How To Draw A Nucleotide
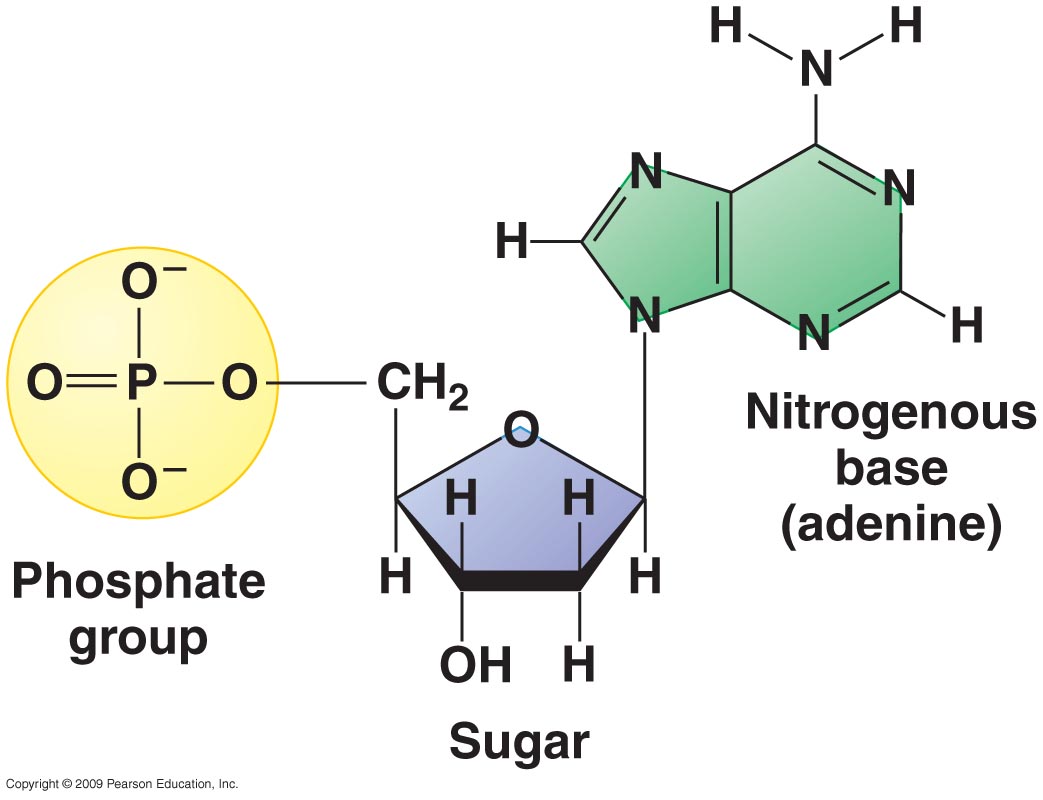
How To Draw A Nucleotide - Include all parts of the dna molecule. Web molecular structure of dna. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. The sugar molecule has a central position in the nucleotide, with the base attached to one of its carbons and the phosphate group (or groups) attached to another. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. Color (orange)phosphate group color (red)5. Web each nucleotide is made up of three parts: The above structure is a #color (magenta)nucleotide#. (use the given dna strand.
Begin drawing pairs of straight, parallel lines within each rounded opening. Color (orange)phosphate group color (red)5. Web identify the sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base, 5' and 3' carbons in a nucleotide and the key difference between dna and rna. Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. Explain the structure of the double helix, including the role of hydrogen bonds and covalent (phosphodiester) bonds. Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in cells. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: Web using this strand of dna as a template, draw a picture of the complete dna molecule. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure.
Include all parts of the dna molecule. This is why dna is the storage molecule and. Web please support the channelmy videos are funded by people like you. A replication unit is any chunk of dna that is capable of being replicated — e.g. A ribose sugar with a hydroxyl (oh) group at the 2' position; Here is a closer look at the components of a nucleotide. Color (orange)phosphate group color (red)5. A nitrogenous base attached with the sugar is called “nucleoside”. Web each nucleotide is made up of three parts: Label the 3' and 5' carbons.
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
The four nitrogenous bases in dna are adenine, cytosine. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains deoxyribose sugar and rna (ribonucleic acid) contains a ribose sugar. Take a look at what a nucleotide is, its structure, and its function in biological processes. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends of your mrna strand. Web the dna molecule is a polymer of nucleotides.
Nucleic Acids Function, Examples, and Monomers
If you enjoy them, please help me make more: A nucleotide is made up of three parts: Take a look at what a nucleotide is, its structure, and its function in biological processes. Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in cells. Notice that each opening contains three such bars,.
How to draw nucleotides in DNA easily/DNA nucleotides easy drawing
This is why dna is the storage molecule and. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. The deoxyribose sugar joined only to the nitrogenous base forms a deoxyribonucleoside called deoxyadenosine, whereas the whole structure along with the phosphate group is.
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Web please support the channelmy videos are funded by people like you. Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. Web this video will be very useful for students to draw the nucleotides in a dna very easily.thanks for watching.
What Is The Basic Shape And Makeup Of A Nucleotide Saubhaya Makeup
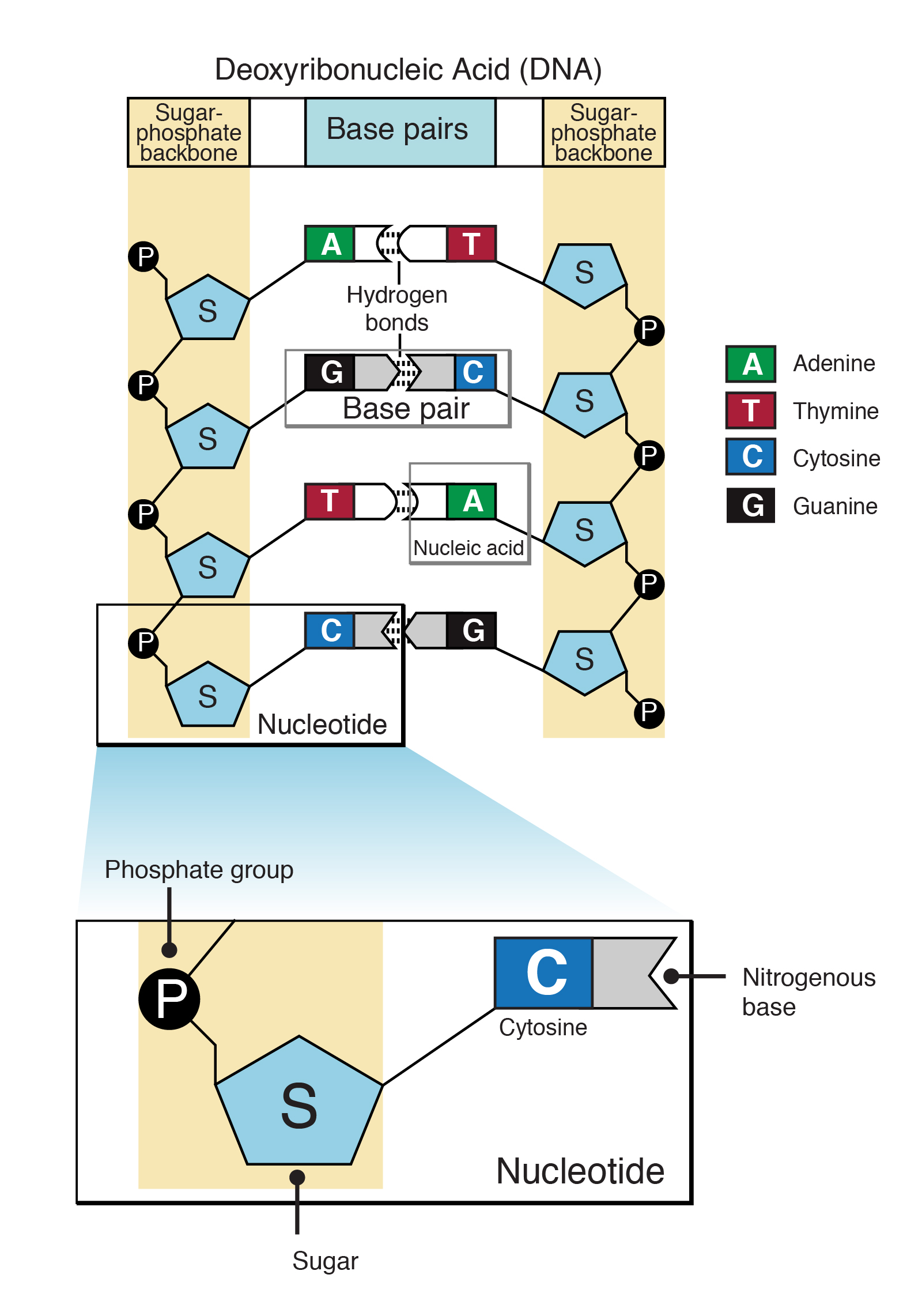
The bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. A plasmid with an origin of replication (ori) is a replication unit. A nitrogenous base attached with the sugar is called “nucleoside”. A replication unit is any chunk of dna that is capable of being replicated — e.g. Enclose them on.
Nucleotides DNA Diagram Labeled Simple
Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in cells. Web molecular structure of dna. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. Include all parts of.
Nucleotide
Here is a closer look at the components of a nucleotide. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Web molecular structure of dna. If you enjoy them, please help me make more: In contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers.
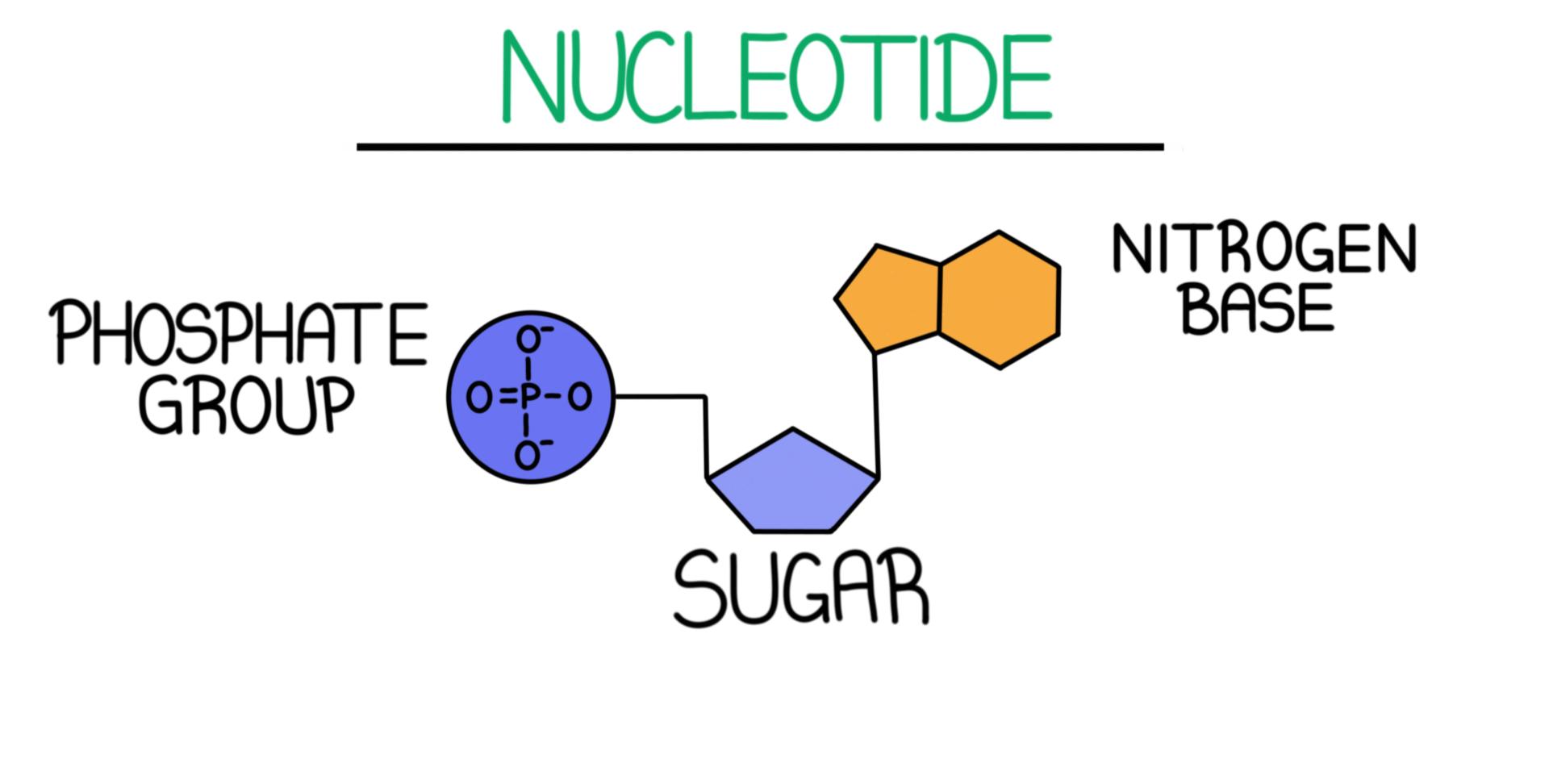
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected
See below the above structure is a color (magenta)nucleotide. Web identify the sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base, 5' and 3' carbons in a nucleotide and the key difference between dna and rna. Web each nucleotide is made up of three parts: Dna and rna code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic.
Structure of a Nucleotide Tutorial Sophia Learning
The presence of the 2' hydroxyl group makes rna more susceptible to hydrolysis. A nucleotide comprises a pentose sugar. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: Phosphate is associated with the sugar of nucleoside by an ester bond with the 5 th c hydroxyl group. Begin drawing pairs of straight, parallel lines within each rounded opening.
Nucleotides Castell Alun High School Biology
Web a diagonal phylogenetic tree, labeled convergent evolution of whiskers. The four nitrogenous bases in dna are adenine, cytosine. Web the three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. This instructional video outlines the external and int. Label the 3' and 5' carbons.
A Replication Unit Is Any Chunk Of Dna That Is Capable Of Being Replicated — E.g.
Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. Alternatively, this can also mean a region of dna that is replicated together. A nucleotide comprises a pentose sugar. A dna molecule is composed of two strands.
Explain The Structure Of The Double Helix, Including The Role Of Hydrogen Bonds And Covalent (Phosphodiester) Bonds.
A plasmid with an origin of replication (ori) is a replication unit. Web this video will be very useful for students to draw the nucleotides in a dna very easily.thanks for watching and please subscribe to the channel for drawing. Explain why the abundance of a is roughly equal to t and g is roughly equal to c in dna. A sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase.
A Nucleotide Is An Organic Molecule That Is The Building Block Of Dna And Rna.
Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in cells. See below the above structure is a color (magenta)nucleotide. Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. A nucleotide is made up of three parts:
Here Is A Closer Look At The Components Of A Nucleotide.
The root splits at a point labeled most recent common ancestor of a through e, to form two branches. Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The sugar molecule has a central position in the nucleotide, with the base attached to one of its carbons and the phosphate group (or groups) attached to another. You do not need to draw your molecule with atomic accuracy.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)


/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
/Nucleotide-58e518d35f9b58ef7e62834d.jpg)