Chromatin Drawing
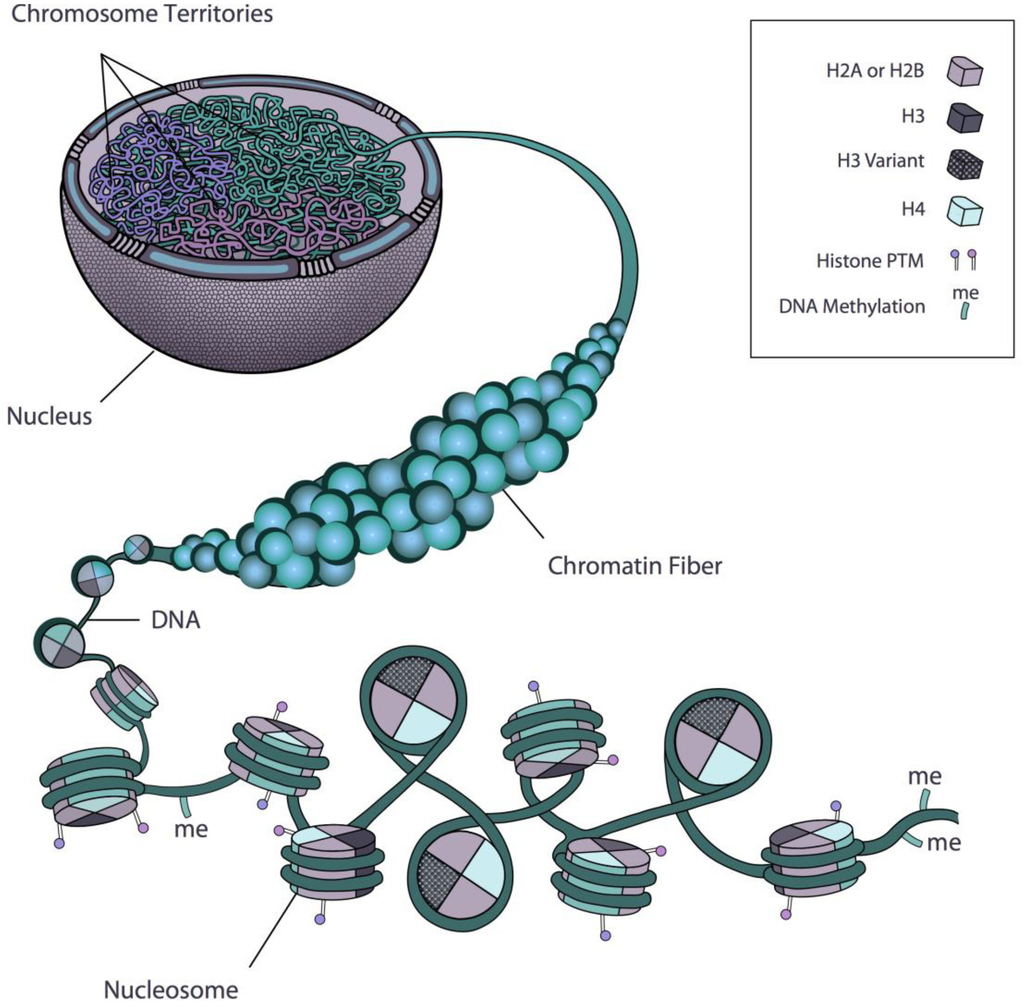
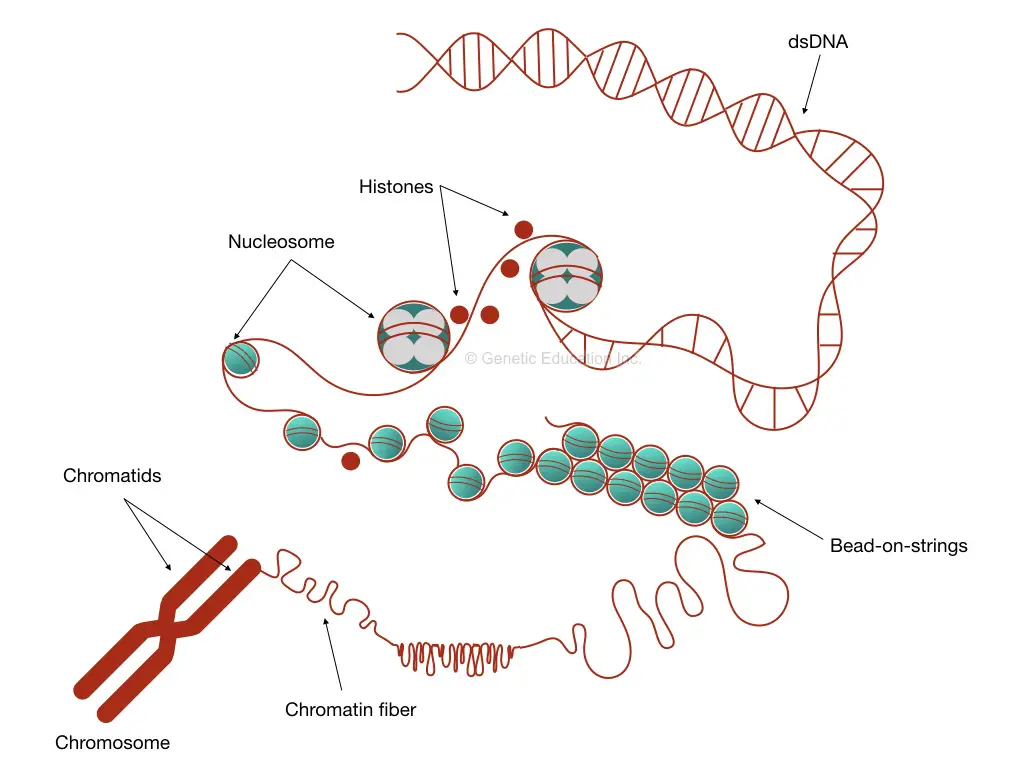
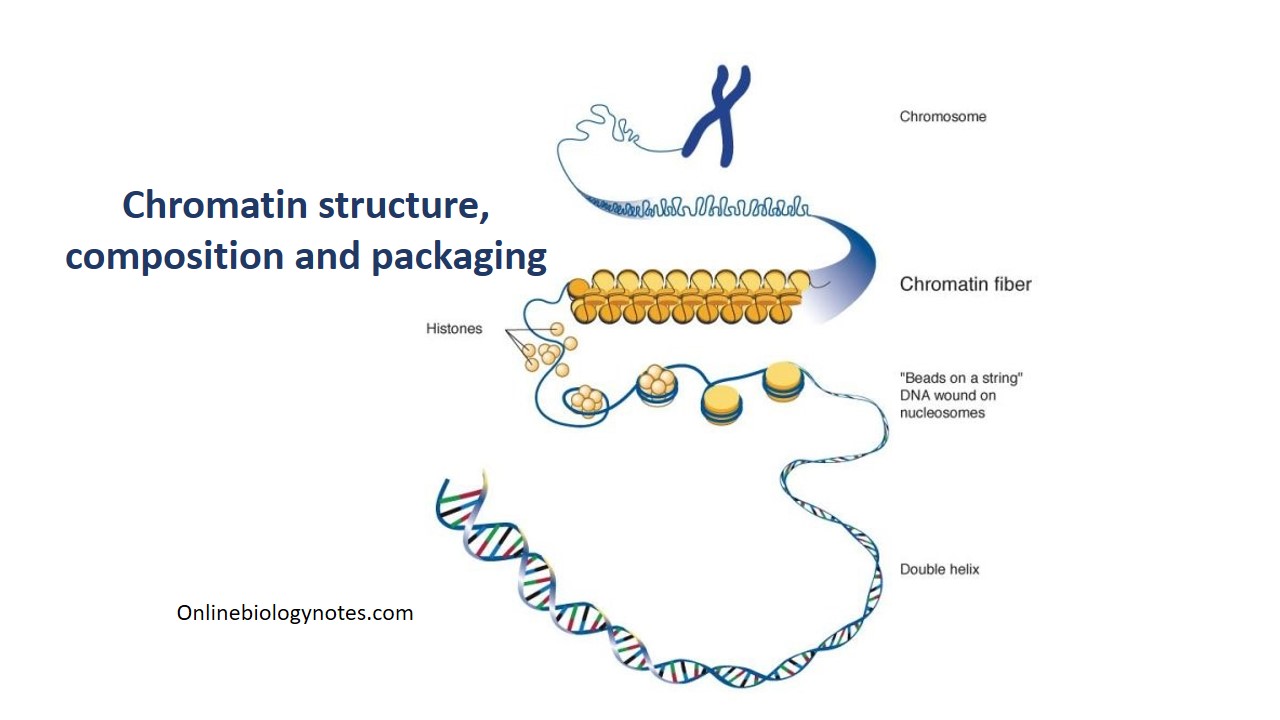
Chromatin Drawing - Histones are a family of small, positively charged proteins termed h1, h2a, h2b, h3, and h4 (van holde, 1988). Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Web in the late 1800s, theodor boveri created the earliest detailed drawings of the spindle based on his observations of cell division in early ascaris embryos (figure 4; Chromatin is located in the nucleus of our cells. Dna, the nucleosome, the 10 nm beads on a string chromatin fibre and the metaphase chromosome. This mark should be used as the starting. Chromatid:each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. The major structures in dna compaction: Diagram of replicated and condensed eukaryotic chromosome (sister chromatids). Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of dna in a genome into a highly compact form that can fit in the cell nucleus.
Web as a result, chromatin can be packaged into a much smaller volume than dna alone. The primary function of chromatin is to compress the dna into a compact unit that will be less voluminous and can fit within the nucleus. Chromatin is located in the nucleus of our cells. This mark should be used as the starting. This zygote then goes through many stages of the replication cycle to create more and more cells called somatic cells or body cells. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Chromatid:each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. Web figure 8.4.3 8.4. Diagram of replicated and condensed eukaryotic chromosome (sister chromatids). Chromatin refers to a mixture of dna and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms.
Chromatin is located in the nucleus of our cells. (3) short arm is termed p; Chromatid:each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. Dna, the nucleosome, the 10 nm beads on a string chromatin fibre and the metaphase chromosome. Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of dna in a genome into a highly compact form that can fit in the cell nucleus. Web in the late 1800s, theodor boveri created the earliest detailed drawings of the spindle based on his observations of cell division in early ascaris embryos (figure 4; Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Chromosomes:a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. [1] the primary function is to package long dna molecules into more compact, denser structures. Diagram of replicated and condensed eukaryotic chromosome (sister chromatids).
What are chromatin? Definition, Types and Importance biology AESL
Web the two gametes (sperm and ovum) contain 23 chromosomes (n) each and when the sperm fertilizes the egg (ovum), the zygote now has a total of 46 chromosomes and becomes diploid (2n). Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Chromatin is a complex of dna and protein found in eukaryotic cells. Long arm is termed q. Web chromatin is a mass.
Chromatin structure Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
Web chromatin is a mass of genetic material composed of dna and proteins that condense to form chromosomes during eukaryotic cell division. Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of dna in a genome into a highly compact form that can fit in the cell nucleus. Long arm is termed q. Start practicing—and saving your.
[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Chromatin
Diagram of replicated and condensed eukaryotic chromosome (sister chromatids). Chromatin is a complex of dna and protein found in eukaryotic cells. This zygote then goes through many stages of the replication cycle to create more and more cells called somatic cells or body cells. Web the two gametes (sperm and ovum) contain 23 chromosomes (n) each and when the sperm.
Everything to Know about Chromatin In Plant Cell Garden Bagan
Web as a result, chromatin can be packaged into a much smaller volume than dna alone. Chromatin refers to a mixture of dna and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms. The major structures in dna compaction: Histones are a family of small, positively charged proteins termed h1, h2a, h2b, h3, and.
Biology Free FullText Insights into Chromatin Structure and
Dna, the nucleosome, the 10 nm beads on a string chromatin fibre and the metaphase chromosome. Chromatin is located in the nucleus of our cells. Web figure 8.4.3 8.4. Long arm is termed q. This mark should be used as the starting.
Chromatin Drawing Mitosis, HD Png Download kindpng
This mark should be used as the starting. [1] the primary function is to package long dna molecules into more compact, denser structures. Web in the late 1800s, theodor boveri created the earliest detailed drawings of the spindle based on his observations of cell division in early ascaris embryos (figure 4; Dna, the nucleosome, the 10 nm beads on a.
Chromatin In Plant Cell
Chromatin is located in the nucleus of our cells. Chromatid:each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. Web as a result, chromatin can be packaged into a much smaller volume than dna alone. Long arm is termed q. (3) short arm is termed p;
Chromatin Is the Complex of and Found Within Eukaryotic Chromosomes.
Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of dna in a genome into a highly compact form that can fit in the cell nucleus. Diagram of replicated and condensed eukaryotic chromosome (sister chromatids). Chromosomes:a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form.
Simpli fi ed schematic drawing of chromatin structure showing the
Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: This zygote then goes through many stages of the replication cycle to create more and more cells called somatic cells or body cells. Web the two gametes (sperm and ovum) contain 23 chromosomes (n) each and when the sperm fertilizes the egg (ovum), the zygote now has a total of 46 chromosomes and becomes diploid.
What are chromatin? Definition, Types and Importance biology AESL
The major structures in dna compaction: Chromosomes:a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Chromatid:each of the two threadlike strands into which a chromosome divides longitudinally during cell division. Chromatin refers to a mixture of.
Diagram Of Replicated And Condensed Eukaryotic Chromosome (Sister Chromatids).
Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Web figure 8.4.3 8.4. This zygote then goes through many stages of the replication cycle to create more and more cells called somatic cells or body cells. Web chromatin is a mass of genetic material composed of dna and proteins that condense to form chromosomes during eukaryotic cell division.
Chromatid:each Of The Two Threadlike Strands Into Which A Chromosome Divides Longitudinally During Cell Division.
(3) short arm is termed p; Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Web as a result, chromatin can be packaged into a much smaller volume than dna alone. The major structures in dna compaction:
Chromatin Refers To A Mixture Of Dna And Proteins That Form The Chromosomes Found In The Cells Of Humans And Other Higher Organisms.
This mark should be used as the starting. Web in the late 1800s, theodor boveri created the earliest detailed drawings of the spindle based on his observations of cell division in early ascaris embryos (figure 4; Dna, the nucleosome, the 10 nm beads on a string chromatin fibre and the metaphase chromosome. Chromatin is located in the nucleus of our cells.
Chromosomes:a Threadlike Structure Of Nucleic Acids And Protein Found In The Nucleus Of Most Living Cells, Carrying Genetic Information In The Form Of Genes.
The primary function of chromatin is to compress the dna into a compact unit that will be less voluminous and can fit within the nucleus. [1] the primary function is to package long dna molecules into more compact, denser structures. Web the two gametes (sperm and ovum) contain 23 chromosomes (n) each and when the sperm fertilizes the egg (ovum), the zygote now has a total of 46 chromosomes and becomes diploid (2n). Chromatin is a complex of dna and protein found in eukaryotic cells.


![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Chromatin](https://hercwules.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/chromatin-fiber.jpg)