Haploid Drawing
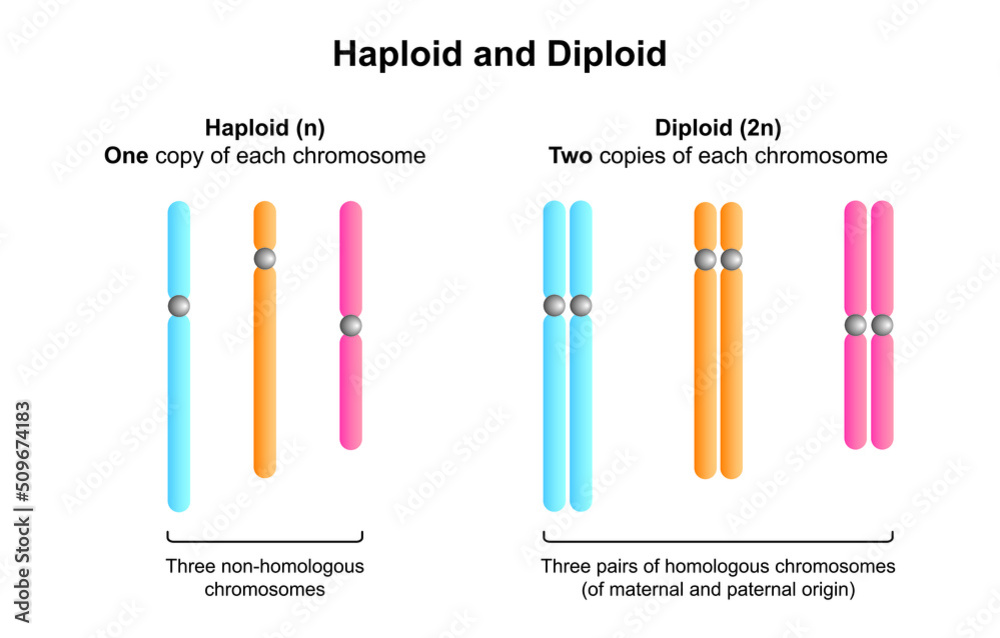
Haploid Drawing - Most cells in humans are diploid rather than haploid, meaning they have two copies of each chromosome. The figure shows a drawing of a cross section of the seminiferous tubules in the testes. Web sperm and egg cells, known as gametes, fuse during fertilization to create a zygote. Or (e) c and e. View the slides available of aspergillus. Web see all videos for this article. Draw a picture of the zygospores you viewed under the microscope. Web haploid is the condition of a cell having a one set of chromosomes. Web in the circle below, sketch a 2n=6 diploid cell in metaphase of mitosis. Compare and contrast the behaviors of chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis.
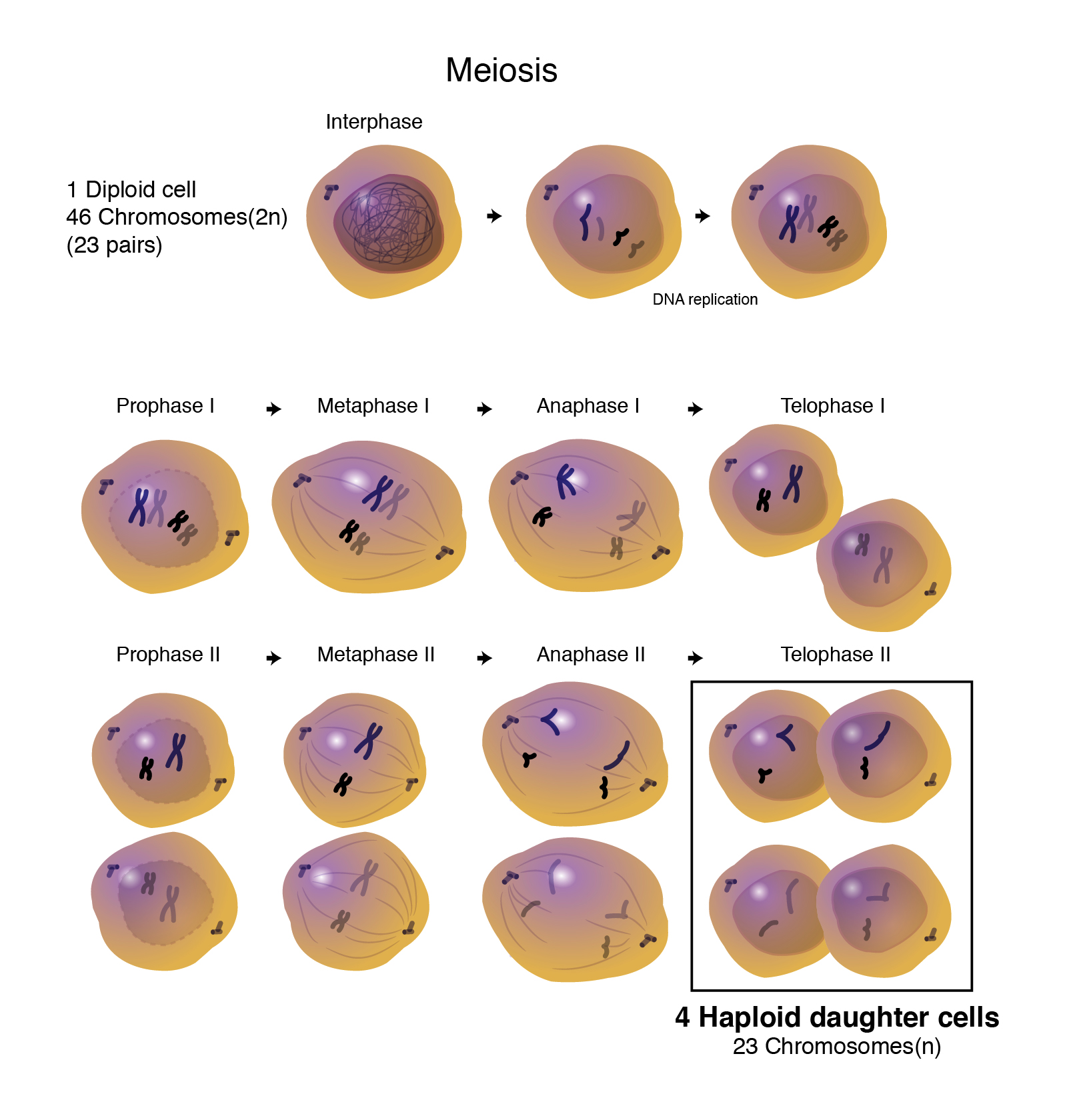
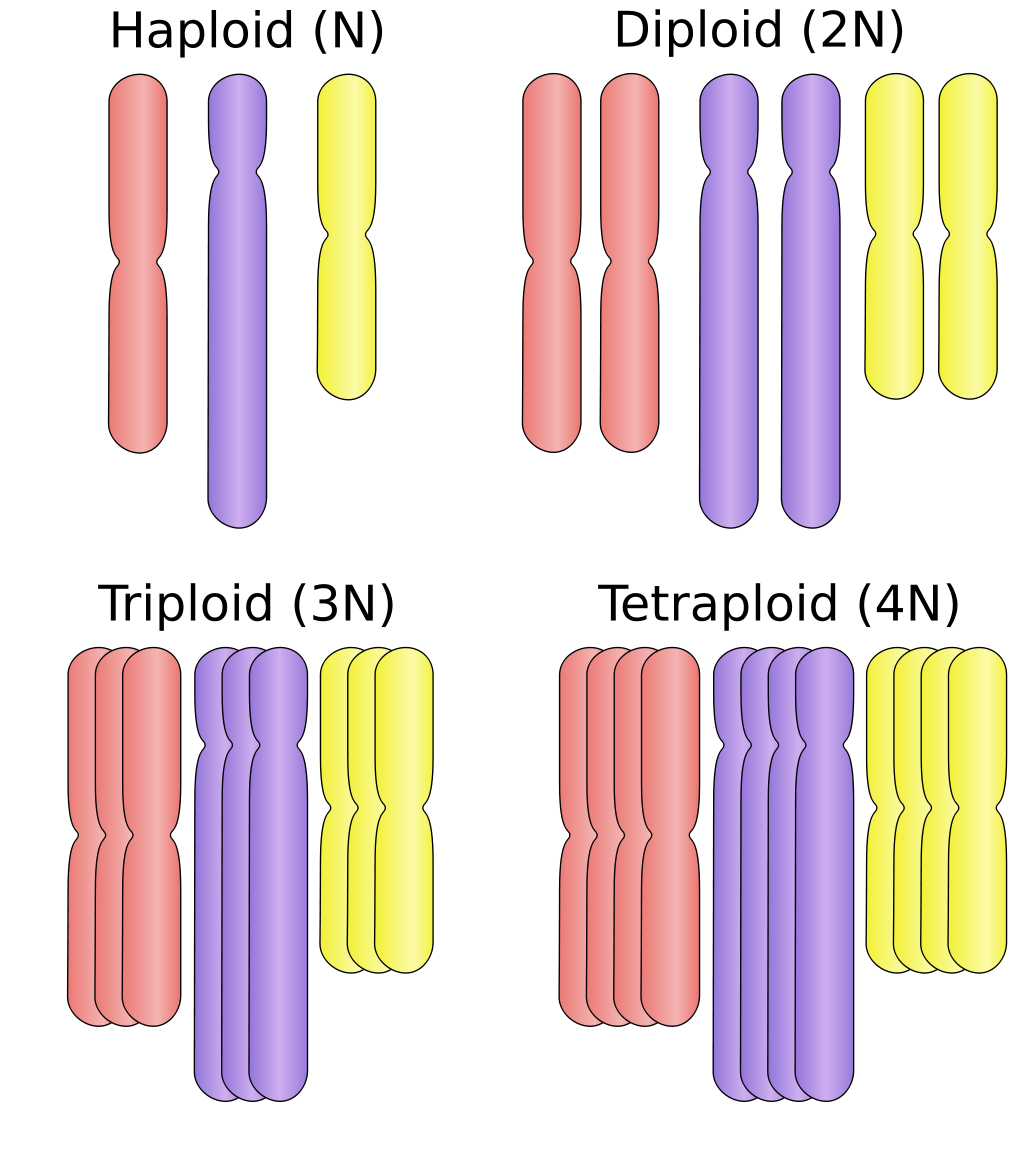
Ploidy refers to the number of copies of the genome. A monogenic gene gives rise to a trait from a single set of alleles. Can you find any conidiospores? An organism's full set of chromosomes can be viewed by taking photographs of cells dividing. Describe the chromosomal makeup of a cell using the terms chromosome, sister chromatid, homologous chromosome, diploid, haploid, and tetrad. Or (e) c and e. The purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes, or sex cells. Web in the circle below, sketch a 2n=6 diploid cell in metaphase of mitosis. During meiosis, four daughter cells are produced, each of which are haploid (containing half as many chromosomes as the parent cell). Meiosis starts with a diploid cell (a cell with two sets of chromosomes) and ends up with four haploid cells (cells with only one set of chromosomes), which are called gametes (eggs.
Problem sets built by lead tutors expert video explanations. Web the result is the production of four haploid cells (n chromosomes; Web haploid cells, containing a single copy of each homologous chromosome, are found only within structures that give rise to either gametes or spores. Download up to 8 free medical animations from nucleus by signing up for a free trial at: The process of meiosis is characteristic of organisms that reproduce sexually. View the slides available of aspergillus. Homologous chromosomes from each parent determine traits, including sex. Describe the chromosomal makeup of a cell using the terms chromosome, sister chromatid, homologous chromosome, diploid, haploid, and tetrad. Four haploid cells in which each chromosome has just one chromatid. Prophase ii, metaphase ii, anaphase ii, and telophase ii.
meiosis_2.html 13_08bAnimalMeiosisTwo.jpg
Because you’re a human being, you can’t just divide in two to make an extra you. Recognize when cells are diploid vs. Can you find any conidiospores? Download up to 8 free medical animations from nucleus by signing up for a free trial at: Web meiosis i practice set.
30 HD Haploid Cells Are Formed In insectza
Compare and contrast the behaviors of chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis. Web in the circle below, sketch a 2n=6 diploid cell in metaphase of mitosis. Four haploid cells in which each chromosome has just one chromatid. Describe the chromosomal makeup of a cell using the terms chromosome, sister chromatid, homologous chromosome, diploid, haploid, and tetrad. Can you find any conidiospores?
FileHaploid English.svg Biological life, Life cycles, Alternation of
This means that the majority of their lifecycle is spent with two copies of the genome in every cell. Ploidy refers to the number of copies of the genome. View the slides available of aspergillus. Web see all videos for this article. This is so that when the sex cells fuse together during fertilization, a complete diploid set is formed.
FileHaploid vs diploid.svg Wikipedia
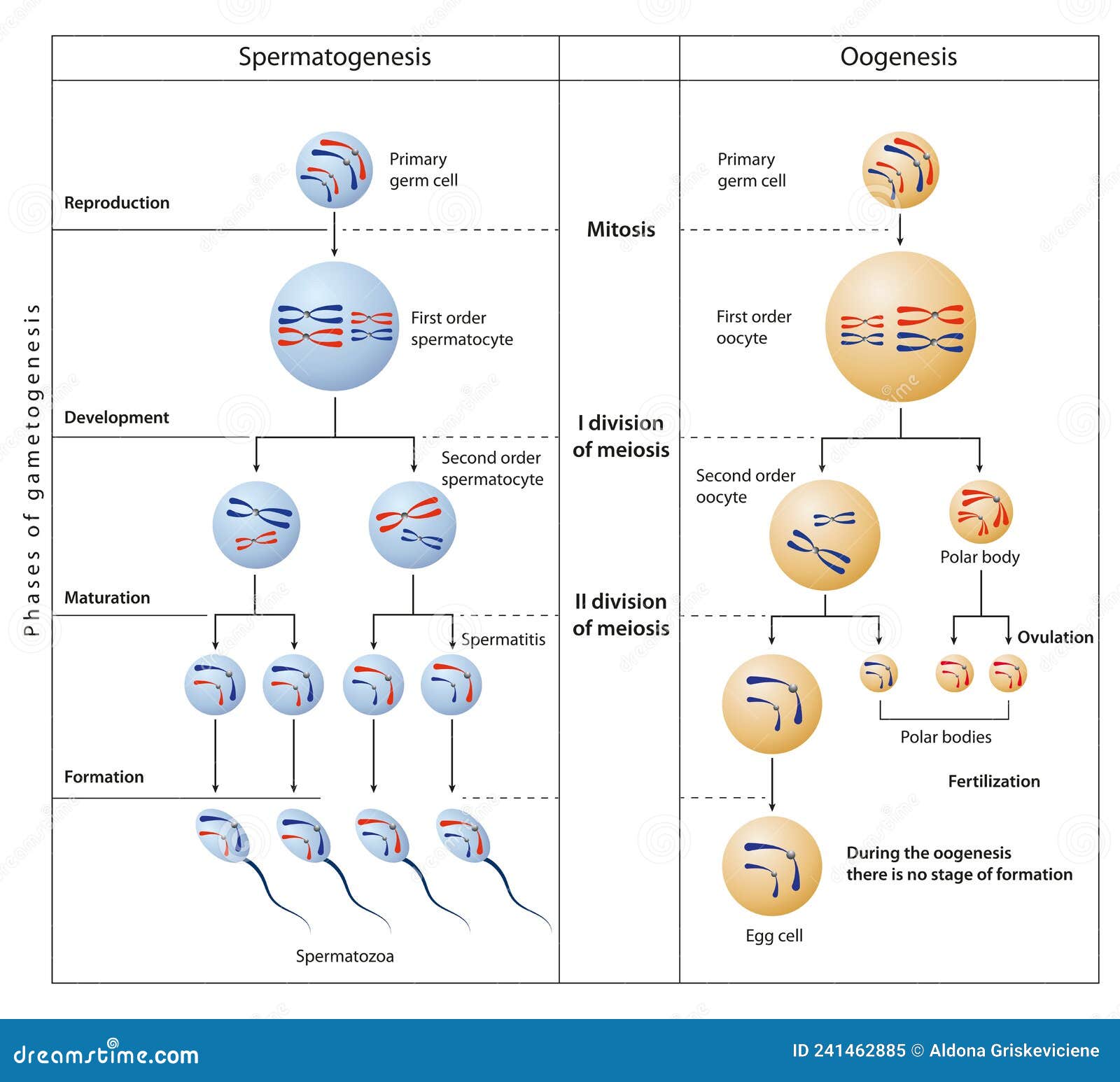
Web sperm and egg cells, known as gametes, fuse during fertilization to create a zygote. This number is always half of the diploid number. View the slides available of aspergillus. Web during prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, creating more variation. Types of sexual life cycles:
Scientific Designing of Differences Between Haploid and Diploid
Download up to 8 free medical animations from nucleus by signing up for a free trial at: Web for employees of hospitals, schools, universities and libraries: One seminiferous tubule has been represented here as the large, circular structure in the center of this diagram. Problem sets built by lead tutors expert video explanations. A haploid cell has only a single.
Haploid
Gametes have half the chromosomes (haploid) of a typical body cell, while zygotes have the full set (diploid). Spores are haploid cells that can produce a haploid organism or can fuse with another spore to form a diploid cell. Meiosis starts with a diploid cell (a cell with two sets of chromosomes) and ends up with four haploid cells (cells.
Diagrammatic representation two haploid cells enter meiosis II
Humans, and many other organisms, are diploid organisms. Web for employees of hospitals, schools, universities and libraries: Dna replicates once, but the cells divide twice. The four main steps of meiosis ii are: Web this video explains the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells and also how to draw the stages.
Fusion De Deux Gamètes Haploïdes Pour Former Un Zygote Diploïde
In humans, the products of meiosis are sperm or egg cells. The figure shows a drawing of a cross section of the seminiferous tubules in the testes. The four main steps of meiosis ii are: The purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes, or sex cells. Because you’re a human being, you can’t just divide in two to make an.
During Gametogenesis, Diploid or Haploid Precursor Cells Divide and
Web the sex cells of a human are haploid (n), containing only one homologous chromosome from each pair. (c) b, c, and d. This is so that when the sex cells fuse together during fertilization, a complete diploid set is formed. Ploidy refers to the number of copies of the genome. Gametes have half the chromosomes (haploid) of a typical.
Meiosis QCE Biology Revision
Describe the makeup of a haploid set and a diploid set. Are conidiospores used in sexual or asexual reproduction? The four main steps of meiosis ii are: In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Do you ever wish you could clone yourself (for example, so you could get twice as much done in a day)?
Homologous Chromosomes From Each Parent Determine Traits, Including Sex.
Web is the zygospore diploid or haploid? Humans, and many other organisms, are diploid organisms. Web the process of meiosis, the division of the contents of the nucleus that divides the chromosomes among gametes, reduces the chromosome number by half, while fertilization, the joining of two haploid gametes, restores the diploid condition. Do you ever wish you could clone yourself (for example, so you could get twice as much done in a day)?
Web See All Videos For This Article.
Ploidy refers to the number of copies of the genome. Describe the makeup of a haploid set and a diploid set. 23 in humans) from the two haploid cells (with n chromosomes, each consisting of two sister chromatids) [clarification needed] produced in meiosis i. A haploid cell has only a single set of chromosomes.
View The Slides Available Of Aspergillus.
Draw a picture of the zygospores you viewed under the microscope. Web is the zygospore diploid or haploid? Meiosis starts with a diploid cell (a cell with two sets of chromosomes) and ends up with four haploid cells (cells with only one set of chromosomes), which are called gametes (eggs. A monogenic gene gives rise to a trait from a single set of alleles.
Or (E) C And E.
Draw a picture of the zygospores you viewed under the microscope. Most cells in humans are diploid rather than haploid, meaning they have two copies of each chromosome. Identify the cells that are haploid. Anaphase i separates homologous pairs, while telophase i forms two new cells with a haploid number of chromosomes.