Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key
Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key - When heat flows from one object to another one it is in contact with (from hot to cold) thermal equilibrium. 212 on the _________, the number 0 is absolute zero, the temperature. Web summary when matter gets warmer, the atoms or molecules in the matter move faster. Web science engineering electrical engineering hvac quiz chapter 21,22,23, and 24 the process of removing heat from a place where it is not wanted and transferring that heat to a place where it makes little or no. Web rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 5 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 4 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 3 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 2 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key. Explain how a common liquid thermometer works. Web heat flows according to temperature differences. Explore the definition and an example of. K e e = h f − b e. Each sketch shows the bridge at a different season of the year.
Web chapter 21 temperature, heat, and expansion 103. The computational example on page 312 of your textbook shows the technique ofunit conversion, called dimensional analysis, which indicates whether to multiply or divide when. After objects, in contact with each other, read the same temperature and no heat. K e e = h f − b e. Web chapter 21 temperature, heat, and expansion. Match each number with the corresponding description. That is, average molecular kinetic energy differences, not based on which substance has more molecular kinetic energy. David considers a piece of silver of mass 88.9 g. End of chapter 21b answers… Web test and improve your knowledge of chapter 21:
Web chapter 21 temperature, heat, and expansion 103. The energy that flows from a substance of higher temperature to a substance of lower temperature, commonly measured in calories or joules. That is, average molecular kinetic energy differences, not based on which substance has more molecular kinetic energy. K e e = h f − b e. Explore the definition and an example of. When two substances of different temperatures are in thermal contact, heat flows from higher temperature to lower temperature. End of chapter 21b answers… Briefl y defend your answer… The computational example on page 312 of your textbook shows the technique ofunit conversion, called dimensional analysis, which indicates whether to multiply or divide when. A measure of the average translational kinetic energy per molecule in a substance,.
13+ Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key WalterIylah
Web unlock answers 16. Web chapter 21 temperature, heat, and expansion 103. David considers a piece of silver of mass 88.9 g. After objects, in contact with each other, read the same temperature and no heat. Maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron.
13+ Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key WalterIylah
(a) size 12 {2 . 75 k %omega } {} (b) size 12 {27 . 5 %omega } {} 3. Each sketch shows the bridge at a different season of the year. The property of water to resist changes in temperature improves the climate in many places. When two objects in thermal. Energy that transfers from one object to another.
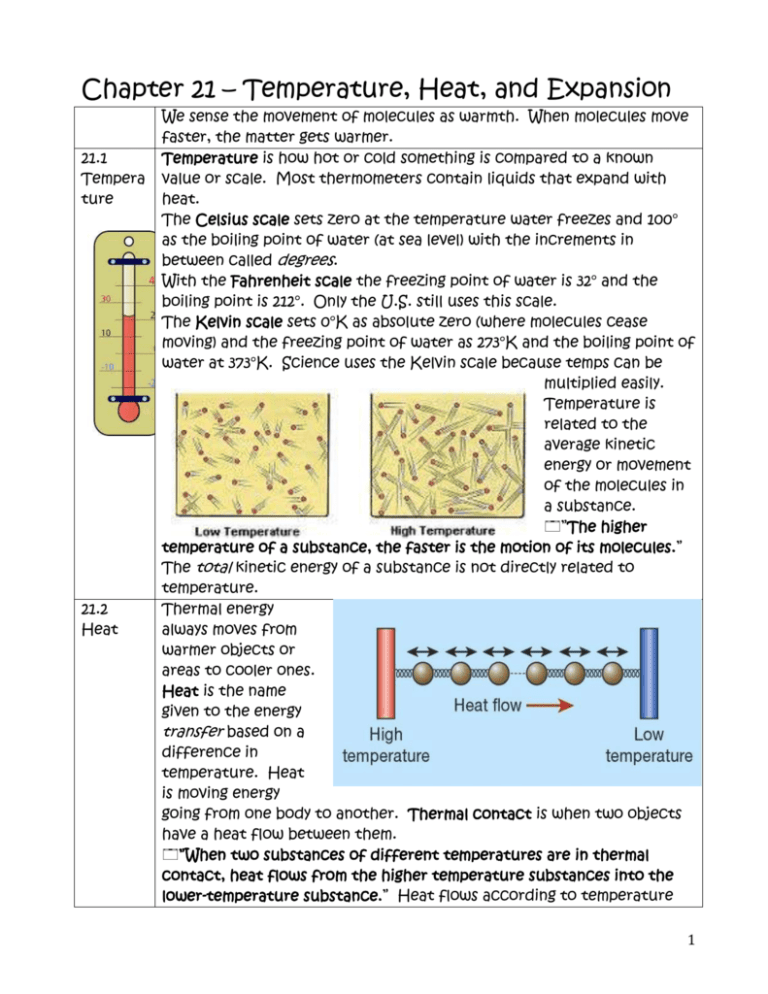
Chapter 21 Temperature, Heat, and Expansion We sense the
The energy that flows from a substance of higher temperature to a substance of lower temperature, commonly measured in calories or joules. Web on the _____ scale, the number _____ designates the temperature at which water freezes, and the number _____ is the temperature at which water boils (at 1 atm). Web rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer.
13+ Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key WalterIylah
The property of water to resist changes in temperature improves the climate in many places. Web chapter 21 temperature, heat, and expansion. Kee = hf − be. Web summary when matter gets warmer, the atoms or molecules in the matter move faster. Principles and problems (merrill physics, 1995 release) chapter 12:
Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key Study Finder
Long steel bridges often have one end fi xed while the other end rests on rockers, as shown. Click the card to flip 👆. 21.1 temperature the higher the temperature of a substance, the faster is the motion of its molecules. Principles with applications (giancoli, 6th edition) chapter 13: David considers a piece of silver of mass 88.9 g.
Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key Study Finder
Maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron. Web heat flows according to temperature differences. Click the card to flip 👆. Web chapter 21 temperature, heat, and expansion 1. Match each number with the corresponding description.
30 Temperature And Heat Worksheet Answers support worksheet
Explain how a common liquid thermometer works. Principles and problems (merrill physics, 1995 release) chapter 12: Each sketch shows the bridge at a different season of the year. Web rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 5 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 4 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion.
PHYSICS Chapter21 Temperature, Heat and Expansion PDF PDF Calorie
Briefl y defend your answer… 21.1 temperature the higher the temperature of a substance, the faster is the motion of its molecules. Click the card to flip 👆. Web on the _____ scale, the number _____ designates the temperature at which water freezes, and the number _____ is the temperature at which water boils (at 1 atm). When two objects.
13+ Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key BreigeMeryem
Web chapter 21 temperature, heat, and expansion 1. The hole expands yes cific heat. Energy that transfers from one object to another because of a temperature difference. K e e = h f − b e. 212 on the _________, the number 0 is absolute zero, the temperature.
13+ Chapter 21 Temperature Heat And Expansion Answer Key BreigeMeryem
Briefl y defend your answer… The capacity of a substance to store heat. After objects, in contact with each other, read the same temperature and no heat. Temperature, heat, and expansion with fun multiple choice exams you can take online with study.com for teachers for schools for working scholars. When two objects in thermal.
Principles With Applications (Giancoli, 6Th Edition) Chapter 13:
Briefl y defend your answer… Temperature and specific heat notes. Long steel bridges often have one end fi xed while the other end rests on rockers, as shown. Web rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 5 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 4 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 3 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key as 2 stars rate chapter 21 temperature heat and expansion answer key.
Pullingers Apparatus Is Used To Determine The Linear Expansion Of A Metallic Rod In The Laboratory.
David considers a piece of silver of mass 88.9 g. Kee = hf − be. Web chapter 21 temperature, heat, and expansion. K e e = h f − b e.
End Of Chapter 21B Answers…
That is, average molecular kinetic energy differences, not based on which substance has more molecular kinetic energy. Web test and improve your knowledge of chapter 21: Energy that transfers from one object to another because of a temperature difference. When two objects in thermal.
K E E = H F − B E.
The computational example on page 312 of your textbook shows the technique ofunit conversion, called dimensional analysis, which indicates whether to multiply or divide when. The capacity of a substance to store heat. 21.1 temperature the higher the temperature of a substance, the faster is the motion of its molecules. The property of water to resist changes in temperature improves the climate in many places.