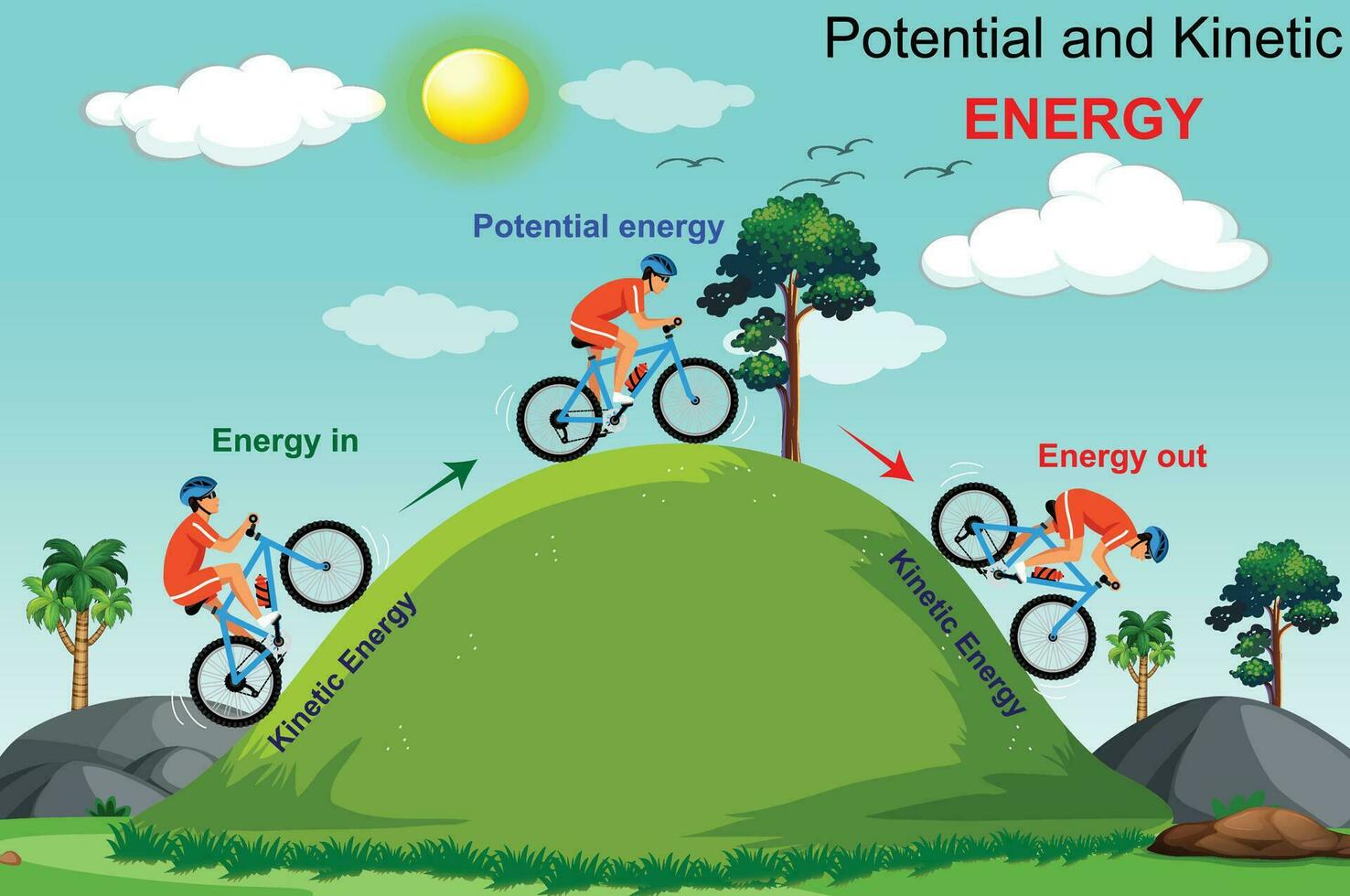
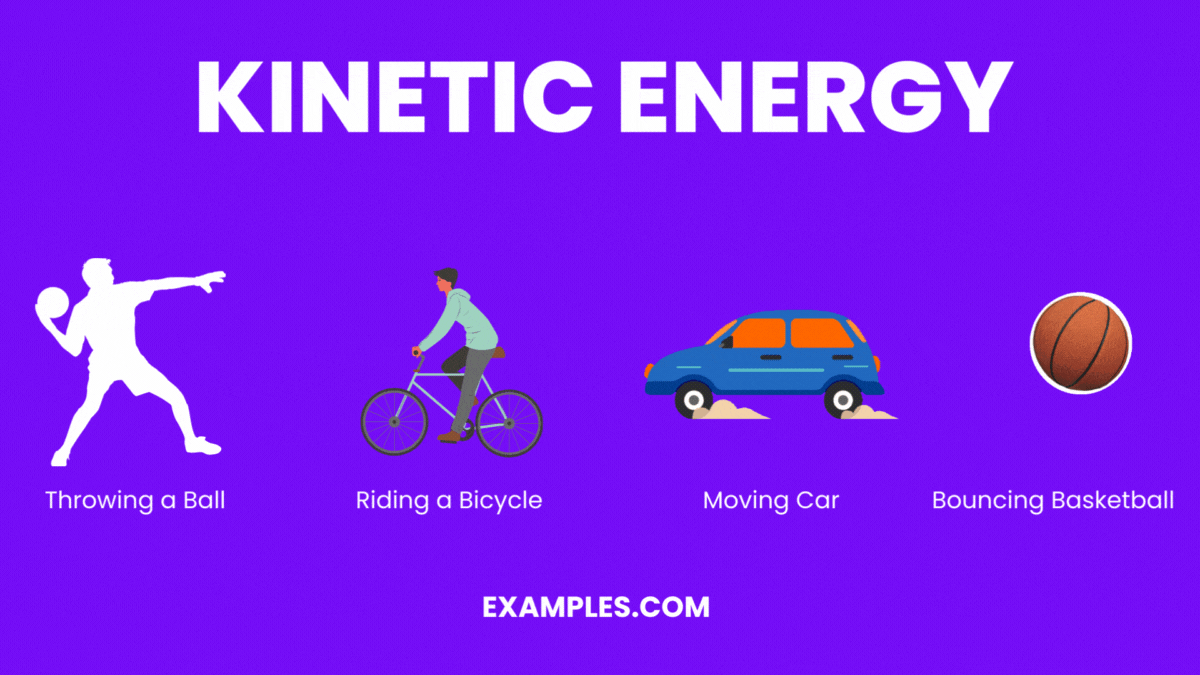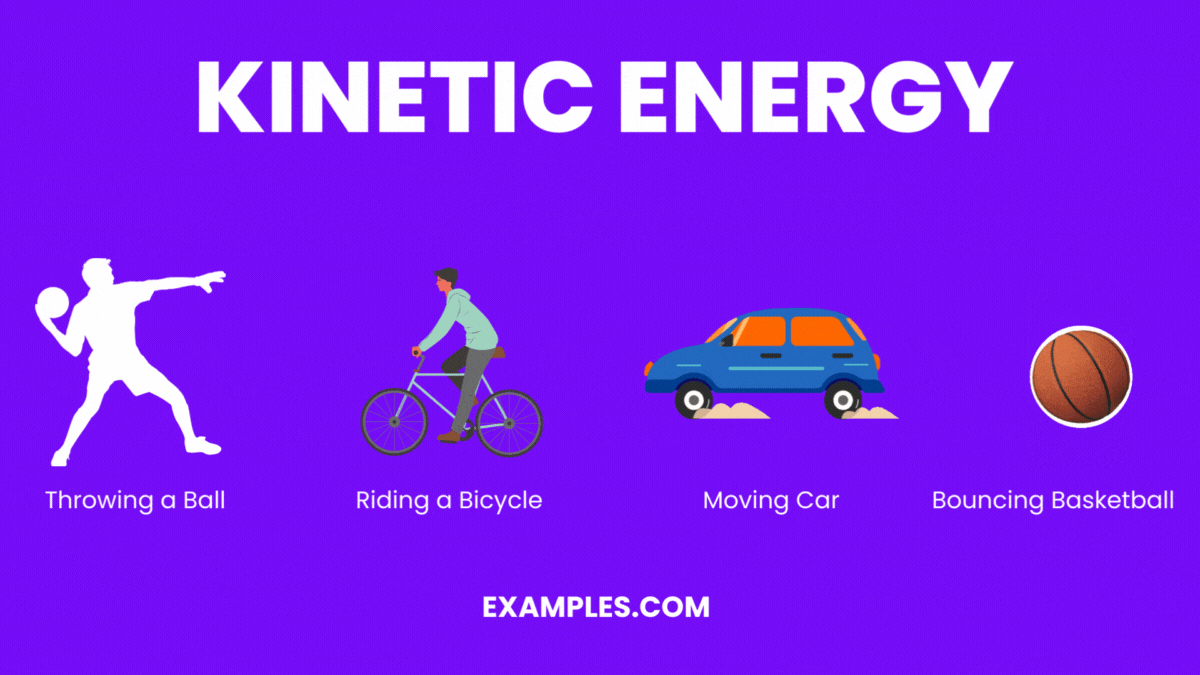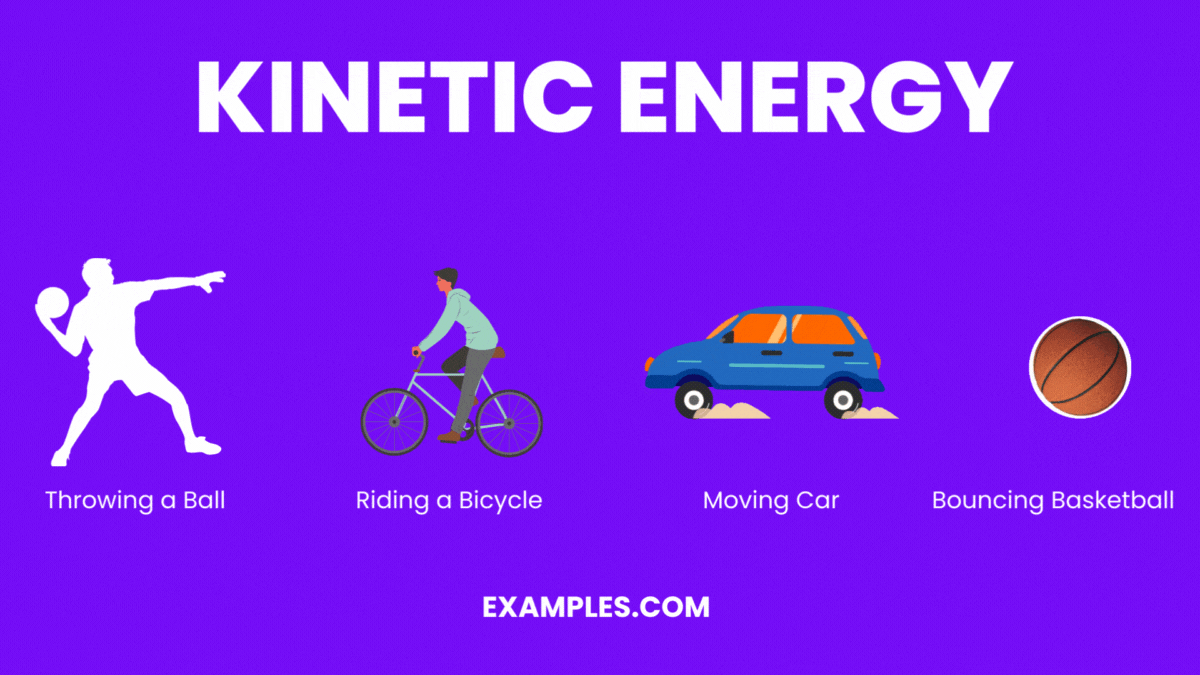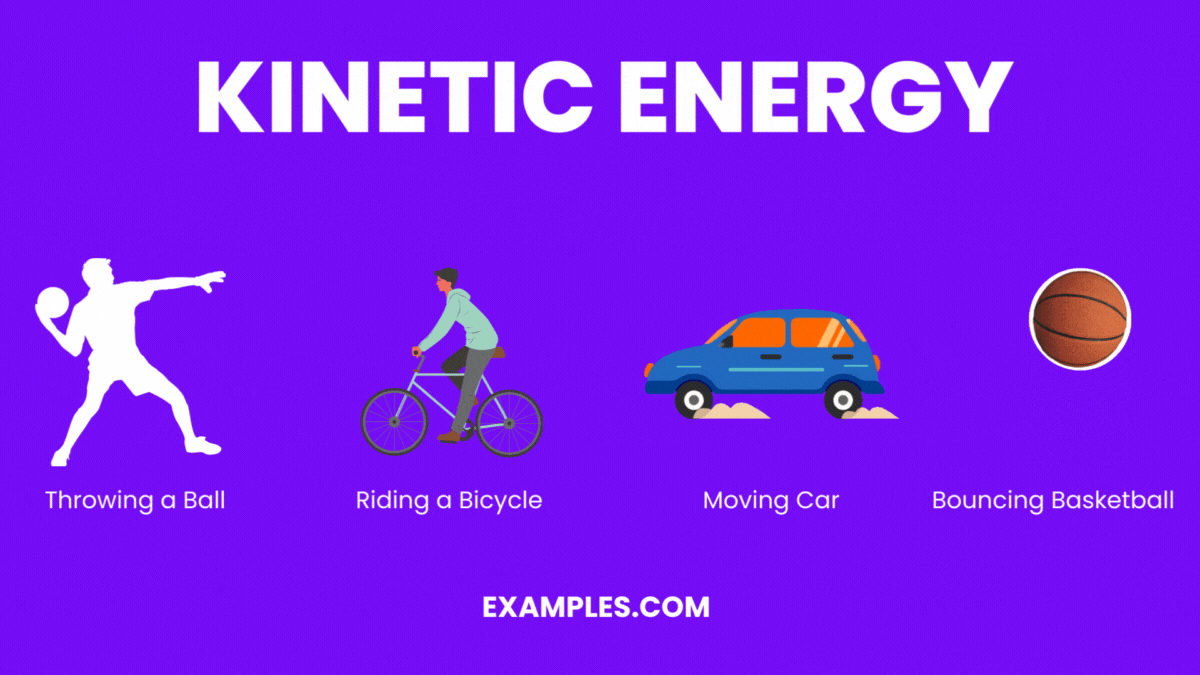
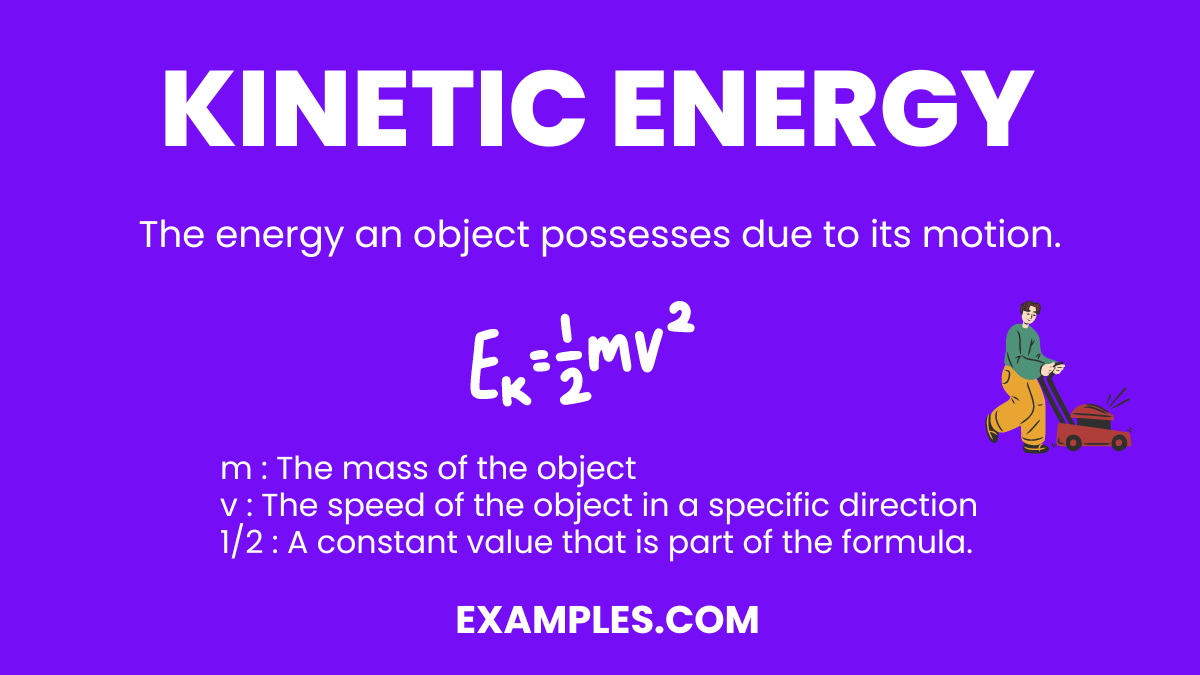
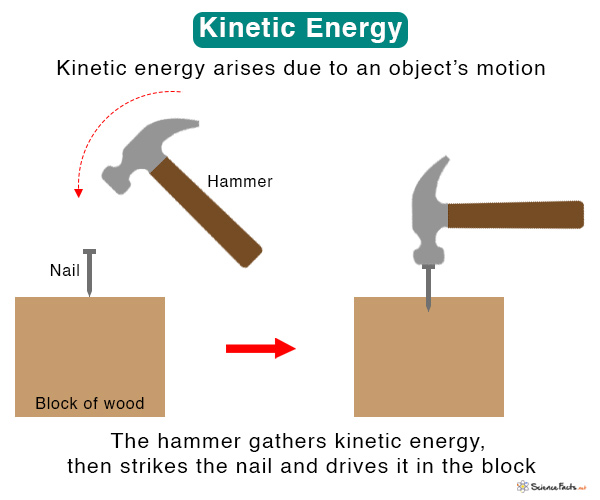
Kinetic Energy Drawing
Kinetic Energy Drawing - How to construct an energy graph. Imagine two objects moving at the same speed. Web they are typically used to represent the kinetic and potential energy within a system, in addition to a horizontal line that depicts the total mechanical energy of the system. To draw the energy graph of a system, the following method should be used: How to calculate kinetic energy. Speed is the magnitude of velocity, so you can use it in the. Drawing of kinetic energy stock illustrations K = 1 2 m v 2. We take precisely the same steps to draw the energy diagram for a mass on a spring, but there are some differences, such as two forbidden regions and a different slope for every position, and there is one additional feature for this potential that doesn't exist for the case of gravity: K = ∑ 1 2 m v 2.
K = 1 2 m v 2. This is the energy between interacting objects, and this energy can be either attractive or repulsive. K = ∑ 1 2mv2. Drawing of kinetic energy stock illustrations Web kinetic energy is k on an energy graph and has the formula [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{2}mv^2 }[/math]. An object’s kinetic energy is directly related to its mass. How to calculate kinetic energy. To draw the energy graph of a system, the following method should be used: We take precisely the same steps to draw the energy diagram for a mass on a spring, but there are some differences, such as two forbidden regions and a different slope for every position, and there is one additional feature for this potential that doesn't exist for the case of gravity: We then extend this definition to any system of particles by adding up the kinetic energies of all the constituent particles:
Web the kinetic energy formula works in classical physics, but it starts to deviate from true energy when the velocity approaches the speed of light (c). Web for example a standard baseball is about 145 g or 0.145 kg and has a terminal velocity of about 33 m/s so it has a kinetic energy of ek = 0.145 * 33^2 = 0.145 * 1089 = 157.9 j. If one object has twice the mass of the other, it will also have twice the kinetic energy. K = 1 2 m v 2. An object’s kinetic energy is directly related to its mass. Determine if the potential energy is attractive or repulsive for example, gravitational. To draw the energy graph of a system, the following method should be used: If an object is not moving, it has no kinetic energy. We take precisely the same steps to draw the energy diagram for a mass on a spring, but there are some differences, such as two forbidden regions and a different slope for every position, and there is one additional feature for this potential that doesn't exist for the case of gravity: We then extend this definition to any system of particles by adding up the kinetic energies of all the constituent particles:
and potential energy explanation labeled vector illustration
Web the kinetic energy formula works in classical physics, but it starts to deviate from true energy when the velocity approaches the speed of light (c). How to construct an energy graph. K = 1 2 m v 2. Action plan concept with icons action plan concept with icons kinetic energy drawing stock illustrations. An object’s kinetic energy is directly.
Energy Definition Formula Examples Teachoo vrogue.co
An object’s kinetic energy is directly related to its mass. K = ∑ 1 2 m v 2. Speed is the magnitude of velocity, so you can use it in the. This is the energy between interacting objects, and this energy can be either attractive or repulsive. Web kinetic energy is the energy that any object with mass has simply.
Potential and energy diagram. 27798551 Vector Art at Vecteezy
K = 1 2 m v 2. Action plan concept with icons action plan concept with icons kinetic energy drawing stock illustrations. Web for example a standard baseball is about 145 g or 0.145 kg and has a terminal velocity of about 33 m/s so it has a kinetic energy of ek = 0.145 * 33^2 = 0.145 * 1089.
Energy 20+ Examples, Definition, Formula, Types
How to calculate kinetic energy. Web they are typically used to represent the kinetic and potential energy within a system, in addition to a horizontal line that depicts the total mechanical energy of the system. We then extend this definition to any system of particles by adding up the kinetic energies of all the constituent particles: We take precisely the.
Energy Definition, Example and Derivation
This is the energy between interacting objects, and this energy can be either attractive or repulsive. Web they are typically used to represent the kinetic and potential energy within a system, in addition to a horizontal line that depicts the total mechanical energy of the system. An object’s kinetic energy is directly related to its mass. K = ∑ 1.
Potential And Energy Diagram Clip Art Cycle Drawing Vector
Speed is the magnitude of velocity, so you can use it in the. Drawing of kinetic energy stock illustrations If an object is not moving, it has no kinetic energy. Imagine two objects moving at the same speed. The key to solving kinetic energy problems is to remember that 1 joule equals 1 kg⋅m 2 ⋅s −2.
Energy Equation Examples Tessshebaylo
Web they are typically used to represent the kinetic and potential energy within a system, in addition to a horizontal line that depicts the total mechanical energy of the system. To draw the energy graph of a system, the following method should be used: This is the energy between interacting objects, and this energy can be either attractive or repulsive..
Diagram Of Energy
The key to solving kinetic energy problems is to remember that 1 joule equals 1 kg⋅m 2 ⋅s −2. Drawing of kinetic energy stock illustrations Determine if the potential energy is attractive or repulsive for example, gravitational. How to calculate kinetic energy. This is the energy between interacting objects, and this energy can be either attractive or repulsive.
Energy 20+ Examples, Definition, Formula, Types
This is the energy between interacting objects, and this energy can be either attractive or repulsive. How to construct an energy graph. The key to solving kinetic energy problems is to remember that 1 joule equals 1 kg⋅m 2 ⋅s −2. If an object is not moving, it has no kinetic energy. We take precisely the same steps to draw.
Energy Definition Formula Examples Teachoo vrogue.co
Action plan concept with icons action plan concept with icons kinetic energy drawing stock illustrations. If one object has twice the mass of the other, it will also have twice the kinetic energy. Determine if the potential energy is attractive or repulsive for example, gravitational. The key to solving kinetic energy problems is to remember that 1 joule equals 1.
To Draw The Energy Graph Of A System, The Following Method Should Be Used:
How to calculate kinetic energy. Web for example a standard baseball is about 145 g or 0.145 kg and has a terminal velocity of about 33 m/s so it has a kinetic energy of ek = 0.145 * 33^2 = 0.145 * 1089 = 157.9 j. So as the baseball accelerates from 0 to 33 m/s it will gain kinetic energy but when the velocity stops increasing the kinetic energy stops increasing as well. Web kinetic energy is the energy that any object with mass has simply because it is moving.
Speed Is The Magnitude Of Velocity, So You Can Use It In The.
Drawing of kinetic energy stock illustrations Imagine two objects moving at the same speed. K = ∑ 1 2mv2. An object’s kinetic energy is directly related to its mass.
Web Kinetic Energy Is K On An Energy Graph And Has The Formula [Math]\Displaystyle{ \Frac{1}{2}Mv^2 }[/Math].
Determine if the potential energy is attractive or repulsive for example, gravitational. If an object is not moving, it has no kinetic energy. Web the kinetic energy formula works in classical physics, but it starts to deviate from true energy when the velocity approaches the speed of light (c). K = 1 2 m v 2.
How To Construct An Energy Graph.
Web they are typically used to represent the kinetic and potential energy within a system, in addition to a horizontal line that depicts the total mechanical energy of the system. This is the energy between interacting objects, and this energy can be either attractive or repulsive. If one object has twice the mass of the other, it will also have twice the kinetic energy. The key to solving kinetic energy problems is to remember that 1 joule equals 1 kg⋅m 2 ⋅s −2.