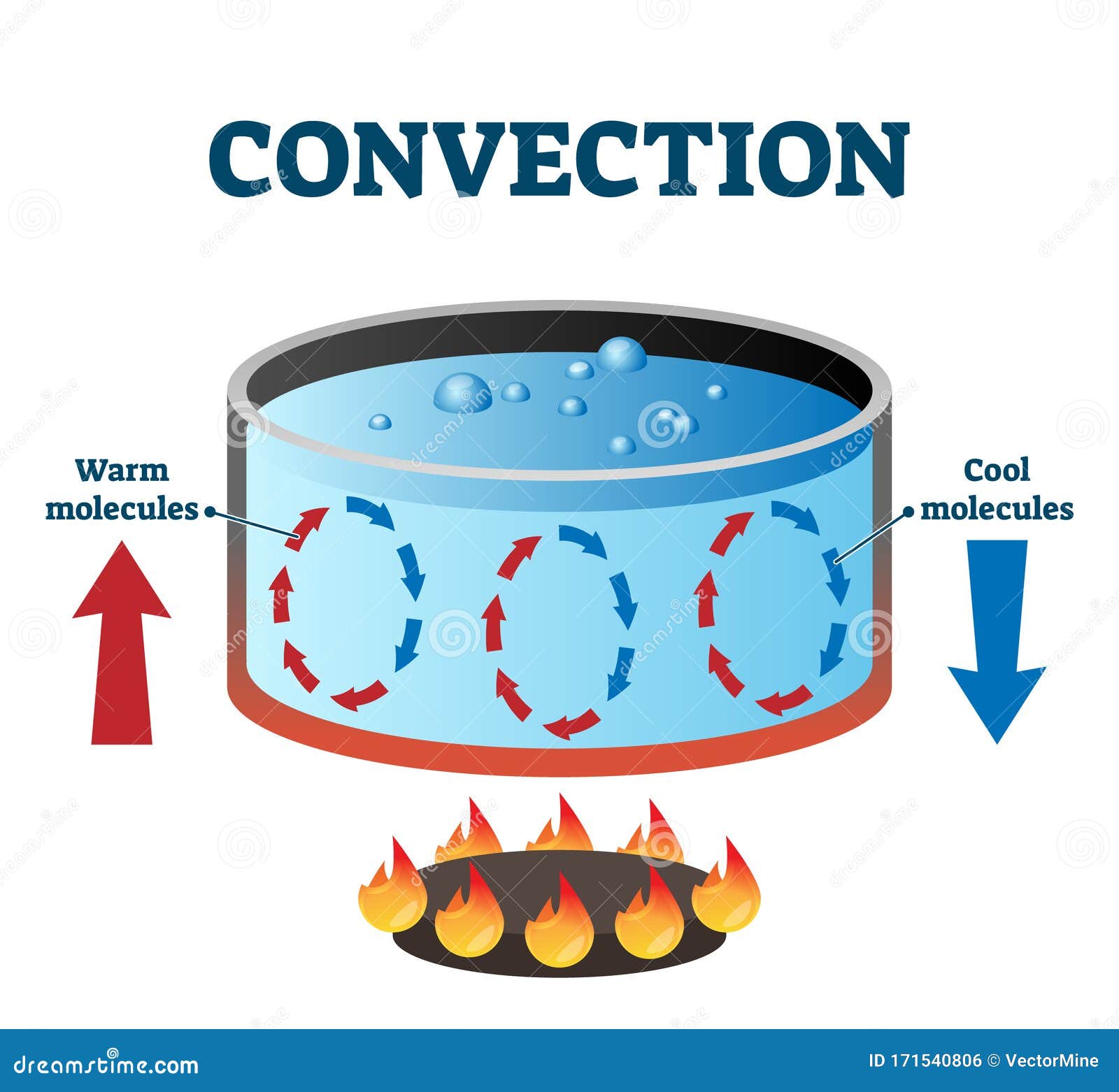
Convection Drawing
Convection Drawing - Web convection (or convective heat transfer) is the transfer of heat from one place to another due to the movement of fluid. Heat transfer, conduction, convection and radiation with examples. Conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. Web convection currents are flowing fluid that is moving because there is a temperature or density difference within the material. The distance from new york city to los angeles is ~4,000 km) a b The thermal convection in this model is similar to the convection that is inferred for the earth's mantle. Web convection, process by which heat is transferred by movement of a heated fluid such as air or water. The heat from the sun. Once conducted to the inside, heat transfer to other parts of the pot is mostly by convection. Web learn step by step drawing tutorial.
Thermal radiation happens when accelerated charged particles. Warm air from the heated floor rises, heating the room. Natural convection results from the tendency of most fluids to expand when heated—i.e., to become less dense and to rise as a result of the increased buoyancy. Web thermal resistance example problem shows how to draw a thermal circuit in series and how to find the thermal resistance equations for conduction thermal resi. Convection plays an important role in heat transfer inside this pot of water. Web 2.) convection cells on the sun are about 1000 km in diameter. Web convection currents, and these are very important for studying weather. There are three forms of thermal energy transfer: The distance from new york city to los angeles is ~4,000 km) a b Investigate the viscosity of a fluid and.
The ability of a fluid in a system to circulate continuously under gravity, with transfer of heat energy. Hot air rising inside toasts the bread evenly. Web learn the basics of heat transfer and the differences between conduction, convection and radiation in this engaging and animated video. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through collisions. > a hot object will give off ir radiation; Usually, it is heat transfer through a solid. Because particles within a solid are fixed in place, convection currents are seen only in gases and liquids. Think about your question then watch the video again and you will see that sal is reenforcing your point using. Web convection (or convective heat transfer) is the transfer of heat from one place to another due to the movement of fluid. Web orangus, what you said is correct, though not in contradiction to what sal was saying in the video.
How Do Convection Currents Work Inside The Earth CONVEKTION CDE
All of these examples use heating of gases or liquids to create movement through convection. The hotter it is, the more intense the radiation (e.g., a bonfire vs. Web 2.) convection cells on the sun are about 1000 km in diameter. Convection plays an important role in heat transfer inside this pot of water. The heat from the sun.
Convection Currents Vector Illustration Labeled Diagram Stock Vector
Heat transfer, conduction, convection and radiation with examples. The driving force for natural convection is gravity. Hot air rising inside toasts the bread evenly. > a hot object will give off ir radiation; Radiation does not require any medium.
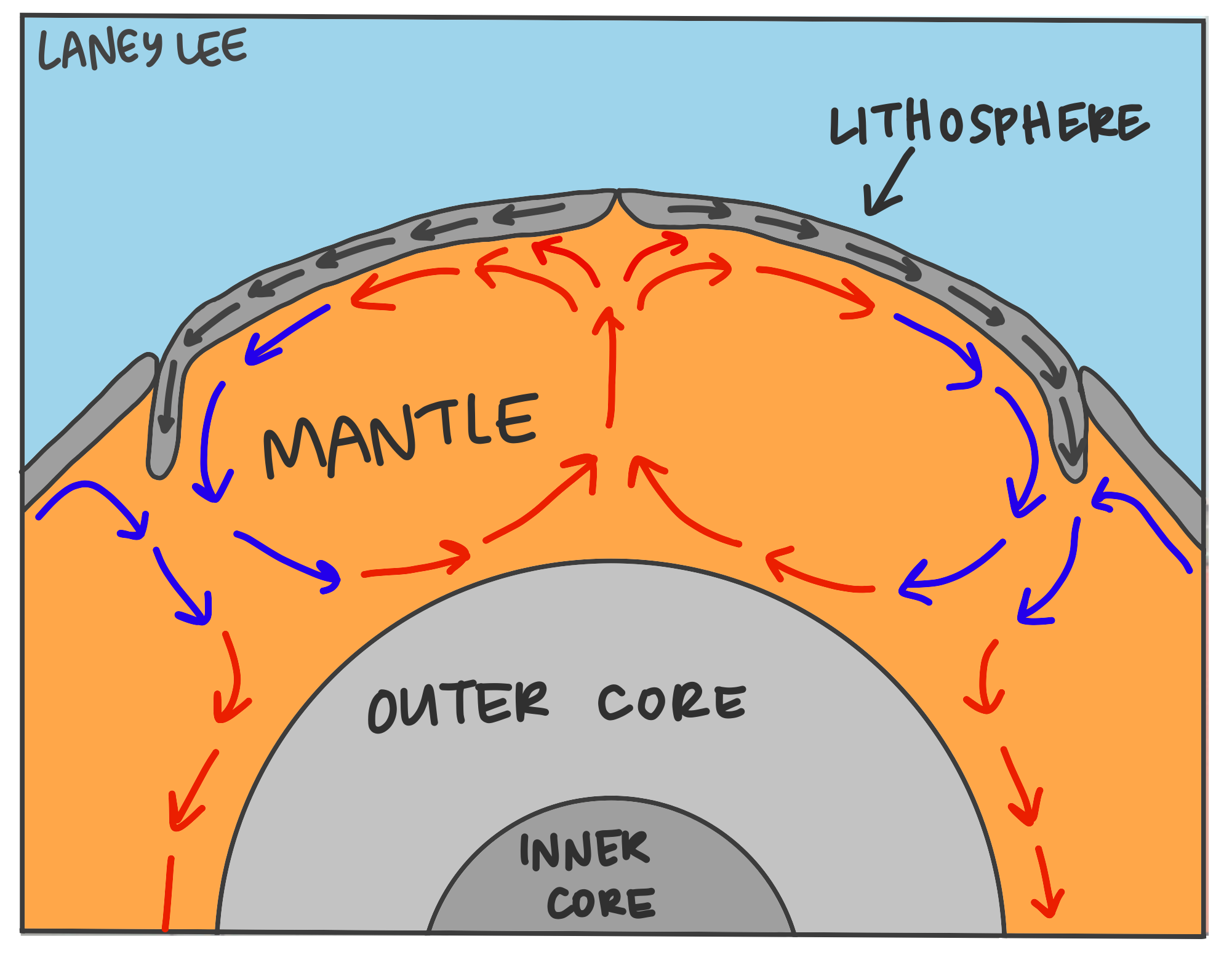
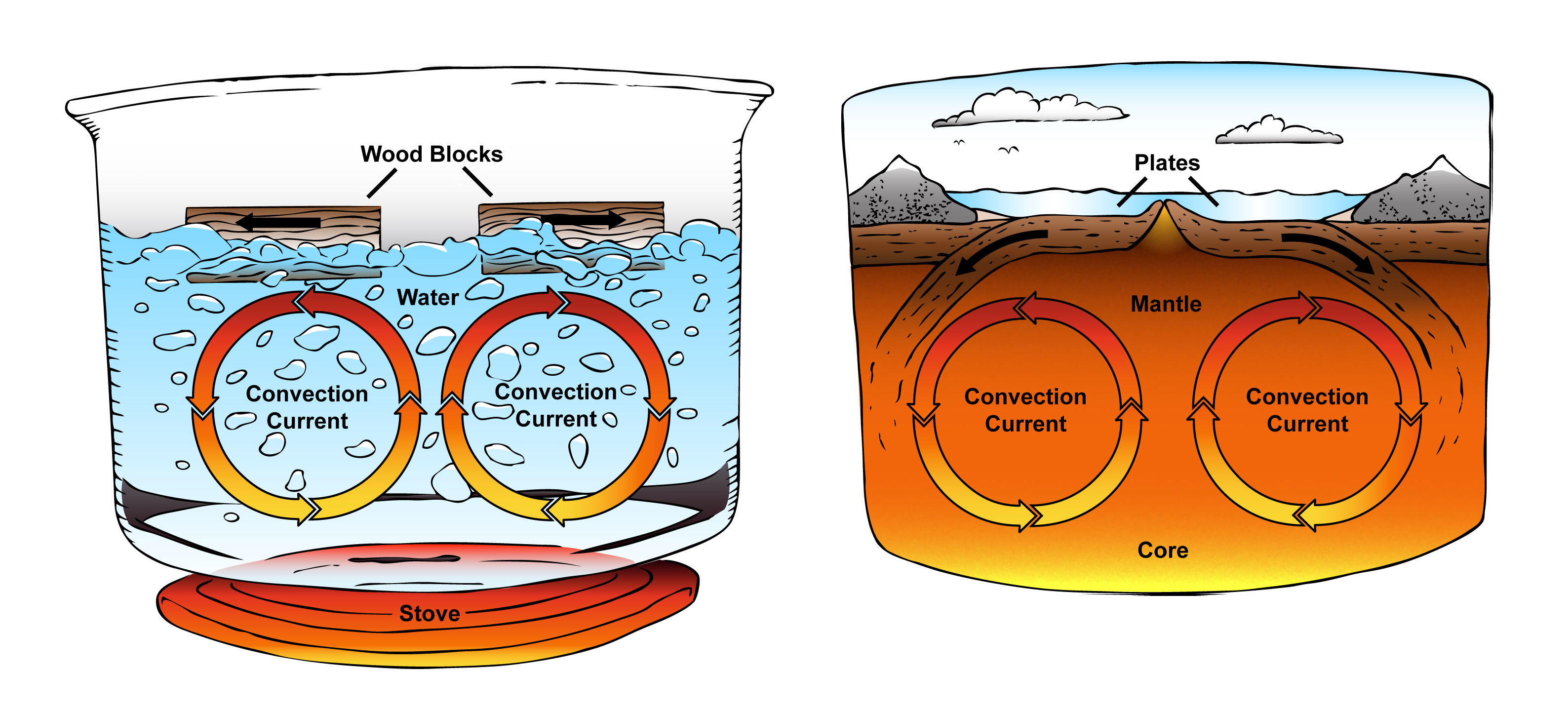
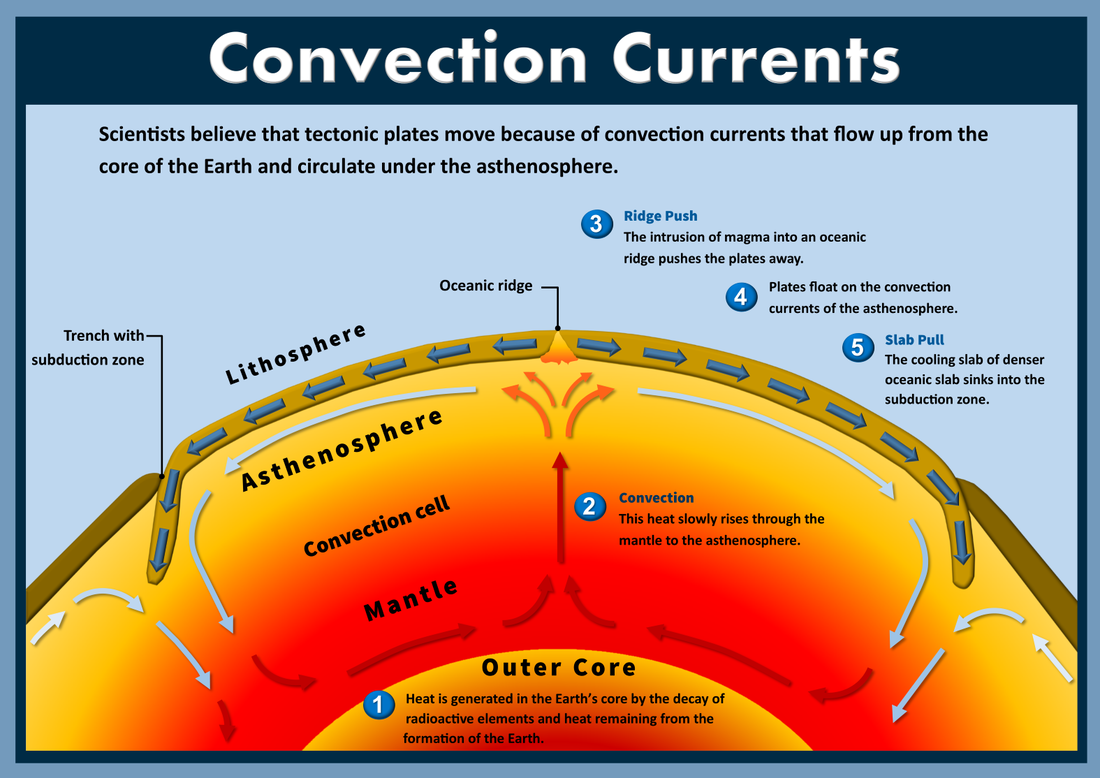
Convection Currents & Plate Tectonics Laney Lee
Web radiant heat is thermal radiation emitted by matter, and can be felt from the sun across the vacuum of space. Radiant heat from a fire heats surrounding air which expands and rises, transferring heat upwards by convection; Web the three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: Web natural convection is.
Convection the process Labster
Although often discussed as a distinct method of heat transfer, convective heat transfer involves the combined processes of conduction (heat diffusion) and advection (heat transfer by bulk fluid flow ). If you don't have a printer just keep this open. Web convection is the process of heat transfer by the bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and.
A simple model of convection to study the atmospheric surface layer
Web convection currents are flowing fluid that is moving because there is a temperature or density difference within the material. This can be felt above the fire. Heat transfer by radiation occurs when microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, or another form of electromagnetic radiation is emitted or absorbed. The thermal convection in this model is similar to the convection that.
How to Draw Heat Transfer 🔥 Conduction, Convection, Radiation Step by
Sal was explaining the intuition behind the formula for thermal conductivity, he was not solving for specific heat ratios. Web radiant heat is thermal radiation emitted by matter, and can be felt from the sun across the vacuum of space. Radiation does not require any medium. The ability of a fluid in a system to circulate continuously under gravity, with.
Introduction to Heat Transfer Let's Talk Science
Web convection currents, and these are very important for studying weather. Heat transfer by ir radiation. Energy is transferred between the earth's surface and the atmosphere in a variety of ways, including radiation, conduction, and convection. Web the three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: Web convection currents are flowing fluid.
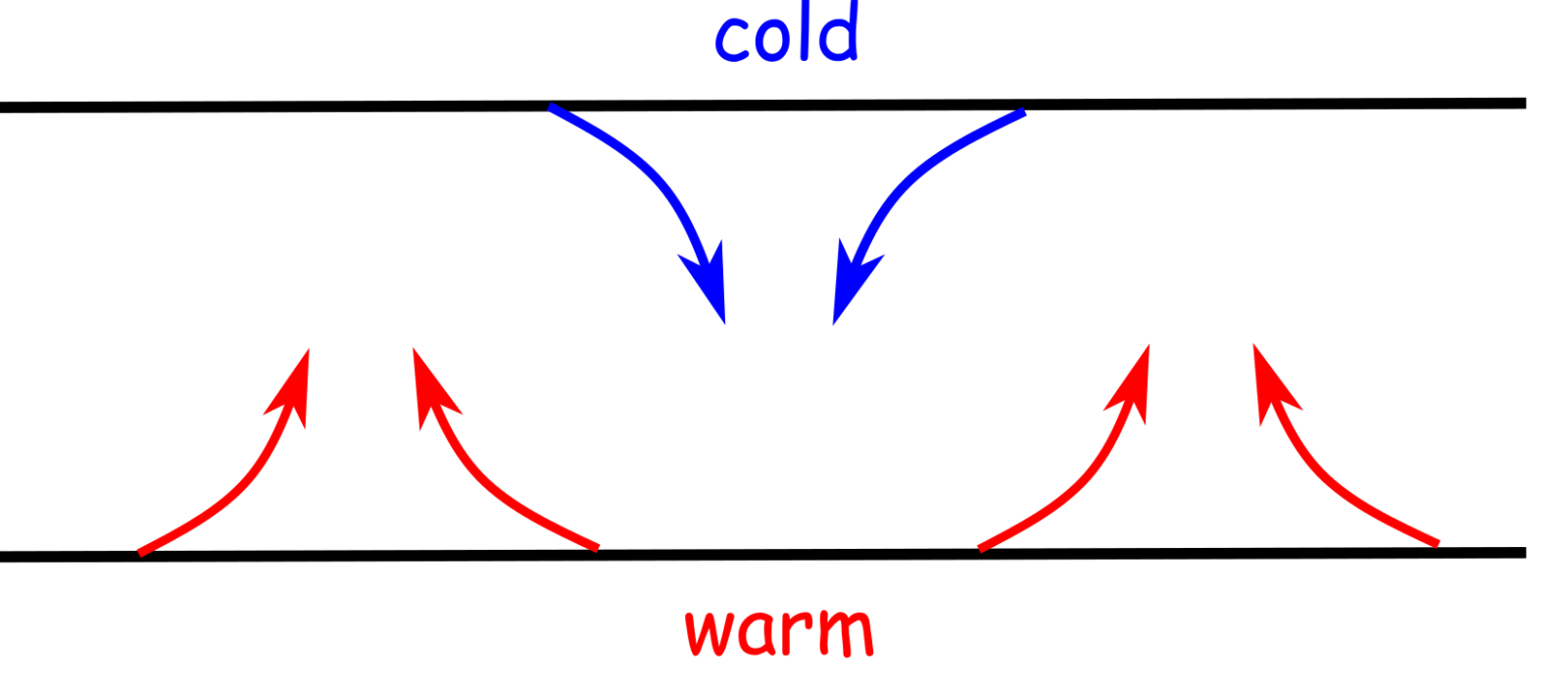
What are Convection Currents?
Web convection is the process of heat transfer by the bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. > a hot object will give off ir radiation; Investigate the viscosity of a fluid and. Web convection is the heat transfer by the macroscopic movement of a fluid. The ability of a fluid in a system to circulate.
Convection Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
If you don't have a printer just keep this open. > a hot object will give off ir radiation; Web three examples of convection are: Heat transfer by ir radiation. Web learn step by step drawing tutorial.
Describe the Convection Currents That Occur Inside Earth CodyhasKing
This can be felt above the fire. > a hot object will give off ir radiation; Download a free printable outline of this video and draw along with us. Convection occurs when hot air rises, allowing cooler air to come in and be heated. The heat from the sun.
Investigate The Viscosity Of A Fluid And.
Sal was explaining the intuition behind the formula for thermal conductivity, he was not solving for specific heat ratios. Web convection (or convective heat transfer) is the transfer of heat from one place to another due to the movement of fluid. Web convection currents are flowing fluid that is moving because there is a temperature or density difference within the material. Hot air rising inside toasts the bread evenly.
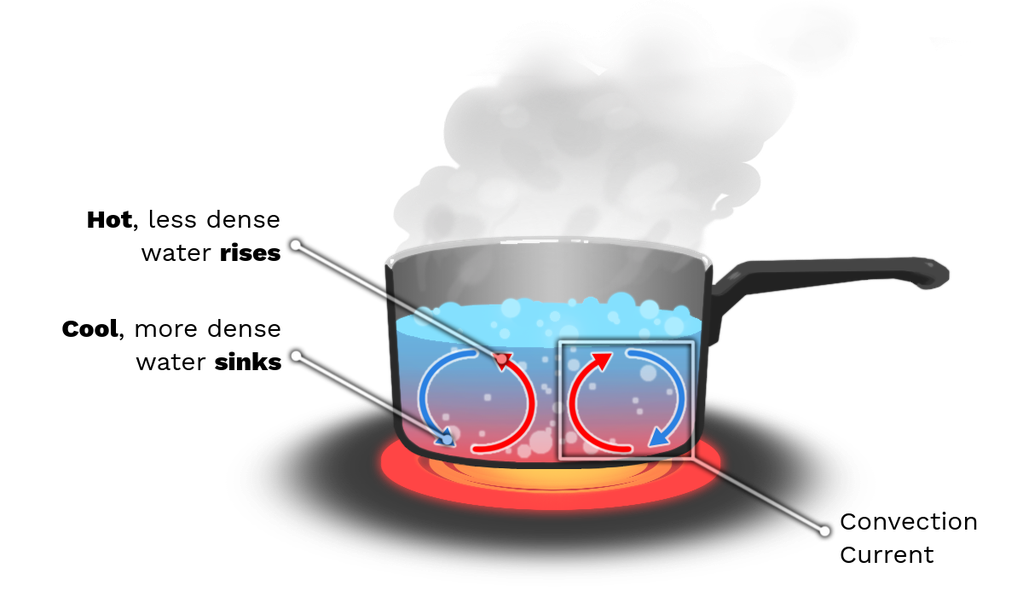
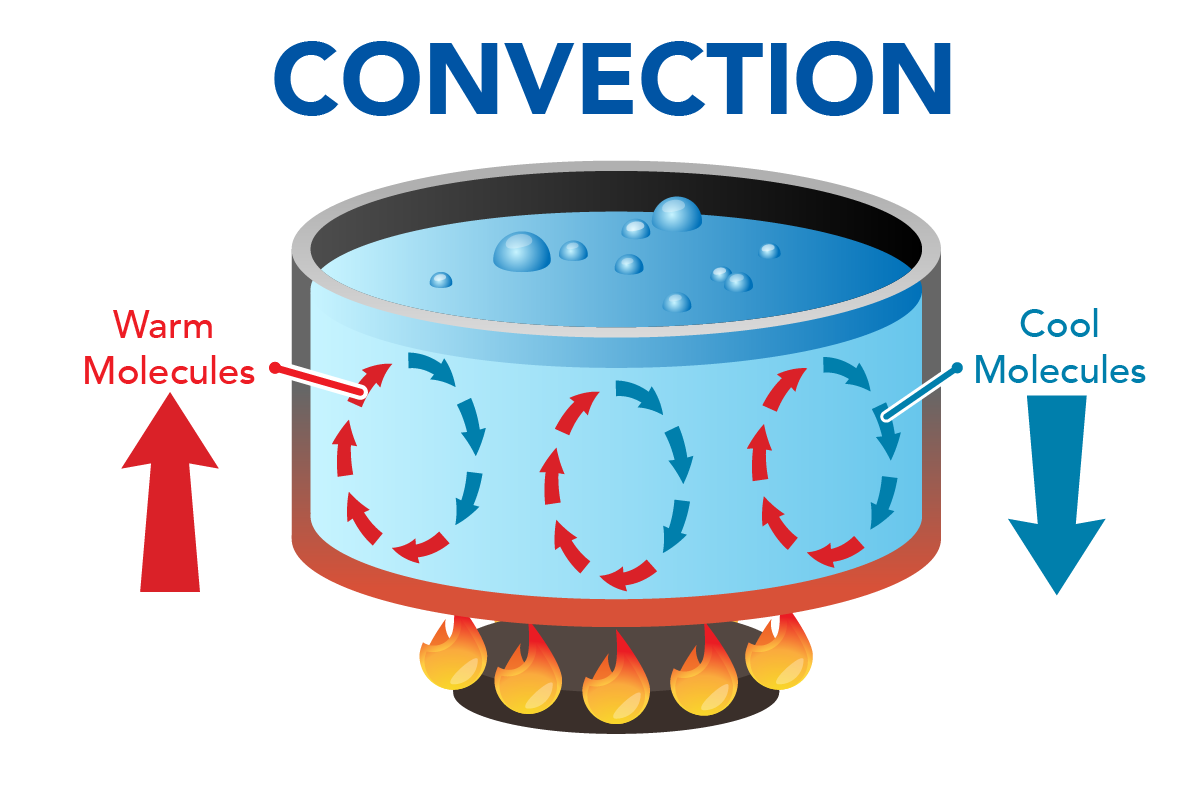
The Hotter Water Expands, Decreases In Density, And Rises To Transfer Heat To Other Regions Of The Water, While Colder Water Sinks To The Bottom.
Web convection is the process of heat transfer by the bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. How heat is transferred through space; Think about your question then watch the video again and you will see that sal is reenforcing your point using. Although often discussed as a distinct method of heat transfer, convective heat transfer involves the combined processes of conduction (heat diffusion) and advection (heat transfer by bulk fluid flow ).
Web Three Examples Of Convection Are:
Once conducted to the inside, heat transfer to other parts of the pot is mostly by convection. Web thermal resistance example problem shows how to draw a thermal circuit in series and how to find the thermal resistance equations for conduction thermal resi. This can be felt above the fire. Web convection is the heat transfer by the macroscopic movement of a fluid.
If You Don't Have A Printer Just Keep This Open.
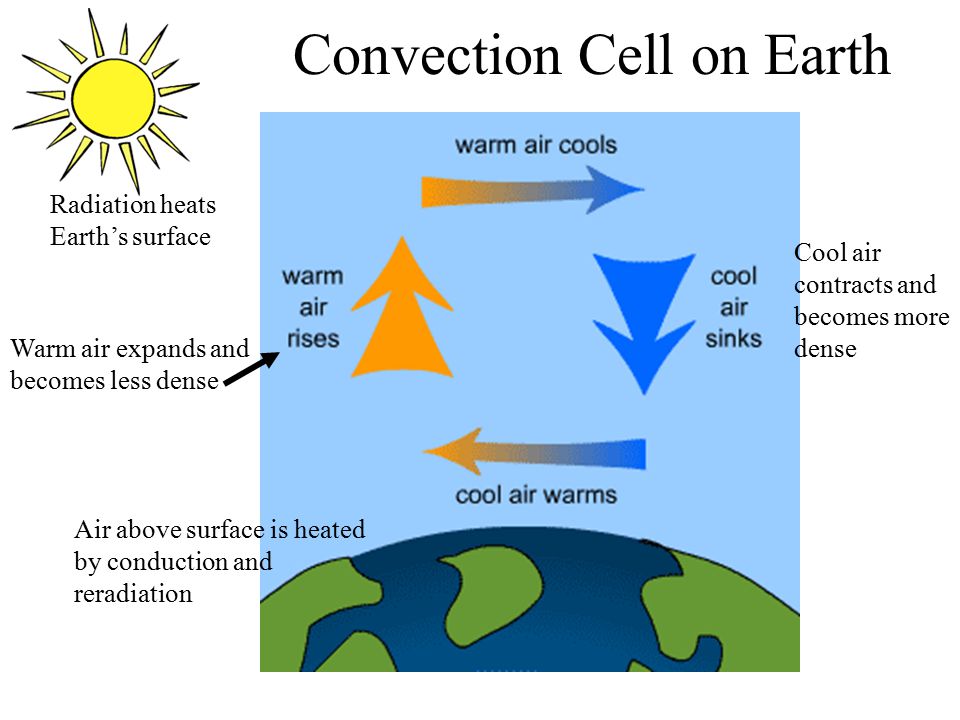
Heat transfer, conduction, convection and radiation with examples. Web convection, process by which heat is transferred by movement of a heated fluid such as air or water. Circulation caused by this effect accounts for the uniform heating of water in a. Warm air from the heated floor rises, heating the room.