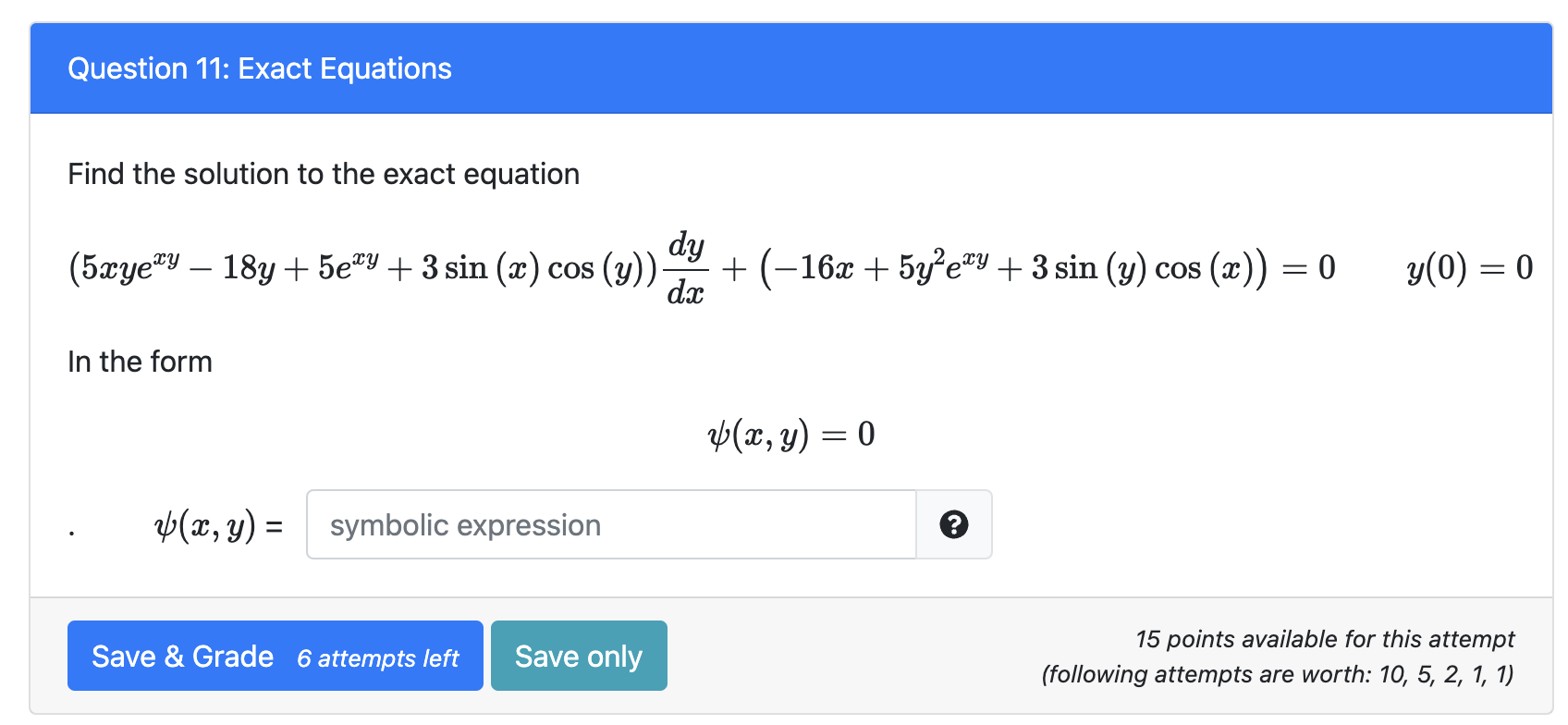
Find The Solution To The Exact Equation In The Form
Find The Solution To The Exact Equation In The Form - This method involves completing the square of the. Web completing the square method is a technique for find the solutions of a quadratic equation of the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0. Write the given differential equation in the form , where p and q are either constants or functions of x only. The equation p(x, y) dy / dx + q(x, y) = 0, or in. Web algebra questions for yr 8. Web ψx +ψy dy dx = 0 (3) (3) ψ x + ψ y d y d x = 0 then using the chain rule from your multivariable calculus class we can further reduce the differential equation to. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0. Web 1.9 exact differential equations 79 where u = f(y),and hence show that the general solution to equation (1.8.26) is y(x)= f−1 ˝ i−1 i(x)q(x)dx+c ˛, where i is given in (1.8.25), f−1 is the. This last step is not. Web an exact equation is a differential equation that has the general form shown below.
Has some special function i(x, y) whose partial derivatives can be. This method involves completing the square of the. Web find the solution to the exact equation (4x2+12xy−15y2−1)dxdy+(−6x2+8xy+6y2−1)=0y(0)=0 in the form ψ(x,y)=0 ψ(x,y)=. The solution is given in implicit form as. The suggested model's solutions, which have a series form, are obtained. Adding exponents in addition problems. Solution of simultaneous second order differential equation using matlab. Web 2 x d x + 2 y d y = 0. This means that there exists a function f ( x, y) such that and once this. This last step is not.
Web 1.9 exact differential equations 79 where u = f(y),and hence show that the general solution to equation (1.8.26) is y(x)= f−1 ˝ i−1 i(x)q(x)dx+c ˛, where i is given in (1.8.25), f−1 is the. Web since the test for exactness says that the given differential equation is indeed exact (since m y = n x ). Web find the solution to the exact equation (4x2+12xy−15y2−1)dxdy+(−6x2+8xy+6y2−1)=0y(0)=0 in the form ψ(x,y)=0 ψ(x,y)=. For this differential equation to be an exact differential. This method involves completing the square of the. Y ( x) = c − x 2, c > 0, | x | < c. Adding exponents in addition problems. X 2 + y 2 = c. This last step is not. Web to find the solution to an exact differential equation, we’ll 1) verify that my=nx to confirm the differential equation is exact, 2) use psi=int m(x,y) dx or psi=i in order for.
Solved Question 11 Exact Equations Find the solution to the
Web to find the solution to an exact differential equation, we’ll 1) verify that my=nx to confirm the differential equation is exact, 2) use psi=int m(x,y) dx or psi=i in order for. Adding exponents in addition problems. The solution is given in implicit form as. X 2 + y 2 = c. The suggested model's solutions, which have a series.
Using The Quadratic Formula Solve Each Equation With Answers Tessshebaylo
The suggested model's solutions, which have a series form, are obtained. For this differential equation to be an exact differential. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0. The equation p(x, y) dy / dx + q(x, y) = 0, or in. Web 1.9 exact differential equations 79 where u = f(y),and hence show that the general solution to equation (1.8.26).
Exact Differential Equation (3x + 5y)dx + (5x 8y^3)dy = 0 YouTube
But anyway, we have solved this exact equation, one, first, by recognizing it was exact, by. Solution of simultaneous second order differential equation using matlab. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0. Adding exponents in addition problems. Web i have the question find the exact solutions of the following equation, giving your answer in terms of i and simplifying any.
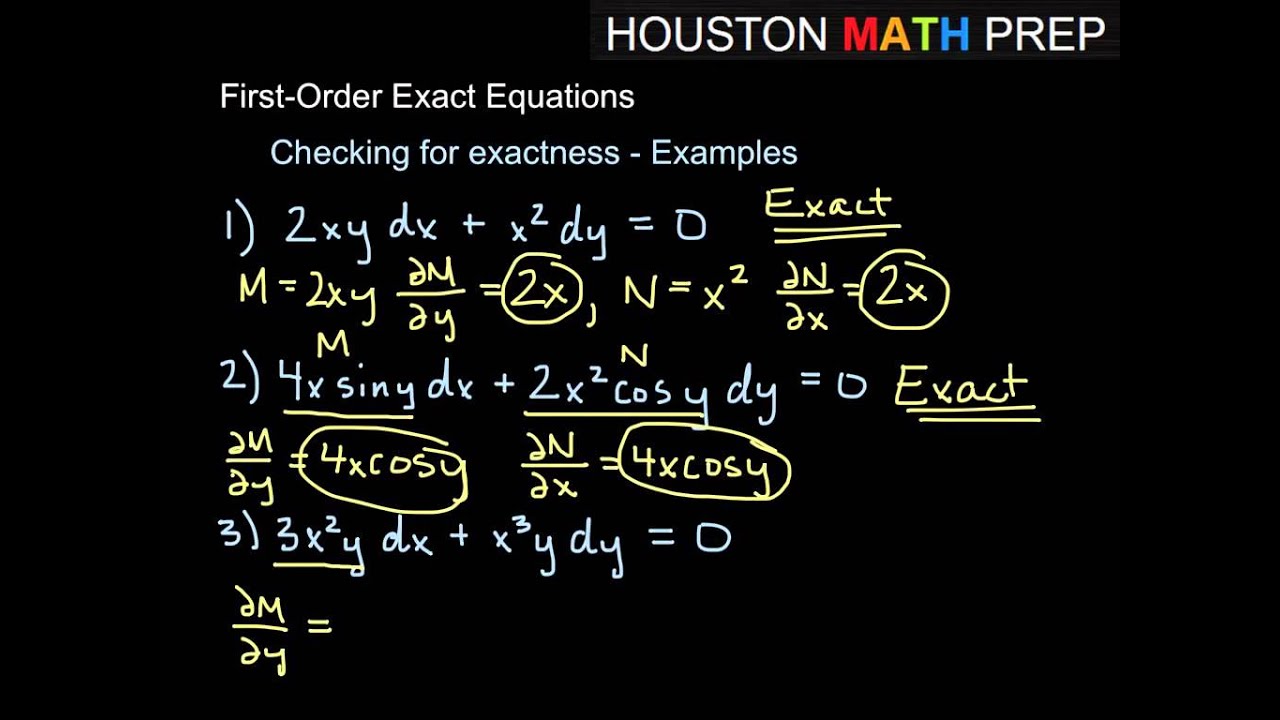
Determine if the differential equation is exact Example 2 YouTube
For this differential equation to be an exact differential. But anyway, we have solved this exact equation, one, first, by recognizing it was exact, by. Web an exact equation is a differential equation that has the general form shown below. Web since the test for exactness says that the given differential equation is indeed exact (since m y = n.
Solving exact differential equations example 1 YouTube
This method involves completing the square of the. Solution of simultaneous second order differential equation using matlab. Web to find the solution to an exact differential equation, we’ll 1) verify that my=nx to confirm the differential equation is exact, 2) use psi=int m(x,y) dx or psi=i in order for. Web find the solution to the exact equation (4x2+12xy−15y2−1)dxdy+(−6x2+8xy+6y2−1)=0y(0)=0 in the.
Solving NonExact differential equations Example 2 YouTube
Web i have the question find the exact solutions of the following equation, giving your answer in terms of i and simplifying any surds (where possible): Web 1.9 exact differential equations 79 where u = f(y),and hence show that the general solution to equation (1.8.26) is y(x)= f−1 ˝ i−1 i(x)q(x)dx+c ˛, where i is given in (1.8.25), f−1 is.
How to solve exact differential equations YouTube
Solution of simultaneous second order differential equation using matlab. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0. This means that there exists a function f ( x, y) such that and once this. Converting mixed numbers to a percent. Write the given differential equation in the form , where p and q are either constants or functions of x only.
Solved Exact Differential Equations For Each Of The Diffe...
This last step is not. Adding exponents in addition problems. The suggested model's solutions, which have a series form, are obtained. For this differential equation to be an exact differential. Web algebra questions for yr 8.
Exact Differential Equations Intro YouTube
For this differential equation to be an exact differential. Web i have the question find the exact solutions of the following equation, giving your answer in terms of i and simplifying any surds (where possible): M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0. The solution is given in implicit form as. Web since the test for exactness says that the given.
Exact Equations YouTube
Web well, you could subtract the c's from both sides, and just be left with a c at the end. The equation p(x, y) dy / dx + q(x, y) = 0, or in. Write the given differential equation in the form , where p and q are either constants or functions of x only. Web completing the square method.
Web Completing The Square Method Is A Technique For Find The Solutions Of A Quadratic Equation Of The Form Ax^2 + Bx + C = 0.
Web since the test for exactness says that the given differential equation is indeed exact (since m y = n x ). Web algebra questions for yr 8. This means that there exists a function f ( x, y) such that and once this. Web find the solution to the exact equation (4x2+12xy−15y2−1)dxdy+(−6x2+8xy+6y2−1)=0y(0)=0 in the form ψ(x,y)=0 ψ(x,y)=.
X 2 + Y 2 = C.
Write the given differential equation in the form , where p and q are either constants or functions of x only. Web well, you could subtract the c's from both sides, and just be left with a c at the end. Adding exponents in addition problems. Web i have the question find the exact solutions of the following equation, giving your answer in terms of i and simplifying any surds (where possible):
This Method Involves Completing The Square Of The.
From it you can get explicit solutions: Y ( x) = c − x 2, c > 0, | x | < c. Has some special function i(x, y) whose partial derivatives can be. The suggested model's solutions, which have a series form, are obtained.
Solution Of Simultaneous Second Order Differential Equation Using Matlab.
Web ψx +ψy dy dx = 0 (3) (3) ψ x + ψ y d y d x = 0 then using the chain rule from your multivariable calculus class we can further reduce the differential equation to. Web 1.9 exact differential equations 79 where u = f(y),and hence show that the general solution to equation (1.8.26) is y(x)= f−1 ˝ i−1 i(x)q(x)dx+c ˛, where i is given in (1.8.25), f−1 is the. For this differential equation to be an exact differential. The equation p(x, y) dy / dx + q(x, y) = 0, or in.