Drawing Orbitals
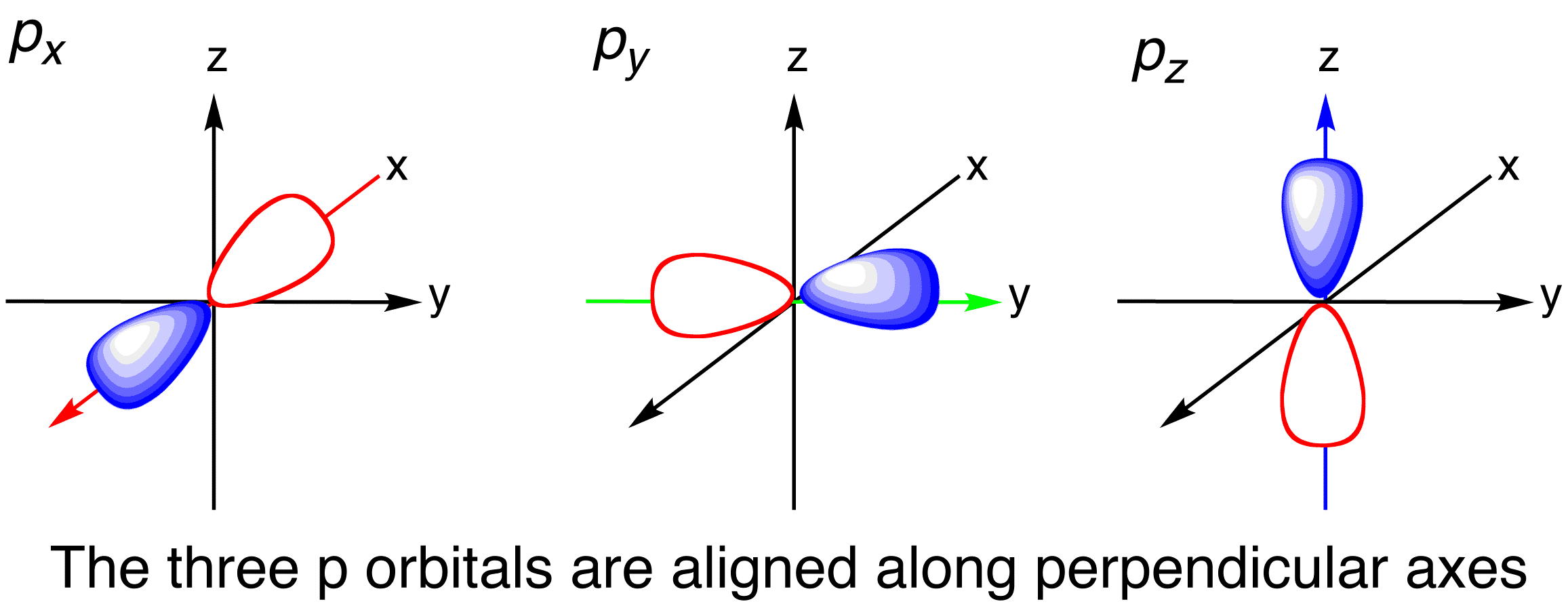
Drawing Orbitals - There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels: Web these are arbitrarily given the symbols px, py and pz. A p orbital consists of two lobes of electron density on either side of the nucleus. The five equivalent 3d orbitals of the hydrogen atom. The angular functions for are complex and depend on , , or. Web so the atomic orbital diagram is simply those orbitals in that order of energy. Note that the #1s# orbitals are significantly lower in energy than the #2s# orbitals. The shape of d orbitals. Web electron configurations have the format: The x, y, and z directions change constantly as the atom tumbles in space.
Note that the #1s# orbitals are significantly lower in energy than the #2s# orbitals. Web orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. The surfaces shown enclose 90% of the total electron probability for the. In two dimensions, we draw it as a circle. You need to know what type of pi electron contribution each type of. Web similar to s orbitals the size, and energy of p orbitals increase with an increase in the principal quantum number (4p > 3p > 2p). At the first energy level, the only orbital available to electrons is the 1s orbital, but at the second level, as well as a 2s orbital, there are also orbitals called 2p orbitals.a p orbital is rather like 2 identical balloons tied together at the nucleus. As the 2s orbital was slightly different in shape from the 1s orbital due to the introduction of a node, so the 3s and 3p orbitals differ slightly in shape from the 2s and 2p. The five d orbitals have m l values of −2, −1, 0, +1, and +2. There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels:
1 = s, 2 = p, 3 = d and 4 = f) for the orbital, and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital. The second shell has 2 subshells: There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels: Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web the first two are familiar, the s orbital and p orbitals. The aufbau principle, the pau. An s orbital is a sphere. We usually draw p orbitals as figure eights, but. In two dimensions, we draw it as a circle. Web when drawing an element's electron configuration, arrows are used to represent electrons, and lines or boxes are used to represent the orbitals.
How do you draw s,p,d,f orbitals? Socratic
The second shell has 2 subshells: Electron shells consist of one or more subshells, and subshells consist of one or more atomic orbitals. Web the first two are familiar, the s orbital and p orbitals. Get out your pencil (and eraser) because we are about to learn how to draw atomic orbitals. For a p orbital, draw a figure eight;
6.6 The Shapes of Atomic Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
Web for the p orbitals, draw one arrow pointing up on each of the lines first. Additional resources for drawing molecular orbitals. Web the first two are familiar, the s orbital and p orbitals. An s orbital is a sphere. There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels:
What is the shape of forbital??? + Example
For a p orbital, draw a figure eight; In two dimensions, we draw it as a circle. Any molecule can be formed using linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao). As the 2s orbital was slightly different in shape from the 1s orbital due to the introduction of a node, so the 3s and 3p orbitals differ slightly in shape from.
Atomic orbitals explained polizhuge
Web these are arbitrarily given the symbols px, py and pz. This means that the first shell can hold 2 electrons. Electron shells consist of one or more subshells, and subshells consist of one or more atomic orbitals. Web electron configurations have the format: Electrons in the same subshell have the same energy, while electrons in different shells or subshells.
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals — Overview & Examples Expii
This includes all hybrid orbitals. Web bohr's atomic model and its limitations (de broglie's equation, heisenberg’s uncertainty principle), concept of shells, subshells, orbitals. As the 2s orbital was slightly different in shape from the 1s orbital due to the introduction of a node, so the 3s and 3p orbitals differ slightly in shape from the 2s and 2p. In two.
Orbitals 2. Shape Biochemistry Flashcards ditki medical and
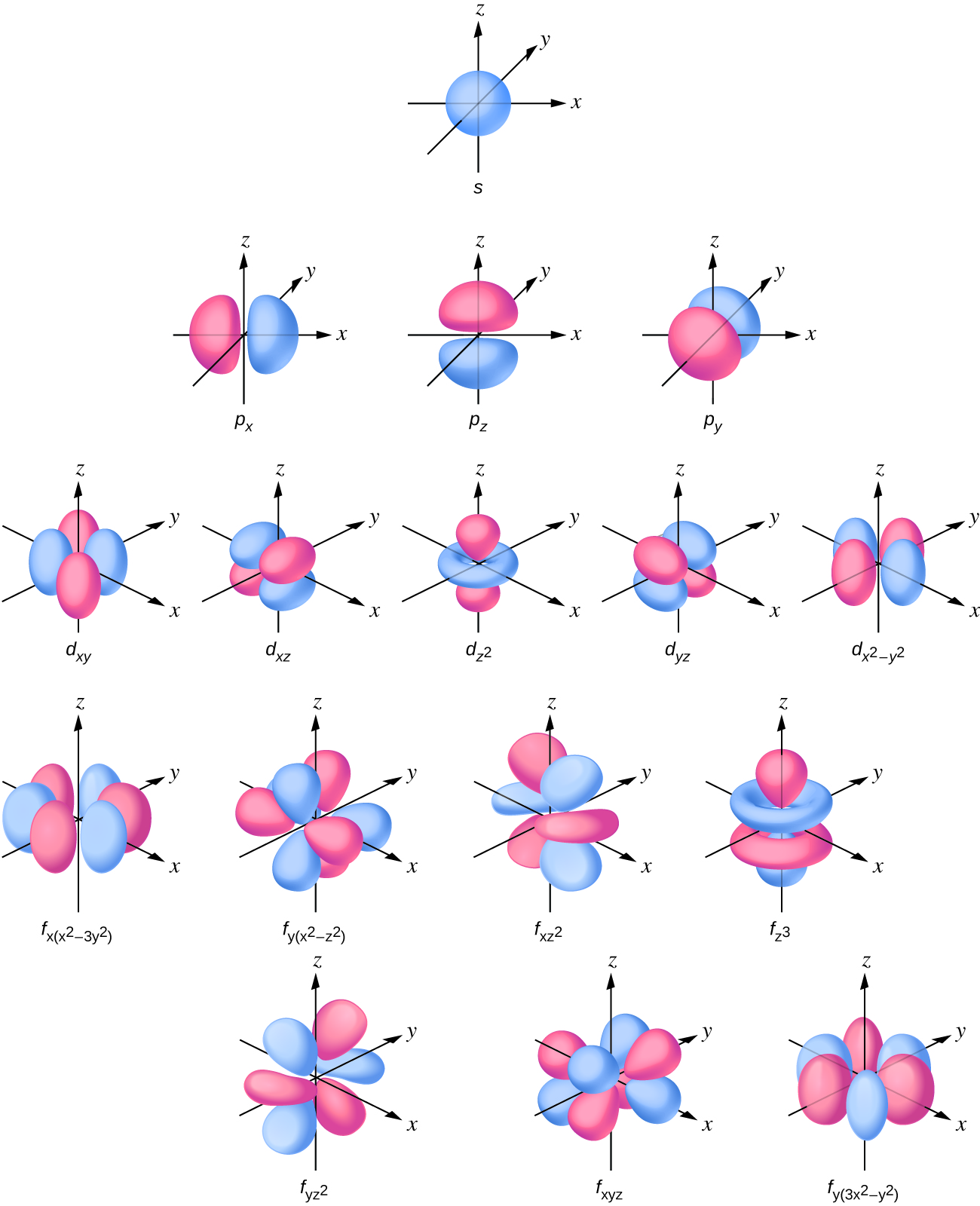
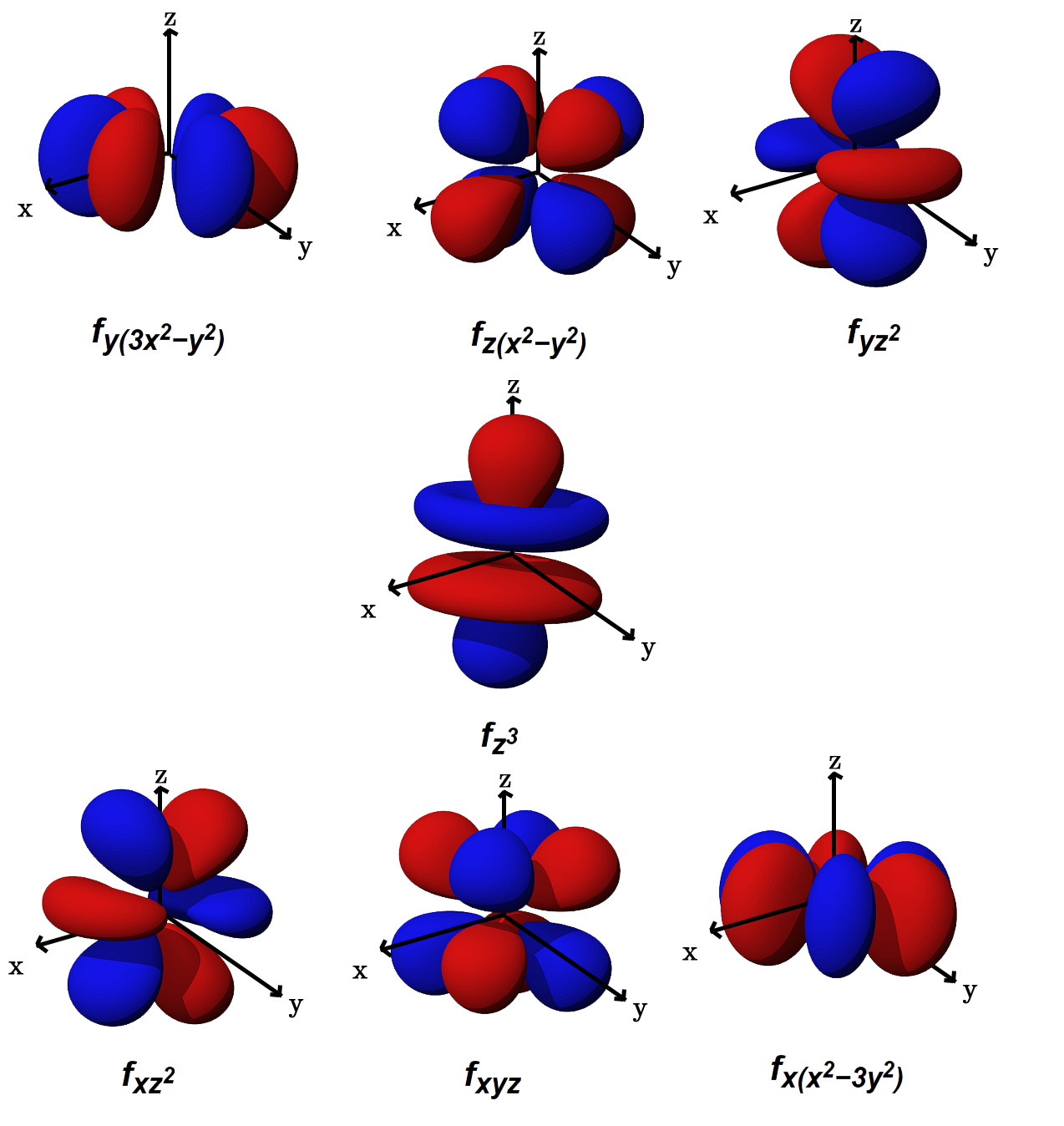
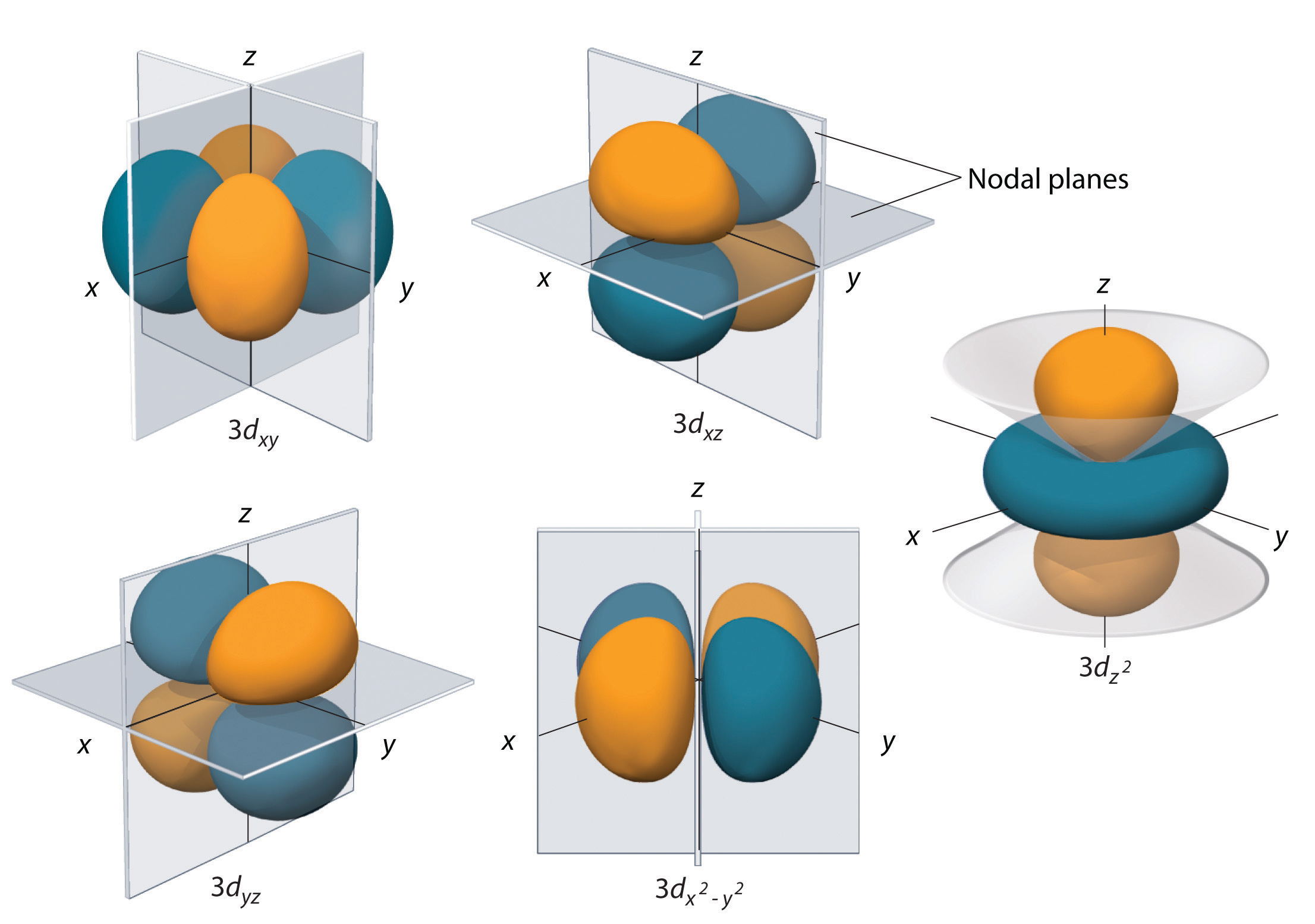
Web d orbitals (l=2) subshells with l = 2 have five d orbitals; Web orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Web this organic chemistry video tutorial explains the hybridization of atomic orbitals. The set of shapes in the snapshots is given for and for combinations of. Web for the p.
Atoms and Atomic Structure HubPages
The set of shapes in the snapshots is given for and for combinations of. Web when drawing an element's electron configuration, arrows are used to represent electrons, and lines or boxes are used to represent the orbitals. The five equivalent 3d orbitals of the hydrogen atom. The following image demonstrates the order for filling, which should always follow the electron..
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals — Overview & Examples Expii
Web bohr's atomic model and its limitations (de broglie's equation, heisenberg’s uncertainty principle), concept of shells, subshells, orbitals. This is simply for convenience; Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: Web for a given atom, the s orbitals also become higher in energy as n increases because of their increased distance from the nucleus. In chemistry orbitals can be classified according.
Radial and Angular Parts of Atomic Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
Web electron configurations have the format: The second shell has 2 subshells: For an f orbital, see below. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The x, y, and z directions change constantly as the atom tumbles in space.
How to Draw Shapes of Orbitals
Web these are arbitrarily given the symbols px, py and pz. We usually draw p orbitals as figure eights, but. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. Below are representations of the 3s orbital, and the 3p orbitals. Point probability plots, polygon surface plots, and raytracing (both probability.
This Is Simply For Convenience;
Then, fill the lines with an arrow pointing down, until the number of arrows drawn is equal to the electron occupancy. As the 2s orbital was slightly different in shape from the 1s orbital due to the introduction of a node, so the 3s and 3p orbitals differ slightly in shape from the 2s and 2p. Note that the #1s# orbitals are significantly lower in energy than the #2s# orbitals. The surfaces shown enclose 90% of the total electron probability for the.
Web The First Two Are Familiar, The S Orbital And P Orbitals.
The five equivalent 3d orbitals of the hydrogen atom. Web for a given atom, the s orbitals also become higher in energy as n increases because of their increased distance from the nucleus. Web when drawing an element's electron configuration, arrows are used to represent electrons, and lines or boxes are used to represent the orbitals. Web electron configurations have the format:
The Aufbau Principle, The Pau.
This means that the first shell can hold 2 electrons. You need to know what type of pi electron contribution each type of. Web orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. 1 = s, 2 = p, 3 = d and 4 = f) for the orbital, and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital.
Electron Shells Consist Of One Or More Subshells, And Subshells Consist Of One Or More Atomic Orbitals.
There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels: Web so the atomic orbital diagram is simply those orbitals in that order of energy. Quantum numbers, shapes of s, p and d orbitals. Web d orbitals (l=2) subshells with l = 2 have five d orbitals;