File Drawer Problem Psychology
File Drawer Problem Psychology - Web the file drawer effect: Web 6 oct 2000. Such a selection process increases the likelihood that published results reflect type i errors rather than true population. Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. Web selective reporting of scientific findings is often referred to as the “file drawer” problem ( 2 ). Like many psychologists, i was dismayed to see the results of a recent study that attempted to replicate 100 different psychology studies, and managed to support the results in only 36% of cases. Web replication, validity, and the file drawer problem in psychological research. Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. It has been contended that drug companies have hidden, in the “file drawer,” the results of unsuccessful clinical trials while publishing the results of more successful trials ( 1 ). A term that describes the fact that a large number of all studies conducted are not available to review because.
Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. Like many psychologists, i was dismayed to see the results of a recent study that attempted to replicate 100 different psychology studies, and managed to support the results in only 36% of cases. Web replication, validity, and the file drawer problem in psychological research. Web the file drawer effect: Web 6 oct 2000. Publication bias is more widespread than scientists might like to think. Web the file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. We conducted the begg and mazumdar rank correlation test, and egger's test of the intercept to determine whether the results were likely to have been influenced by. Web selective reporting of scientific findings is often referred to as the “file drawer” problem ( 2 ). Web the file drawer problem refers to the higher probability of significant results being published relative to nonsignificant results (easterbrook et al., 1991;
It has been contended that drug companies have hidden, in the “file drawer,” the results of unsuccessful clinical trials while publishing the results of more successful trials ( 1 ). Quantitative procedures for computing the tolerance for filed and future null results are reported and illustrated, and the implications are discussed. Web the file drawer effect: Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. Web replication, validity, and the file drawer problem in psychological research. Web 6 oct 2000. Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. Publication bias is more widespread than scientists might like to think. As a library, nlm provides access to scientific literature. Web the file drawer problem refers to the higher probability of significant results being published relative to nonsignificant results (easterbrook et al., 1991;
Replication, Validity, and the File Drawer Problem in Psychological
Web the file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Web in this paper, we describe two methodological issues, publication bias, and its corollary the “file drawer effect,” which have been identified by researchers throughout the scientiic community as serious threats to scientific integrity. Web publication bias is also called the file drawer problem, especially when the nature of the.
(PDF) REVISITING THE FILE DRAWER PROBLEM IN METAANALYSIS
Like many psychologists, i was dismayed to see the results of a recent study that attempted to replicate 100 different psychology studies, and managed to support the results in only 36% of cases. A term that describes the fact that a large number of all studies conducted are not available to review because. Such a selection process increases the likelihood.
(PDF) Selection Models and the File Drawer Problem
Web replication, validity, and the file drawer problem in psychological research. Publication bias is more widespread than scientists might like to think. Quantitative procedures for computing the tolerance for filed and future null results are reported and illustrated, and the implications are discussed. Web 6 oct 2000. Web the extreme view of the file drawer problem is that journals are.
File Drawer Problem Fragility Vaccine
Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. A term that describes the fact that a large number of all studies conducted are not available to review because. Web replication, validity, and the file drawer problem in psychological research. Web the extreme view of the file drawer.
[PDF] [Selection Models and the File Drawer Problem] Comment
Publication bias is more widespread than scientists might like to think. Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. Web in this paper, we describe two methodological issues, publication bias, and its corollary the “file drawer effect,” which have been identified by researchers throughout the scientiic community.
13. "Negative Data" and the File Drawer Problem YouTube
Web the file drawer problem refers to the higher probability of significant results being published relative to nonsignificant results (easterbrook et al., 1991; Web replication, validity, and the file drawer problem in psychological research. Web the extreme view of the file drawer problem is that journals are filled with the 5% of the studies that show type i errors, while.
PPT MetaAnalysis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2181371
Web the file drawer problem refers to the higher probability of significant results being published relative to nonsignificant results (easterbrook et al., 1991; Web the file drawer effect: Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. Web replication, validity, and the file drawer problem in psychological research..
PPT Declaration of Helsinki PowerPoint Presentation ID4691236
Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. Web in this paper, we describe two methodological issues, publication bias, and its corollary the “file drawer effect,” which have been identified by researchers throughout the scientiic community as serious threats to scientific integrity. Web replication, validity, and the.
Emptying psychology’s file drawer by Alexandra Lautarescu
A term that describes the fact that a large number of all studies conducted are not available to review because. Web the fundamental idea in coping with the file drawer problem is simply to calculate the number of studies averaging null results that must be in the file drawers before the overall probability of a type i error is brought.
Figure 2 from Publication Bias The “FileDrawer” Problem in Scientific
Web 6 oct 2000. Web selective reporting of scientific findings is often referred to as the “file drawer” problem ( 2 ). Like many psychologists, i was dismayed to see the results of a recent study that attempted to replicate 100 different psychology studies, and managed to support the results in only 36% of cases. Quantitative procedures for computing the.
Like Many Psychologists, I Was Dismayed To See The Results Of A Recent Study That Attempted To Replicate 100 Different Psychology Studies, And Managed To Support The Results In Only 36% Of Cases.
This term suggests that results not supporting the hypotheses of researchers often go no further than the researchers' file drawers, leading to a bias in published research. It has been contended that drug companies have hidden, in the “file drawer,” the results of unsuccessful clinical trials while publishing the results of more successful trials ( 1 ). As a library, nlm provides access to scientific literature. Such a selection process increases the likelihood that published results reflect type i errors rather than true population.
Web The Fundamental Idea In Coping With The File Drawer Problem Is Simply To Calculate The Number Of Studies Averaging Null Results That Must Be In The File Drawers Before The Overall Probability Of A Type I Error Is Brought To Any Desired Level Of Significance, Say, P =•.05.
Quantitative procedures for computing the tolerance for filed and future null results are reported and illustrated, and the implications are discussed. Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published. A term that describes the fact that a large number of all studies conducted are not available to review because. We conducted the begg and mazumdar rank correlation test, and egger's test of the intercept to determine whether the results were likely to have been influenced by.
Web In This Paper, We Describe Two Methodological Issues, Publication Bias, And Its Corollary The “File Drawer Effect,” Which Have Been Identified By Researchers Throughout The Scientiic Community As Serious Threats To Scientific Integrity.
Web the file drawer problem refers to the higher probability of significant results being published relative to nonsignificant results (easterbrook et al., 1991; Web the file drawer effect: Web the file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Web studies that yield nonsignificant or negative results are said to be put in a file drawer instead of being published.
Web The Extreme View Of The File Drawer Problem Is That Journals Are Filled With The 5% Of The Studies That Show Type I Errors, While The File Drawers Are Filled With The 95% Of The Studies That Show Nonsignificant Results.
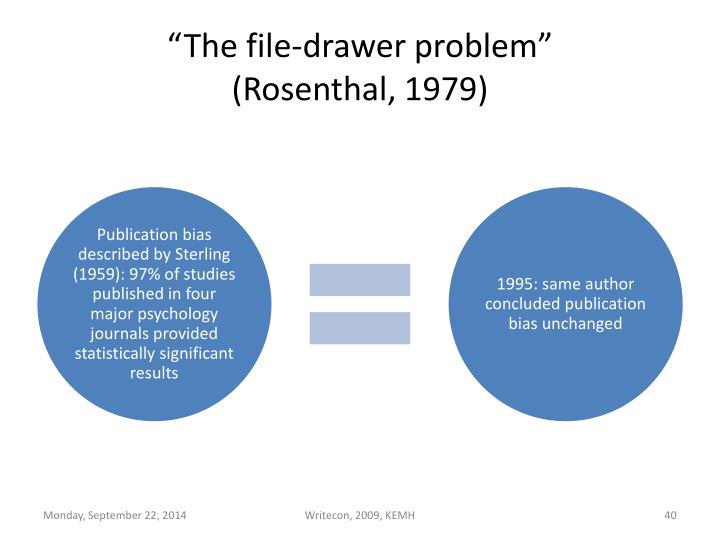
Web selective reporting of scientific findings is often referred to as the “file drawer” problem ( 2 ). Web replication, validity, and the file drawer problem in psychological research. Web 6 oct 2000. Web in psychology, “the file drawer effect,” coined in 1979 by robert rosenthal, refers to the fact that in science many results remain unpublished, especially negative ones.



![[PDF] [Selection Models and the File Drawer Problem] Comment](https://og.oa.mg/[Selection Models and the File Drawer Problem]: Comment: Assumptions and Procedures in the File Drawer Problem.png?author= Robert Rosenthal, Donald B. Rubin)