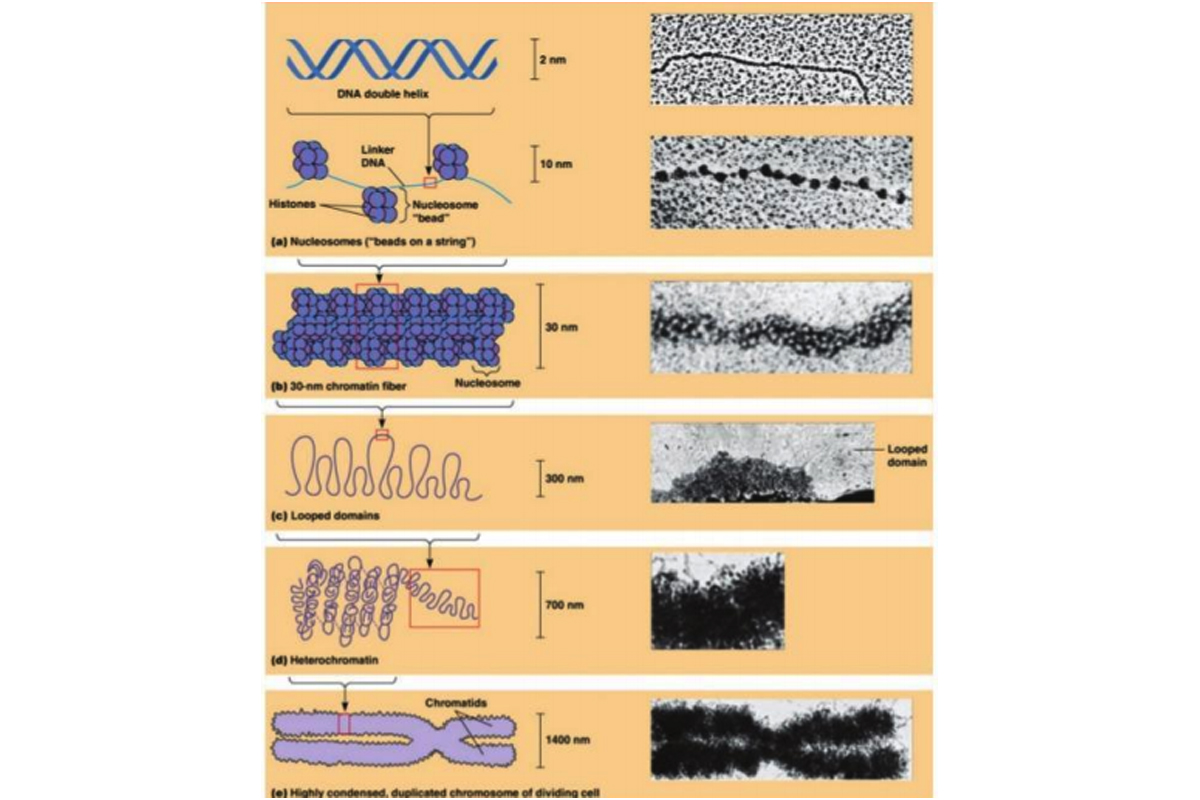
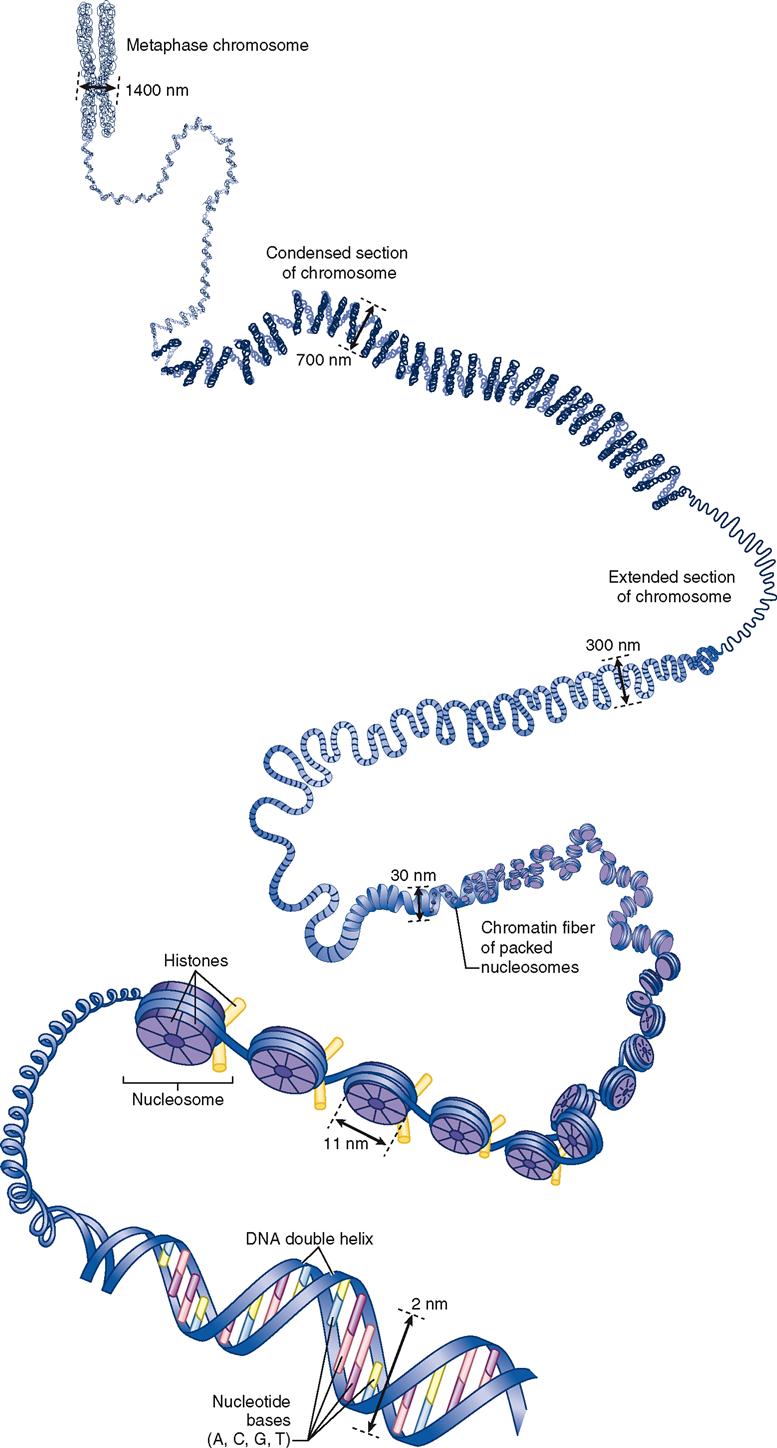
Condensed Form Of Dna
Condensed Form Of Dna - (2002), and many other papers since, much of th… These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Web when a cell is in the process of division, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, so that the dna can be safely transported to the “daughter cells.” the chromosome is. Surface condensation occurs at preferential dna locations suggesting. The highly condensed forms of dna (and proteins) are known as chromosomes. Background [ edit] in many bacteria, the chromosome is a. Web each nucleosome contains eight histone proteins (blue), and dna wraps around these histone structures to achieve a more condensed coiled form. Web when a cell is in the process of division, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, so that the dna can be safely transported to the “daughter cells.” the. Web the dna in each chromosome is a single molecule, on the order of several centimeters in length; Web a) small ligands (inorganic ions, polyamines, etc) may induce dna condensation in vitro.
Chromatin exists in two forms. Web each nucleosome contains eight histone proteins (blue), and dna wraps around these histone structures to achieve a more condensed coiled form. Background [ edit] in many bacteria, the chromosome is a. The highly condensed forms of dna (and proteins) are known as chromosomes. The dna is essentially wound like a. Web in the condensed state, the helical segments are locally aligned, the volume fractions of solvent and dna are comparable, and dna helices may be separated by just. Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of dna or condensed dna, which comes in multiple varieties. Web what is the condensed form of dna referred as? Web when a cell is in the process of division, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, so that the dna can be safely transported to the “daughter cells.” the. Web the dna must be condensed because it is longer than the virus’s capsid, which is the protein shell that contains the dna.
Web when a cell is in the process of division, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, so that the dna can be safely transported to the “daughter cells.” the chromosome is. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the genetic material that carries the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms.it is often described. Web when a cell is in the process of division, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, so that the dna can be safely transported to the “daughter cells.” the. This process is used to model dna compaction in prokaryotes. Web a) small ligands (inorganic ions, polyamines, etc) may induce dna condensation in vitro. Web the dna in each chromosome is a single molecule, on the order of several centimeters in length; Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; Web what does dna mean?. Web in the condensed state, the helical segments are locally aligned, the volume fractions of solvent and dna are comparable, and dna helices may be separated by just. However, according to volpe et al.
Condensed Form Of Dna biome
Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; Web the dna in each chromosome is a single molecule, on the order of several centimeters in length; Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of dna or condensed dna, which comes in multiple varieties. Web when a cell is in the process of.
Condensed Form Of Dna biome
These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Web in the condensed state, the helical segments are locally aligned, the volume fractions of solvent and dna are comparable, and dna helices may be separated by just. Web the full form of dna is deoxyribonucleic acid. It is highly condensed and wrapped around.
Chromatin, illustration. Chromatin is the condensed form of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the genetic material that carries the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms.it is often described. Web each nucleosome contains eight histone proteins (blue), and dna wraps around these histone structures to achieve a more condensed coiled form. Web a) small ligands (inorganic ions, polyamines, etc) may induce dna condensation in vitro. It.
Chromosome Structure Biology for Majors I
Web the dna in each chromosome is a single molecule, on the order of several centimeters in length; Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of dna or condensed dna, which comes in multiple varieties. Web in the condensed state, the helical segments are locally aligned, the volume fractions of solvent and dna are comparable, and dna helices may be separated.
modifications of chromatin structure. Chromosomes are
Web what does dna mean?. Surface condensation occurs at preferential dna locations suggesting. Web what is the condensed form of dna referred as? Both play a role in the expression of genes. Deoxy means lack of an oxygen atom, ribo means ribose sugar, nucleic is found in the nucleus of cell and acid.
Genome Structure, Regulation, and Tissue Differentiation Basicmedical Key
Web the dna in each chromosome is a single molecule, on the order of several centimeters in length; Chromatin exists in two forms. Web in the condensed state, the helical segments are locally aligned, the volume fractions of solvent and dna are comparable, and dna helices may be separated by just. Background [ edit] in many bacteria, the chromosome is.
Levels of DNA wrapping The Statesman
Web in the condensed state, the helical segments are locally aligned, the volume fractions of solvent and dna are comparable, and dna helices may be separated by just. The highly condensed forms of dna (and proteins) are known as chromosomes. Deoxy means lack of an oxygen atom, ribo means ribose sugar, nucleic is found in the nucleus of cell and.
Everything to Know about Chromatin In Plant Cell Garden Bagan
These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Web chromosomes seen in metaphase of mitosis are the ‘highest order’, most condensed form of chromatin. Web what is the condensed form of dna referred as? Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; Web.
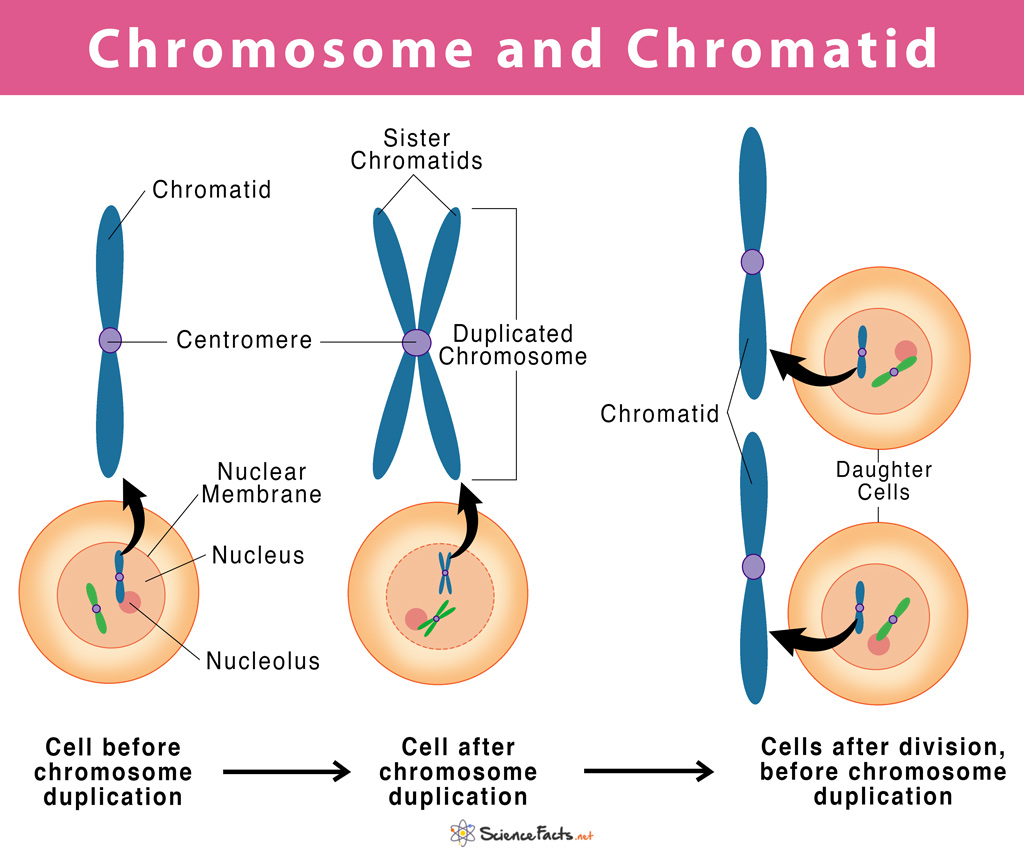
Chromosome vs Chromatid
Web chromosomes seen in metaphase of mitosis are the ‘highest order’, most condensed form of chromatin. It is highly condensed and wrapped around nuclear proteins in order to fit inside the nucleus. The dna is essentially wound like a. Deoxy means lack of an oxygen atom, ribo means ribose sugar, nucleic is found in the nucleus of cell and acid..
image
(2002), and many other papers since, much of th… Background [ edit] in many bacteria, the chromosome is a. Both play a role in the expression of genes. The dna is essentially wound like a. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the genetic material that carries the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms.it is often described.
Web What Is The Condensed Form Of Dna Referred As?
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of dna or condensed dna, which comes in multiple varieties. Web the full form of dna is deoxyribonucleic acid. These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Web when a cell is in the process of division, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, so that the dna can be safely transported to the “daughter cells.” the chromosome is.
Web The Condensed And Organized Form Of The Dna Together With Its Associated Proteins And Rnas Is Called Nucleoid.
The highly condensed forms of dna (and proteins) are known as chromosomes. Web nuclear dna does not appear in free linear strands; The dna is essentially wound like a. The total dna in a eukaryotic cell is as much as three meters long.
Both Play A Role In The Expression Of Genes.
Web in the condensed state, the helical segments are locally aligned, the volume fractions of solvent and dna are comparable, and dna helices may be separated by just. Web a) small ligands (inorganic ions, polyamines, etc) may induce dna condensation in vitro. Web the dna must be condensed because it is longer than the virus’s capsid, which is the protein shell that contains the dna. Web each nucleosome contains eight histone proteins (blue), and dna wraps around these histone structures to achieve a more condensed coiled form.
Chromatin Exists In Two Forms.
It is highly condensed and wrapped around nuclear proteins in order to fit inside the nucleus. Web chromosomes seen in metaphase of mitosis are the ‘highest order’, most condensed form of chromatin. Web the dna in each chromosome is a single molecule, on the order of several centimeters in length; Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed;