Drawing Of Cranial Nerves
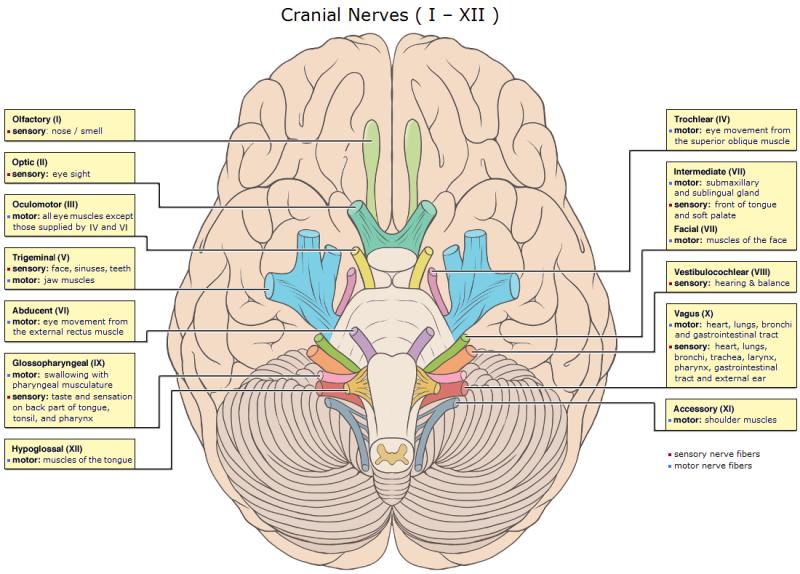
Drawing Of Cranial Nerves - Your cranial nerves help you taste, smell, hear and feel sensations. The longitudinal view of the. The cranial nerves are a 12 nerves which originate from. There are four main nerve plexuses in the human body. Web cranial nerve nuclei. Allows us to move eyeballs. Let us know what you think!what are the cranial nerves? Lynch, medical illustrator derivative work: There are 12 of them, each named for its function or structure. The anatomy of cranial nerves is complex and its knowledge is crucial to detect pathological alterations in case of nervous disorders.
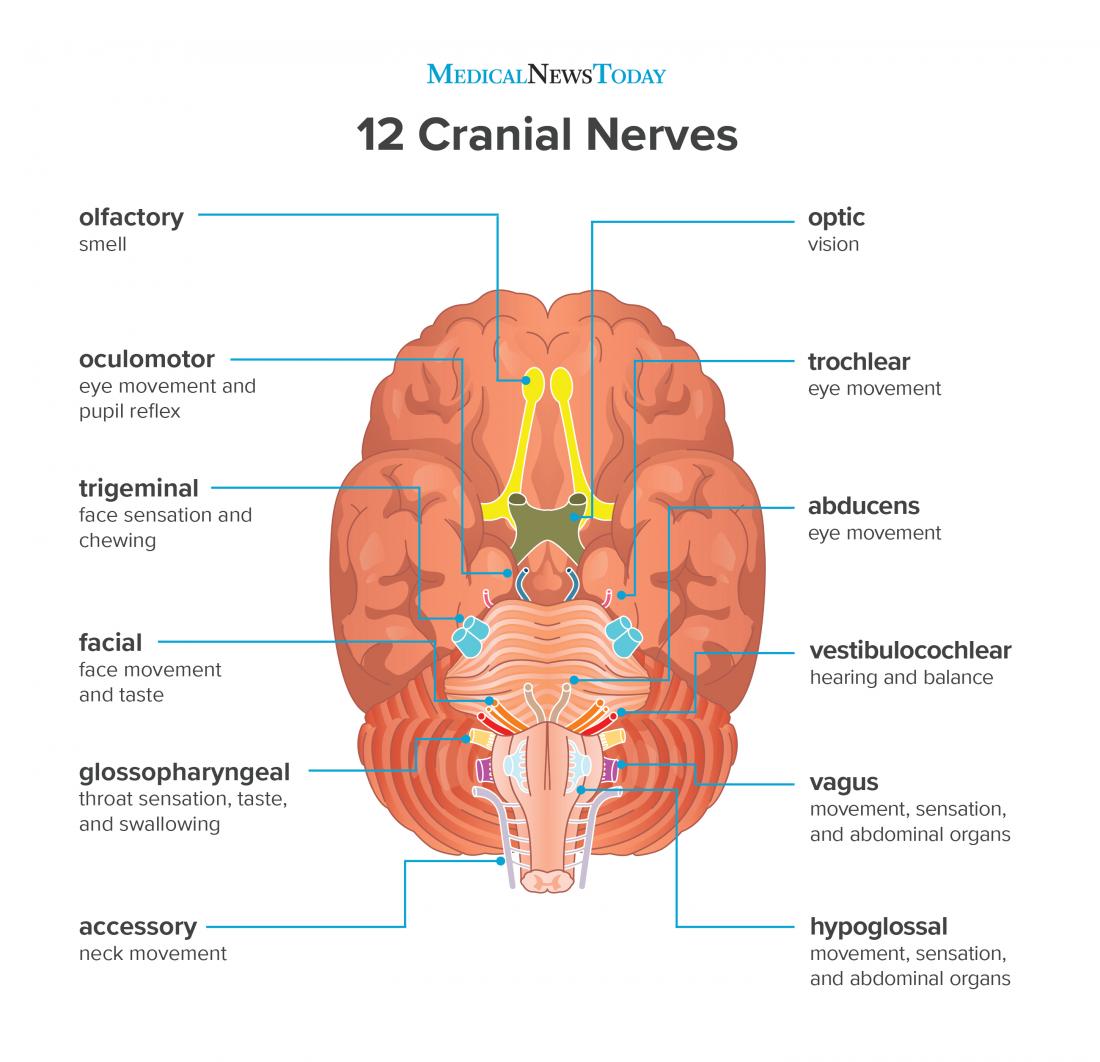
They include the olfactory nerve, which is. Unlike the spinal nerves, cranial. The longitudinal view of the. Web the cranial nerves (cn) are twelve pairs of nerves that, with the exception of the spinal accessory nerve (cn xi), originate in the brain and contribute to the peripheral nervous system (pns), supplying the head and neck. Each cranial nerve has a specific set of functions. Web the cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your brain. Receive sensory information from the skin, skeletal. Let us know what you think!what are the cranial nerves? The second cranial nerve is the optic nerve, which is responsible for relaying sight back from the retina to the. Web in the section on the cranial nerves, we have articles on each of the 12 cranial nerves.
This is a lot of. Web the cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your brain. Dwstultz [cc by 2.5], via wikimedia commons Your cranial nerves help you taste, smell, hear and feel sensations. The cranial nerve nuclei will be covered in more detail in each cranial nerve article. Schematic drawing of the nuclei of cranial nerves. Web the human body has 12 pairs of cranial nerves that control motor and sensory functions of the head and neck. The lumbar plexus supplies nerves to the anterior leg. Web cranial nerve nuclei. Each cranial nerve has a specific set of functions.
Cranial Nerves Names of the 12 Cranial Nerves, Mnemonic and Function
A nucleus refers to a collection of neuronal cell bodies within the central nervous system and they give rise to one of seven major types of fibres (below):. Several of the cranial nerves run. Unlike spinal nerves, whose roots are neural fibers from the spinal grey matter, cranial nerves are composed of the neural processes associated with distinct brainstem nuclei.
Cranial nerves explained Geeky Medics
Web cranial nerve nuclei. In this interactive and animated object, learners read a description of the number, name, and function of the cranial nerves. The second cranial nerve is the optic nerve, which is responsible for relaying sight back from the retina to the. Web the cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your.
Cranial Nerves Function, Table, Anatomy and FAQs
Web here's a drawing of the brain looking up from the bottom, and all of these long stingy looking things coming out of the brain are cranial nerves. A matching quiz completes the activity. Allows us to move eyeballs. Web the cranial nerves provide afferent and efferent innervation principally to the structures of the head and neck. In this interactive.
How to Remember the Cranial Nerves
The anatomy of cranial nerves is complex and its knowledge is crucial to detect pathological alterations in case of nervous disorders. Web your cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that connect your brain to different parts of your head, neck, and trunk. Trigeminal (facial sensation and chewing), vi. Web the 12 cranial nerves are essential nerve pathways that originate in.
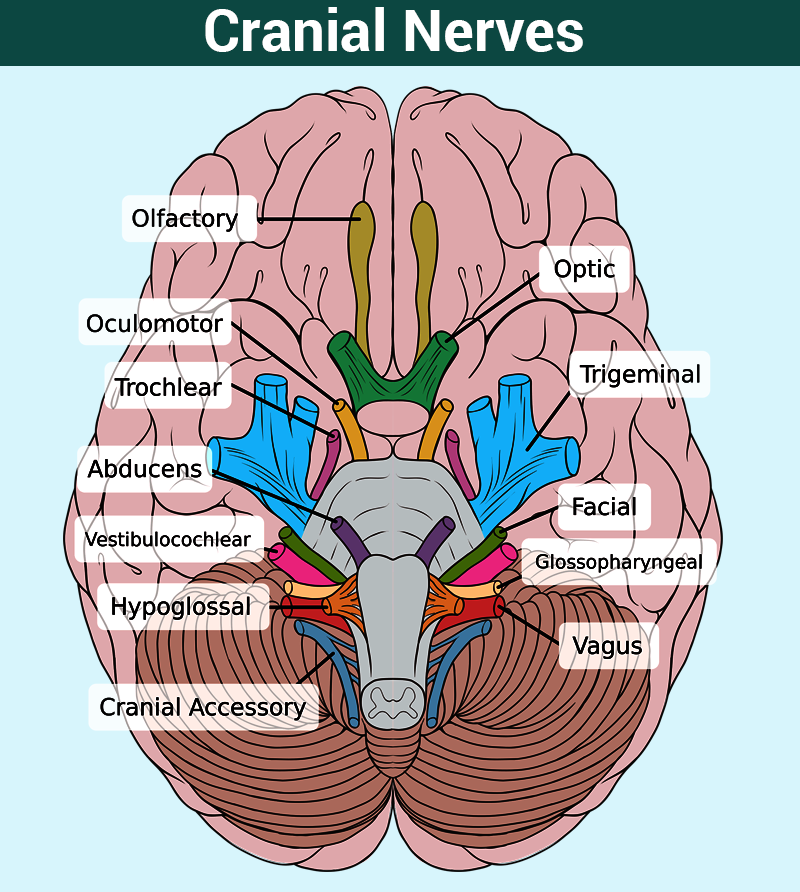
Names, Functions, and Locations of Cranial Nerves
It consists of 15 vector anatomical drawings with 280 anatomical structures labeled. Web cranial nerve nuclei. In this interactive and animated object, learners read a description of the number, name, and function of the cranial nerves. The brachial plexus supplies nerves to the arm. They also help you make facial expressions, blink your eyes and move your tongue.
Drawing Of The Face And Cranial Nerves 1000+ Images About Nursing
Web cranial nerve overview brainstem longitudinal view (gross anatomy) key related anatomy • let's start with an anterior view of the brainstem, which is how we commonly study the brainstem in anatomy lab. Cranial nerves send electrical signals between your brain, face, neck and torso. Web enroll in our course: Allows us to move eyeballs. Trigeminal (facial sensation and chewing),.
Cranial Nerves Neurology Medbullets Step 1
It consists of 15 vector anatomical drawings with 280 anatomical structures labeled. Web in the section on the cranial nerves, we have articles on each of the 12 cranial nerves. Web the human body has 12 pairs of cranial nerves that control motor and sensory functions of the head and neck. Web they each emerge separately from the brain stem,.
Illustration of Cranial Nerves Stock Image F031/5295 Science
Web the cranial nerves provide afferent and efferent innervation principally to the structures of the head and neck. Web the simplest way to draw the #cranial_nerves. Schematic drawing of the nuclei of cranial nerves. The longitudinal view of the. Unlike spinal nerves, whose roots are neural fibers from the spinal grey matter, cranial nerves are composed of the neural processes.
Cranial Nerves Function, Table, Anatomy and FAQs
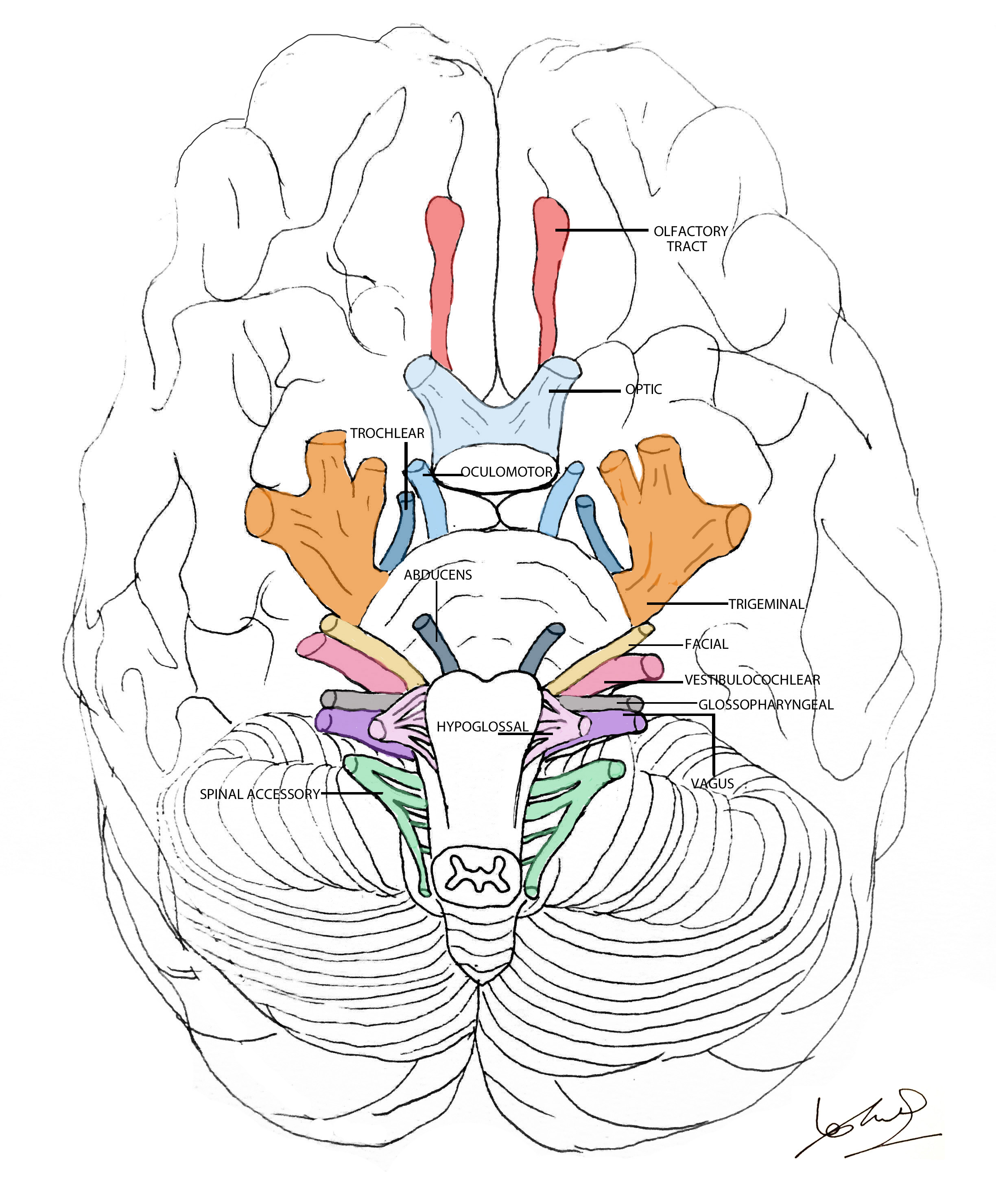
Web here, we will draw the course of cranial nerves 3, 4, and 6 in sagittal view. Cranial nerves send electrical signals between your brain, face, neck and torso. Several of the cranial nerves run. Web the cranial nerves are numbered by their location on the brainstem (superior to inferior, then medial to lateral) and the order of their exit.
What are the 12 cranial nerves? Functions and diagram
They're going to pass through the skull on their way from the brain out into the periphery. A matching quiz completes the activity. Schematic drawing of the nuclei of cranial nerves. First, draw a midsagittal section through the brainstem from the midbrain to the pontomedullary sulcus; Allows us to adjust pupils and eye lens, move eyelids, rotate eyeballs.
The Anatomy Of Cranial Nerves Is Complex And Its Knowledge Is Crucial To Detect Pathological Alterations In Case Of Nervous Disorders.
• to begin, draw the cervical spinal cord. The lumbar plexus supplies nerves to the anterior leg. Each cranial nerve has a specific set of functions. Web in the section on the cranial nerves, we have articles on each of the 12 cranial nerves.
Web Cranial Nerve Overview Brainstem Longitudinal View (Gross Anatomy) Key Related Anatomy • Let's Start With An Anterior View Of The Brainstem, Which Is How We Commonly Study The Brainstem In Anatomy Lab.
Allows us to adjust pupils and eye lens, move eyelids, rotate eyeballs. I won't draw them all in here, but there are a bunch of these cranial nerves that are going to pass through. The second cranial nerve is the optic nerve, which is responsible for relaying sight back from the retina to the. Web here, we will draw the course of cranial nerves 3, 4, and 6 in sagittal view.
First, Draw A Midsagittal Section Through The Brainstem From The Midbrain To The Pontomedullary Sulcus;
Web the cranial nerves (cn) are twelve pairs of nerves that, with the exception of the spinal accessory nerve (cn xi), originate in the brain and contribute to the peripheral nervous system (pns), supplying the head and neck. Allows us to move eyeballs. There are four main nerve plexuses in the human body. Web the human body has 12 pairs of cranial nerves that control motor and sensory functions of the head and neck.
They Also Help You Make Facial Expressions, Blink Your Eyes And Move Your Tongue.
Web the cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your brain. Web the simplest way to draw the #cranial_nerves. Web your cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that connect your brain to different parts of your head, neck, and trunk. Facial nerve (inferior view) finally, the oculomotor nerve, the trochlear nerve, the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (v3), the abducens nerve, the facial nerve, the glossopharyngeal nerve, the vagus nerve, the spinal accessory nerve, and the hypoglossal nerve are responsible for motor functions.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cranial-nerves-2-1e3d489c9104495dbcc609ea188af32d.jpg)