How To Draw A Polypeptide Chain
How To Draw A Polypeptide Chain - By convention, when you are drawing peptide chains,. Web each protein in your cells consists of one or more polypeptide chains. Please select l or d isomer of an amino acid. The peptide bond has two. The chemical properties and order of the amino acids determines the structure and function of the polypeptide. The quaternary structure of a. Web hemoglobin, with four polypeptide chains or subunits, is the most frequently cited example of a protein having quaternary structure (figure 2.1.5). Web peptide bonds are made within ribosomes during a process called «translation» to form polypeptides, which then undergo various molecular processing and modification, before. The backbone of any protein molecule is a polypeptide chain obtained by the condensation of a large number of amino acids with the elimination of. The process for drawing longer.
These chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a. Web peptide bonds are made within ribosomes during a process called «translation» to form polypeptides, which then undergo various molecular processing and modification, before. These proteins are also called polypeptides. Each of these polypeptide chains is made up of amino acids, linked together in a specific order. Web the fundamental molecules of life are polymers. Web each protein in your cells consists of one or more polypeptide chains. Peptide bonds are the vital links that connect amino acids to form polypeptide chains, which fold into functional proteins. Two amino acids combine, with water leaving (dehydration), forming a polypeptide with a. 8.3k views 3 years ago amino acids, peptides, nucleic acids, n'at. Please select l or d isomer of an amino acid.
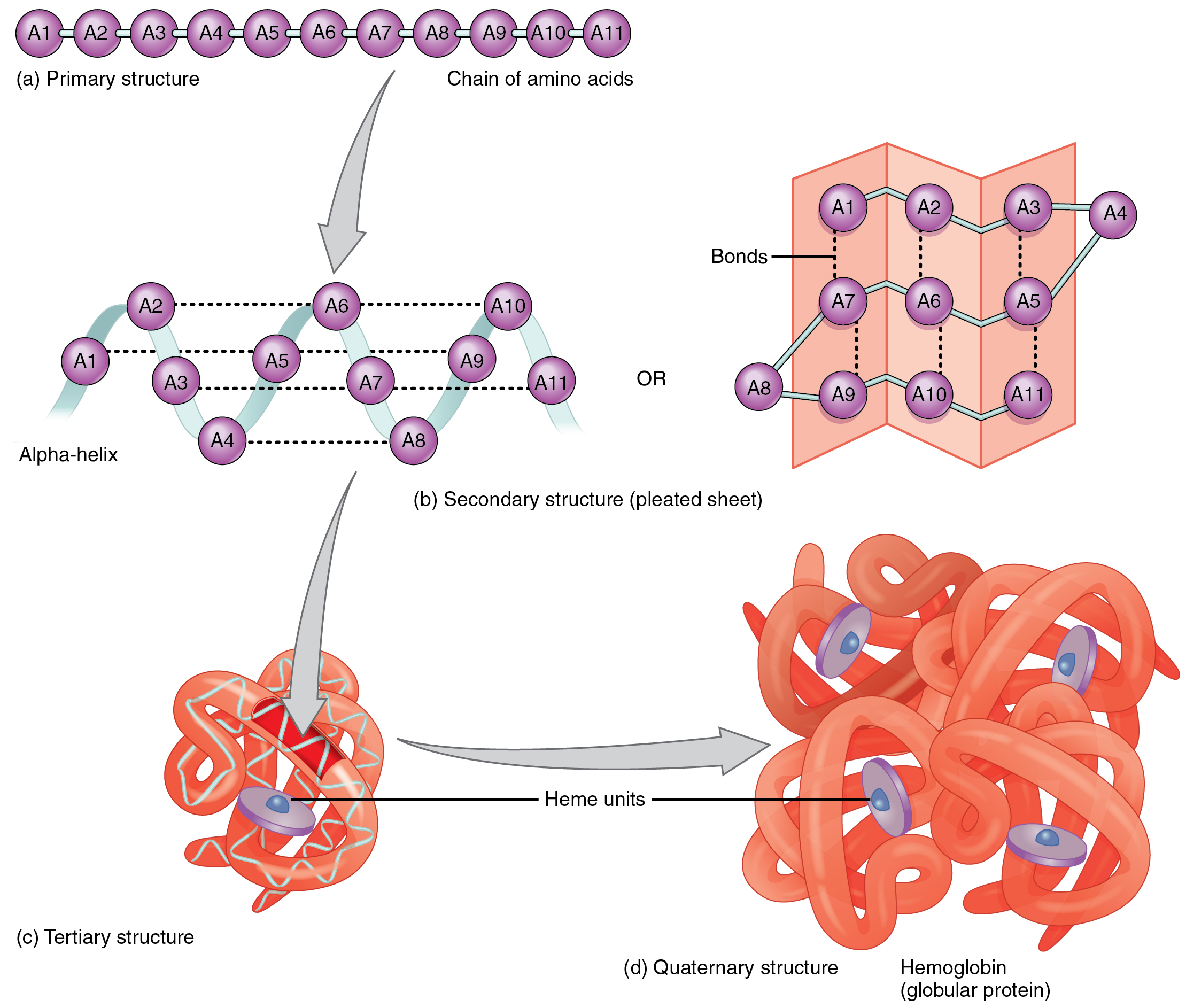
Web the unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is its primary structure. Polypeptides are multiple amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Web many proteins are formed by not only one strand of amino acids, but many. 26k views 14 years ago. These proteins are also called polypeptides. The peptide bond has two. Web each protein contains one or more polypeptide chain. Two amino acids combine, with water leaving (dehydration), forming a polypeptide with a. Therefore if a protein were to contain only one strand of. Peptide bonds are the vital links that connect amino acids to form polypeptide chains, which fold into functional proteins.
How to Draw Peptide Chains 18 Steps (with Pictures) Instructables
Web hemoglobin, with four polypeptide chains or subunits, is the most frequently cited example of a protein having quaternary structure (figure 2.1.5). The chemical properties and order of the amino acids determines the structure and function of the polypeptide. Web peptide bonds are made within ribosomes during a process called «translation» to form polypeptides, which then undergo various molecular processing.
4.7.2 Defining Protein Medicine LibreTexts
Web in this lesson you'll learn some quick rules to draw polypeptides. For example, the hormone insulin has two polypeptide. Web the ensemble of formations and folds in a single linear chain of amino acids — sometimes called a polypeptide — constitutes the tertiary structure of a protein. The backbone of any protein molecule is a polypeptide chain obtained by.
Polypeptide Chain Definition, Structure & Synthesis Video & Lesson
The chemical properties and order of the amino acids determines the structure and function of the polypeptide. Please select l or d isomer of an amino acid. Web amino acid chains that are longer than that are called polypeptides. This tool allows to construct peptide sequence and calculate molecular weight and molecular formula. The process for drawing longer.
Polypeptide Structure Diagram A) The structure of αLA (PDB 1F6S
Two amino acids combine, with water leaving (dehydration), forming a polypeptide with a. The backbone of any protein molecule is a polypeptide chain obtained by the condensation of a large number of amino acids with the elimination of. Web the unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is its primary structure. Each of these polypeptide chains is made.
Polypeptide Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
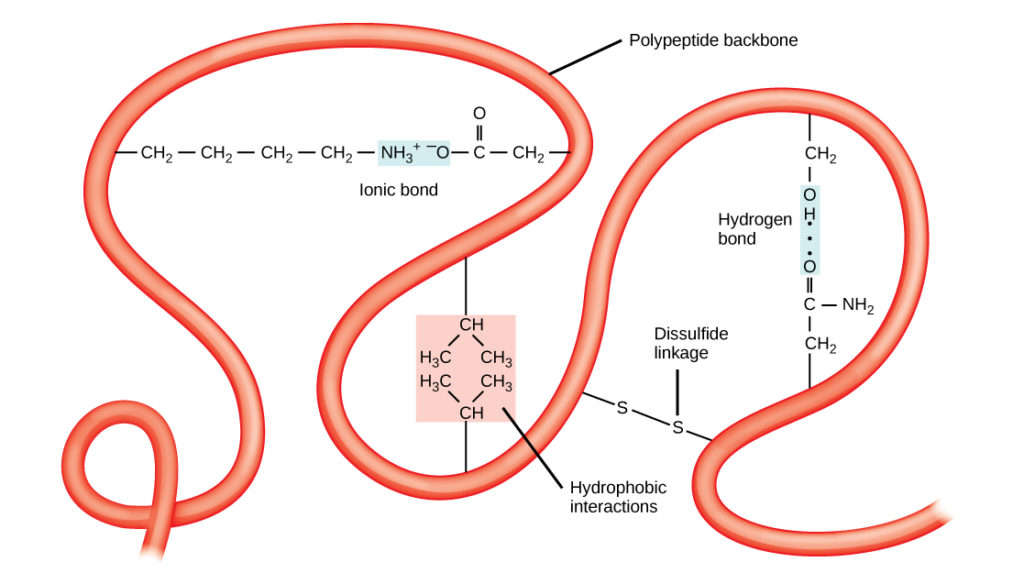
The backbone of any protein molecule is a polypeptide chain obtained by the condensation of a large number of amino acids with the elimination of. Polypeptides are multiple amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. The linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain are held together by peptide. Web the fundamental molecules of life are polymers. Web in.
Amino Acids and Polypeptide Chains Expii
These bonds are formed through. 8.3k views 3 years ago amino acids, peptides, nucleic acids, n'at. Prominent examples include nucleic acids and proteins, both of which assume a vast array of mechanical properties and three. Here are some key features of codons to keep in mind as we move. Web in an mrna, the instructions for building a polypeptide come.
Protein Structure and Function An Interactive Introduction to
Web the fundamental molecules of life are polymers. Web the simplest level of protein structure, primary structure, is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. Web many proteins are formed by not only one strand of amino acids, but many. Web peptide bonds are made within ribosomes during a process called «translation» to form polypeptides, which then.
How to draw polypeptides Real Chemistry YouTube
Web each protein in your cells consists of one or more polypeptide chains. Two amino acids combine, with water leaving (dehydration), forming a polypeptide with a. Web both peptides and proteins fall under a category called polypeptide chains. These chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a. Web in an mrna, the.
Biochemistry Glossary Peptide Bond Formation Draw It to Know It
By convention, when you are drawing peptide chains,. These proteins are also called polypeptides. The chemical properties and order of the amino acids determines the structure and function of the polypeptide. Prominent examples include nucleic acids and proteins, both of which assume a vast array of mechanical properties and three. Each of these polypeptide chains is made up of amino.
Reading Protein Structure Biology I
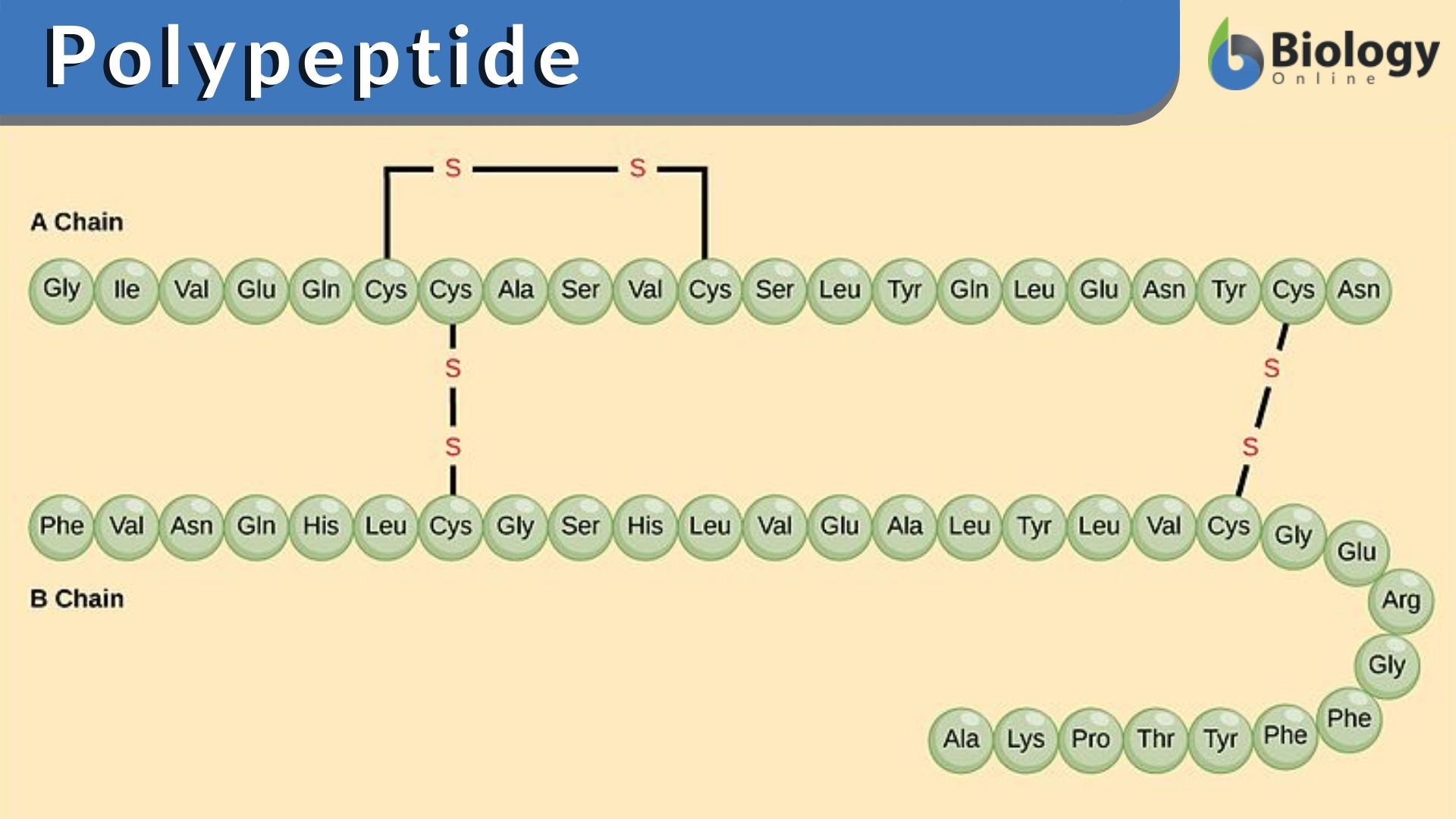
Each of these polypeptide chains is made up of amino acids, linked together in a specific order. For example, the hormone insulin has two polypeptide. Web each protein contains one or more polypeptide chain. Two amino acids combine, with water leaving (dehydration), forming a polypeptide with a. Web amino acid chains that are longer than that are called polypeptides.
Web Each Protein In Your Cells Consists Of One Or More Polypeptide Chains.
Polypeptides are multiple amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Web hemoglobin, with four polypeptide chains or subunits, is the most frequently cited example of a protein having quaternary structure (figure 2.1.5). This tool allows to construct peptide sequence and calculate molecular weight and molecular formula. A tool that draws peptide primary structure and calculates theoretical peptide properties.
These Bonds Are Formed Through.
For example, the hormone insulin has two polypeptide. Web the ensemble of formations and folds in a single linear chain of amino acids — sometimes called a polypeptide — constitutes the tertiary structure of a protein. Please select l or d isomer of an amino acid. This is the first part of making a polypeptide chain.
Web The Unique Sequence Of Amino Acids In A Polypeptide Chain Is Its Primary Structure.
The peptide bond has two. The quaternary structure of a. By convention, when you are drawing peptide chains,. Web in this lesson you'll learn some quick rules to draw polypeptides.
Prominent Examples Include Nucleic Acids And Proteins, Both Of Which Assume A Vast Array Of Mechanical Properties And Three.
The chemical properties and order of the amino acids determines the structure and function of the polypeptide. Web each protein contains one or more polypeptide chain. 26k views 14 years ago. Peptide bonds are the vital links that connect amino acids to form polypeptide chains, which fold into functional proteins.