.7 macromolecules needed for life 2.7 macromolecules needed for life. The elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and.
The chemistry of life study guide 5.0 (4 reviews) term 1 / 72 what are the subatomic particles that make up an atom? Removing energy (cooling) atoms and molecules decreases their motion,. Web it covers atoms, elements, subatomic particles, chemical bonds, and chemical reactions. Web this chapter provides the chemistry background needed to understand the human body, its functions, and its processes. Gas, liquid, solid atoms are the. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Web chapter 2 assessment the chemistry of life term 1 / 33 the positively charged particle in an atom is called the click the card to flip 👆 definition 1 / 33 proton click the card to flip 👆 flashcards learn test match created by. Click the card to flip 👆 definition 1 / 72 protons neutrons electrons click the card. The basic unit of matter. The center of the atom that is formed by protons and neutrons bound together with strong forces.
chapter 2 The chemistry of life Crossword WordMint
2.1 the nature of matter what 3 subatomic particles make up atoms? The basic unit of matter. Removing energy (cooling) atoms and molecules decreases their motion,. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Introduction to the chemistry of life.
Biology Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life
Web chemistry of life chapter 2. Click the card to flip 👆 definition 1 / 72 protons neutrons electrons click the card. If you are author or own the copyright of this. Removing energy (cooling) atoms and molecules decreases their motion,. This document was uploaded by user and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it.
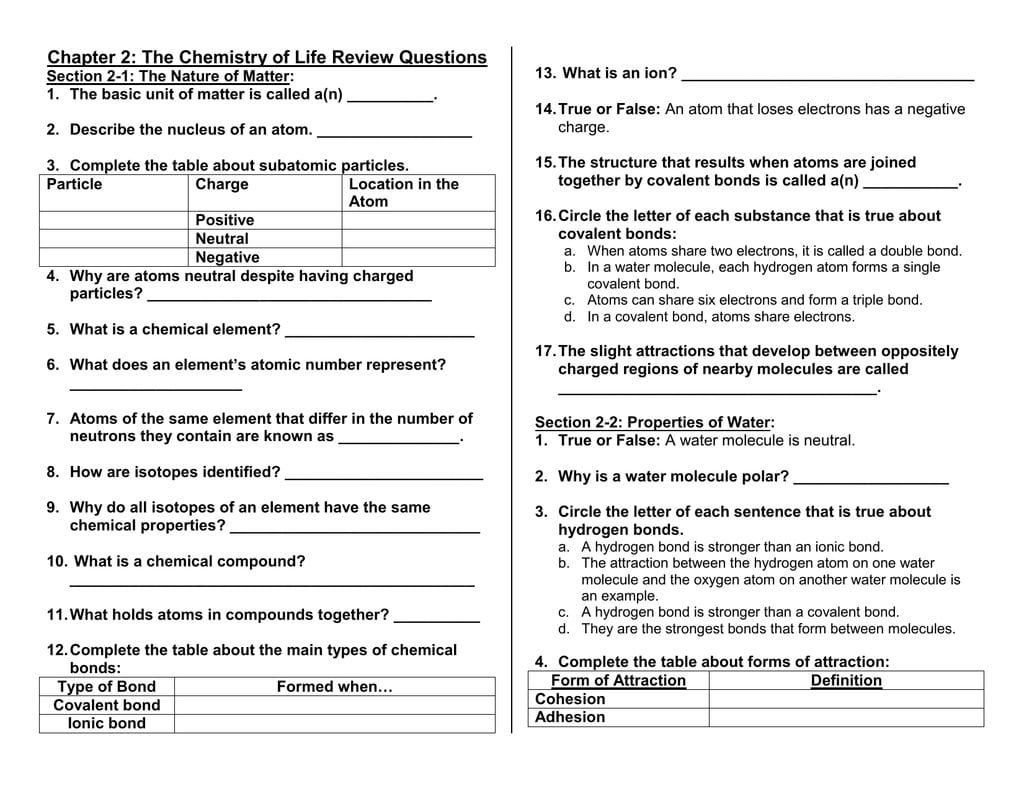
Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life Review Questions —
The chapter describes biochemical compounds and reactions as well as the significance of water to life. If you are author or own the copyright of this. The elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and. 2.1 the nature of matter what 3 subatomic particles make up atoms? Web chapter 2 assessment the chemistry of life term 1 / 33 the positively.
Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life
Web adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature. This document was uploaded by user and they confirmed that they have the permission to share it. Web section summaries/chapter 2 37 name_____ class_____ date _____ four groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Web chapter.
PPT Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web the chemistry of life (chapter 2) chemical bonds join together the molecules and compounds of life. 2.1 the nature of matter what 3 subatomic particles make up atoms? The chemistry of life study guide 5.0 (4 reviews) term 1 / 72 what are the subatomic particles that make up an atom? Removing energy (cooling) atoms and molecules decreases their.
Biology Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life Worksheet Answers —
Web this chapter provides the chemistry background needed to understand the human body, its functions, and its processes. Introduction to the chemistry of life. The chemistry of life study guide 5.0 (4 reviews) term 1 / 72 what are the subatomic particles that make up an atom? There are 3 videos in the series: Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with.
Biology Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life Worksheet Answers —
Click the card to flip 👆 definition 1 / 72 protons neutrons electrons click the card. Introduction to the chemistry of life. Web the subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. 2.1 the nature of matter what 3 subatomic particles make up atoms? In your textbook, read about the role of carbon.
Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life Worksheet Answers —
In this chapter, we will explore the chemistry of how atoms are. Web chemistry of life chapter 2. Web this chapter provides the chemistry background needed to understand the human body, its functions, and its processes. 2.1 the nature of matter what 3 subatomic particles make up atoms? If you are author or own the copyright of this.
PPT Chapter 2 Notes The Chemistry of Life PowerPoint Presentation
Web the chemistry of life chapter 2 the chemistry of life 2.1 atoms and molecules 2.2 chemical compounds 2.3 mixtures 2.4 chemical reactions 2.5 types of reactions 2.6 organic molecules 2.7 macromolecules needed for life 2.7 macromolecules needed for life. Removing energy (cooling) atoms and molecules decreases their motion,. Web chapter 2 the chemistry of life study guide terms in.
PPT Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
If you are author or own the copyright of this. Gas, liquid, solid atoms are the. Web chemistry of life chapter 2. The basic unit of matter. Web the chemistry of life (chapter 2) chemical bonds join together the molecules and compounds of life.
For Each Of The Following.
Web the subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Web start studying chapter 2: Web chemistry of life chapter 2. Web adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature.
Chemistry Of Life (Instructor Materials Preparation) 2:
Web section summaries/chapter 2 37 name_____ class_____ date _____ four groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. In your textbook, read about the role of carbon. Web chapter 2 assessment the chemistry of life term 1 / 33 the positively charged particle in an atom is called the click the card to flip 👆 definition 1 / 33 proton click the card to flip 👆 flashcards learn test match created by. Introduction to the chemistry of life.
Web Chapter 2 The Chemistry Of Life Study Guide Terms In This Set (85) The Main Source Of Energy For Living Things Carbohydrates Help Carry Out Chemical Reactions Proteins Contain Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen,.
The elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and. Web this chapter provides the chemistry background needed to understand the human body, its functions, and its processes. 2.1 the nature of matter what 3 subatomic particles make up atoms? What are the basic chemical principles that affect living things?
This Document Was Uploaded By User And They Confirmed That They Have The Permission To Share It.
Gas, liquid, solid atoms are the. Figure 2.0 foods such as bread, fruit, and cheese are rich sources of biological macromolecules. Web it covers atoms, elements, subatomic particles, chemical bonds, and chemical reactions. Data analysis and presentation (instructor materials preparation) 2.1: