Draw The Ray Diagram
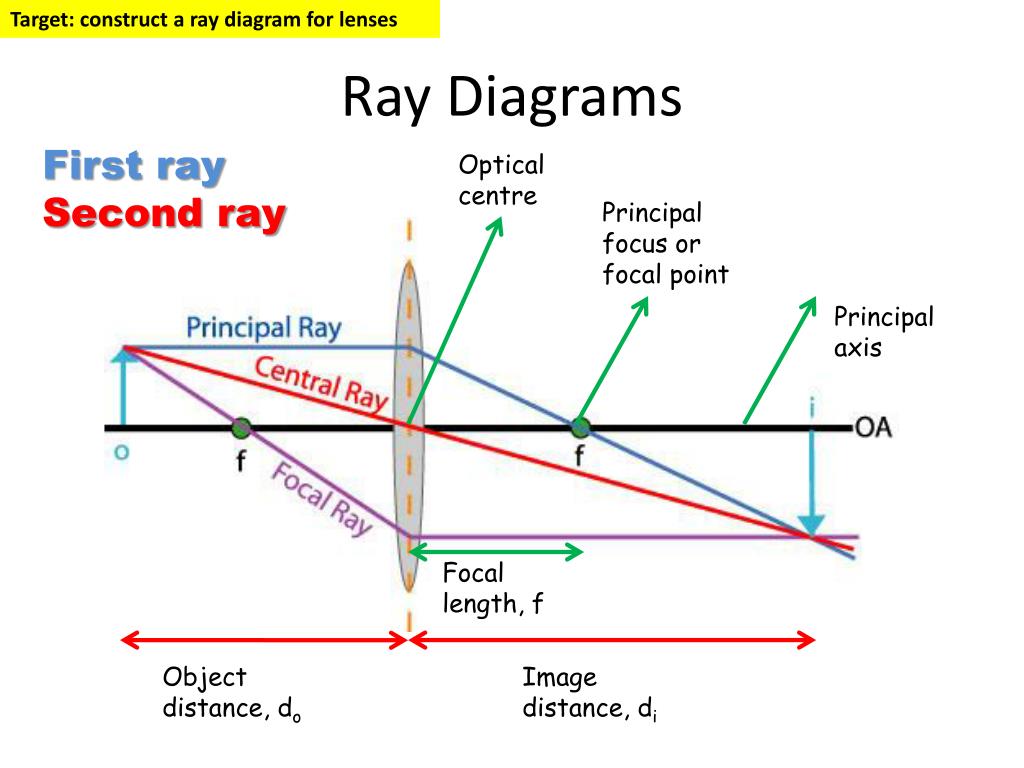
Draw The Ray Diagram - Web the method of drawing ray diagrams for a double concave lens is described below. A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens. Web to draw a ray diagram close ray diagram diagram that represents the direction and angle of travel of light. Web an object is placed outside the focal point of a concave lens. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The smooth side is the reflecting part of the mirror, and the dotted side is the back. Image is in front of the mirror (real image) image is inverted. Web the four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. Use the principle that the object distance is equal to the image distance to determine the exact location of the object.
Draw reflected rays to the image. Use law of reflection to work out incident rays. Pick one extreme on the object and carefully measure the distance from this extreme point. Web ray diagrams for lenses. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. All rays carry an arrow showing the direction of travel of the light. In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: The smooth side is the reflecting part of the mirror, and the dotted side is the back. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray. Web proceure for drawing ray diagram step 1 locate the image:
Draw a line from the top of the object through the middle of the lens. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Therefore, not more than two positions of the object can be obtained in relation to these points unlike concave mirrors where more than two ray diagrams are constructed to find. Where both refracted rays meet is point a'. Convex mirror has two ray diagrams because its principal focus and the centre of curvature lies behind its reflecting surface. Draw a straight line on the paper. Draw the mirror and the object. The symbol ↕ used to draw the ray diagrams indicates. Web ray diagrams for lenses. The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below.
How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10
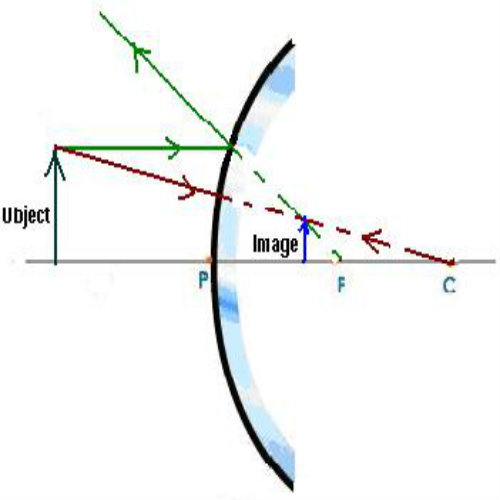
This image is formed at 2f 2. And it is very very small. Draw a straight line on the paper. Web proceure for drawing ray diagram step 1 locate the image: Pick one extreme on the object and carefully measure the distance from this extreme point.
How To Draw Ray Diagrams of all time Don t miss out howtodrawimages1
Web the four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. When you draw ray diagrams on the board or on a transparency: All rays are drawn with a ruler. The image formed by a single lens can be located.
How to Draw a Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors
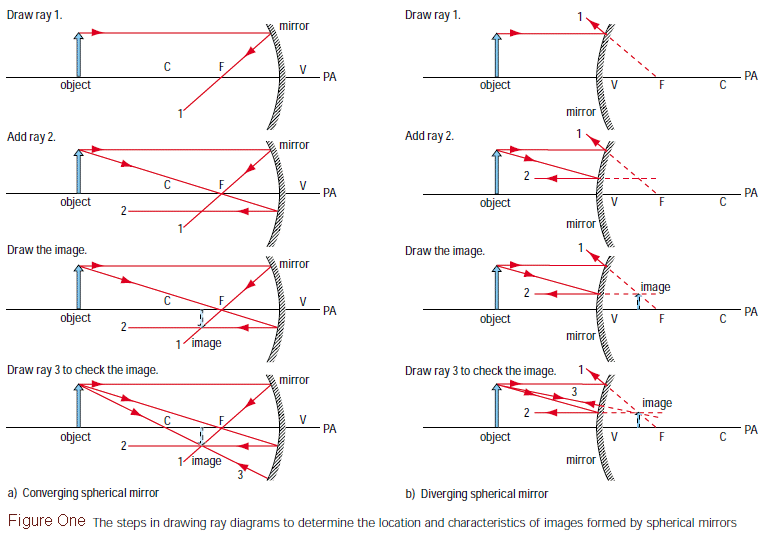
Web ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a concave mirror. Web an object is placed outside the focal point of a concave lens. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging l. On the other hand, a spherical mirror exhibits a consistent curvature. The image formed by a single lens can.
30 Ray Diagram Of Converging Lens Wiring Diagram Database
Web ray diagrams for lenses. The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. Where both refracted rays meet is point a'. All rays carry an arrow showing the direction of travel of the light. Web a ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another.
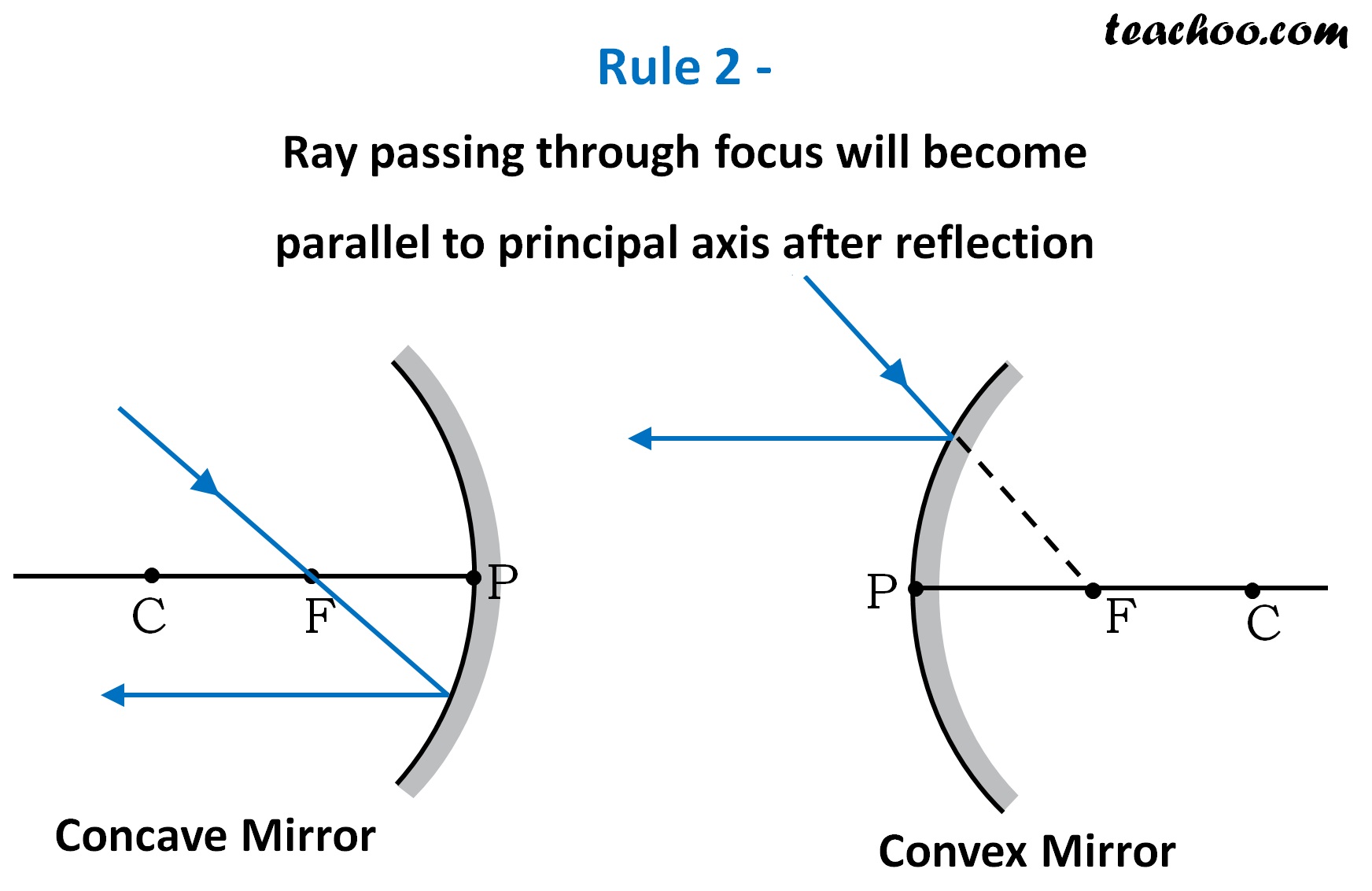
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
This will represent the optical axis. Draw a straight line on the paper. For constructing ray diagrams and for a better understanding of image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. Web a ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. Hence, image.
Ray diagrams for convex mirrors
Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. On the other hand, a spherical mirror exhibits a consistent curvature. Which of the following diagrams shows the reflected ray correctly? When an object is reflected in a plane mirror, it always forms a virtual image that is upright, of the same.
PPT Ray Diagrams PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6878954
This ray will strike the lens before. Web this physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. It possesses a constant radius of curvature (in. The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis.
My Physics Webschool Ray Diagram
Label the ends of the optical axis “o” and “p”. Hence, image is formed at focus. Identify and mark the object distance. The symbol ↕ used to draw the ray diagrams indicates. The intersection of these two rays after reflection gives the position of the image of the object.
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
Web here, object ab is at 2f 1. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray. Draw a line from the top of the object through the middle of the lens. Web to draw a ray diagram close ray diagram diagram that represents the direction and angle of travel of light. We draw another.
How To Draw Ray Diagram (POWERPOINT) PDF
Locate the image of points a and b. Draw in the image at the proper location. Complete the ray diagram by drawing where the image of this object will be seen. Extend the reflected ray with a dashed line back to the image location. Draw a straight line on the paper.
Web Ray Diagrams For Lenses.
Web proceure for drawing ray diagram step 1 locate the image: Complete the ray diagram by drawing where the image of this object will be seen. Web the four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. Image is smaller than the object (highly diminished)
Therefore, Not More Than Two Positions Of The Object Can Be Obtained In Relation To These Points Unlike Concave Mirrors Where More Than Two Ray Diagrams Are Constructed To Find.
It possesses a constant radius of curvature (in. Label these points as a' and b'. Use this diagram and a ruler/straight edge to do the following steps. And it is very very small.
Choose A Point On The Optical Axis, And Label It “A”.
This is definitely a case of the teacher setting the example to be followed! Image is in front of the mirror (real image) image is inverted. Pick one extreme on the object and carefully measure the distance from this extreme point. A ray of light is incident on a spherical mirror at the pole, p.
Web To Draw A Ray Diagram Close Ray Diagram Diagram That Represents The Direction And Angle Of Travel Of Light.
Web a ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Web an increase in magnetic flux through a coil of 100 turns in 0.1 s is 0.001 wb. Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. The intersection of these two rays after reflection gives the position of the image of the object.




.PNG)