Molecular Orbital Drawing
Molecular Orbital Drawing - Web in molecular orbital theory, the bonding between atoms is described as a combination of their atomic orbitals. Web in draw tools window select a tool for analysis/editing, e.g. The applications of the mo theory extend. Draw two lines to create three columns. The molecular orbital energy diagram for [latex]\ce{o2}[/latex] predicts two unpaired electrons. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as shown in figure 7.7.15. Web we draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in figure 7.7.12. Web a new version of strong laser interaction model package for atoms and molecules is presented. Web molecular orbital diagram practice. Top brandsfeatured collections>80% items are newhuge savings
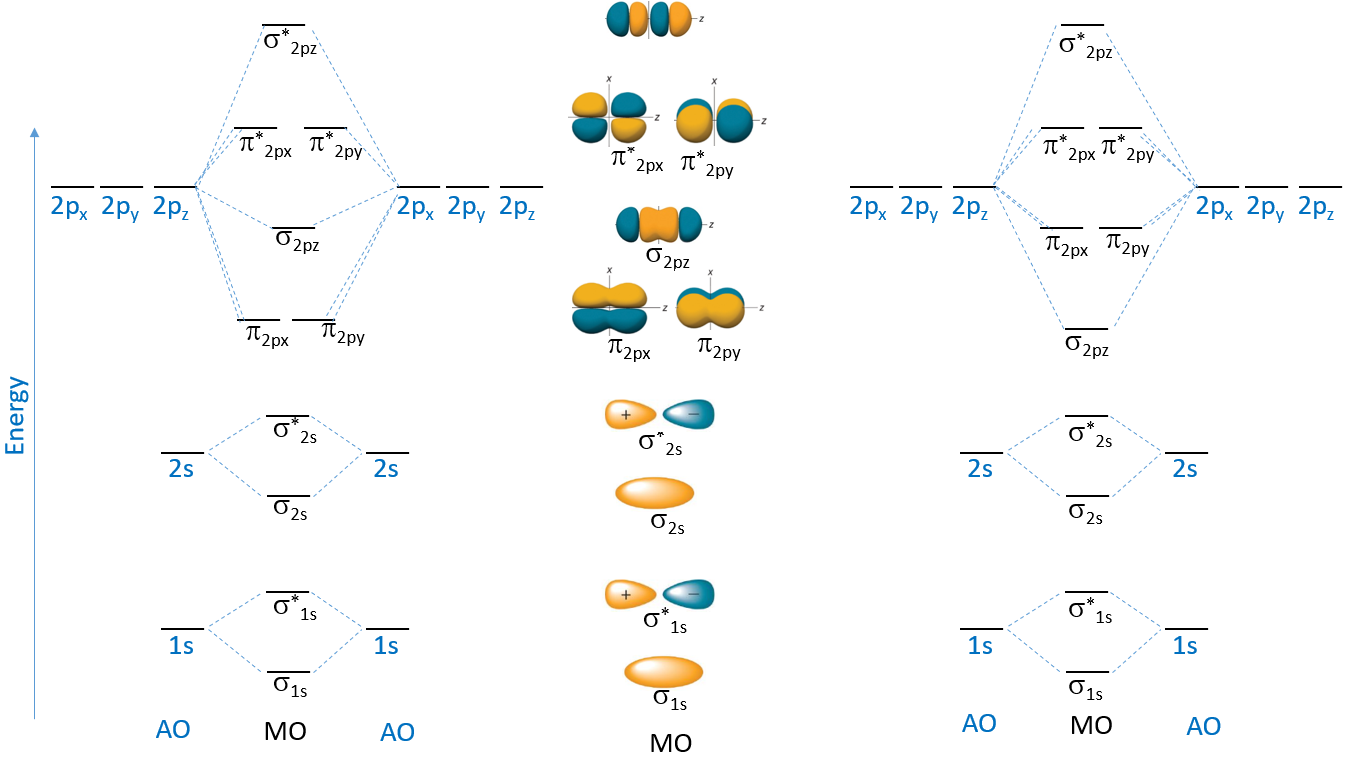
University of sydney has created a practice website for reviewing different parts of molecular orbital diagrams. Mo theory takes the idea of atomic orbitals overlapping to a new level, where new molecular orbitals are generated using a mathematical process called linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao). Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as shown in figure 7.7.15. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the he 2 2 + ion. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. Valence bond theory and molecular. Compare the bond order to that seen in the lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion h 2 +. Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d.) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3.) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories:
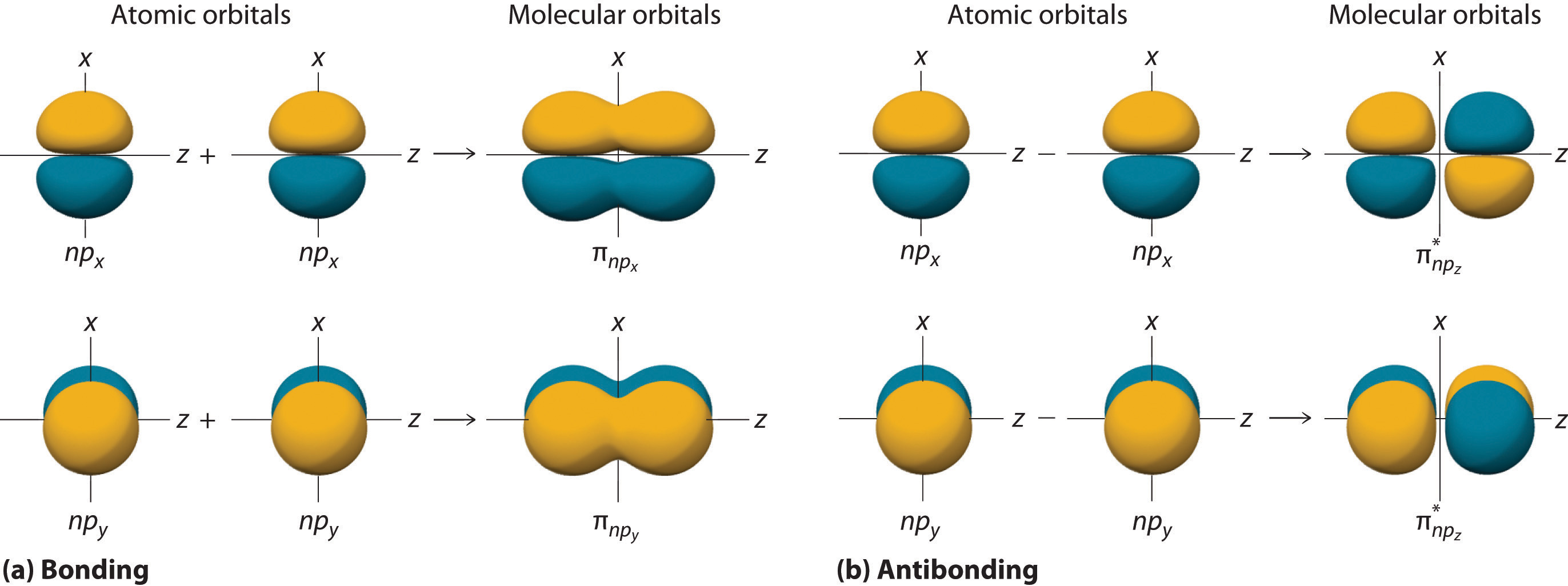
Molecular orbitals share many similarities. If we arbitrarily define the z axis of the coordinate system for the o 2 molecule as the axis along which the. The molecular orbital energy diagram for [latex]\ce{o2}[/latex] predicts two unpaired electrons. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. In the molecular orbital theory, the electrons are delocalized. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion h 2 +. Considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. Now some of them are gonna be so. As atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form. To allow space for the next step, draw the orbitals further apart than you would for an atomic.
10.5 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
Draw two lines to create three columns. Compare the bond order to that seen in the lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). If we arbitrarily define the z axis of the coordinate system for the o 2 molecule as the axis along which.
6.6 3D Representation of Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
Considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. Web drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. To allow space for the next step, draw the orbitals further apart than you would for an atomic. We can,.
Ozone Molecular Orbital Diagram
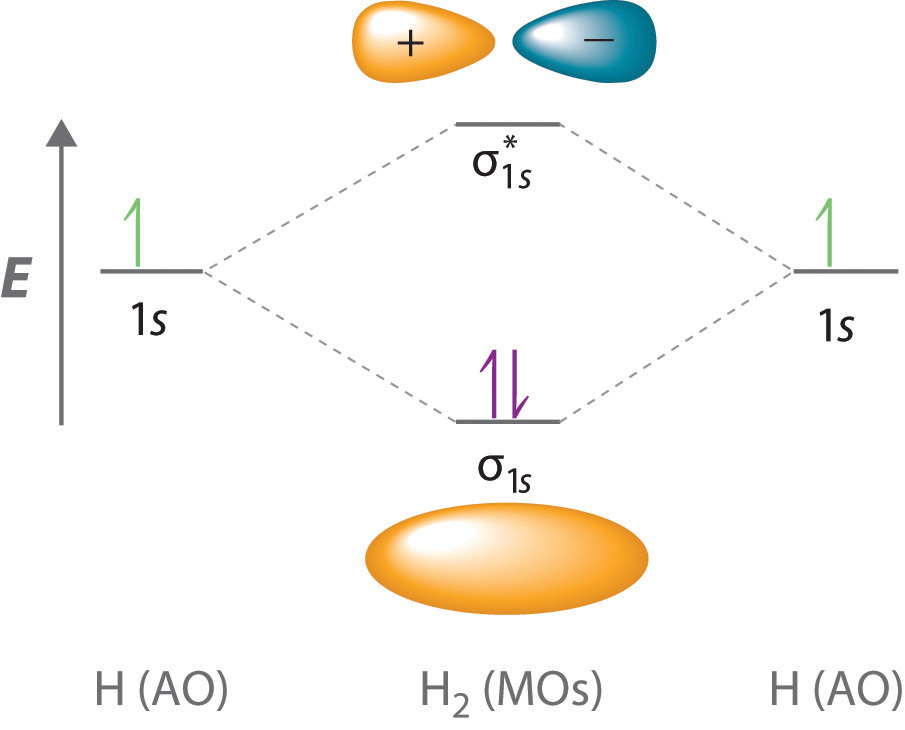
Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d.) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3.) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion h.
Orbital Diagram For Fe3+
The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. The molecular orbital energy diagram for [latex]\ce{o2}[/latex] predicts two unpaired electrons. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion h 2 +. Each.
Molecular Orbitals Diagrams
You're not gonna find these rules anywhere because i made most of them up trying to look at all the different types of molecular orbital's you might have to arrange and figuring out rules that would work for all of them. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Abstract (tl;dr) molecular orbital diagrams are a.
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation
(a) this diagram shows the formation of a bonding σ 1s molecular orbital for h 2 as the sum. By selecting orbital/peak selection tool and clicking on the molecular orbital energy level of interest you will see in ao coefficients window decomposition of the selected molecular orbital into. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms.
9.3 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as shown in figure 7.7.15. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding. The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. Web a new.
37+ Molecular Orbital Geometry Image GM
Web so guys here are seven rules for drawing molecular orbital's and just a heads up. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, cl 2. The molecular orbital energy diagram for [latex]\ce{o2}[/latex] predicts two unpaired electrons. Web a molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital.
[Best Answer] draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 and calculate
Three year warrantyanatomically correctlarge quantity discountshigh quality models Determine the total number of valence electrons in the he 2 2 + ion. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as shown in figure 7.7.15. Valence bond theory and molecular. In the molecular orbital theory, the electrons are delocalized.
4.9 Molecular Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
You're not gonna find these rules anywhere because i made most of them up trying to look at all the different types of molecular orbital's you might have to arrange and figuring out rules that would work for all of them. Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d.) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3.) combines.
Web In Draw Tools Window Select A Tool For Analysis/Editing, E.g.
A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic. To allow space for the next step, draw the orbitals further apart than you would for an atomic. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as shown in figure 7.7.15. Web learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more.
If We Arbitrarily Define The Z Axis Of The Coordinate System For The O 2 Molecule As The Axis Along Which The.
The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. The molecular orbital (mo) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. Web sidra ayub (ucd) 7.3:
Be Sure To Obey The Pauli Principle And Hund’s Rule While Doing So.
Drawing a molecular orbital of benzene with 5 nodes is like solving 5 faces of a rubik’s cube: Valence bond theory and molecular. Molecular orbitals for the h 2 molecule. Top brandsfeatured collections>80% items are newhuge savings
Web So Guys Here Are Seven Rules For Drawing Molecular Orbital's And Just A Heads Up.
You're not gonna find these rules anywhere because i made most of them up trying to look at all the different types of molecular orbital's you might have to arrange and figuring out rules that would work for all of them. (a) this diagram shows the formation of a bonding σ 1s molecular orbital for h 2 as the sum. Web molecular orbital theory. For this example, we will be using chlorine.



![[Best Answer] draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 and calculate](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d20/b492acf8cb9ff01954c3929a3b7a93c7.jpg)