Terrain Features Draw
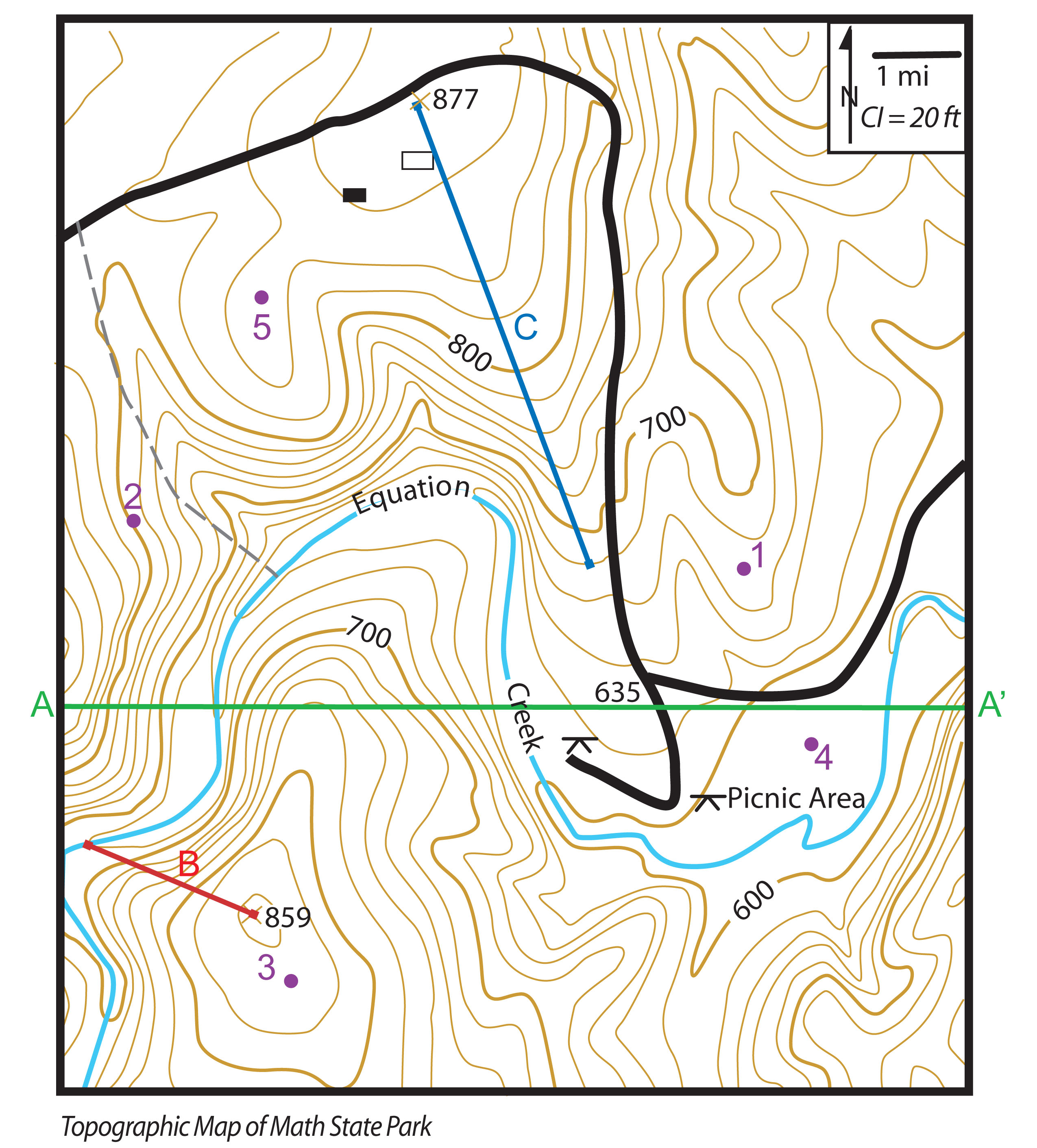
Terrain Features Draw - Not to be confused with a ridge, a ridgeline is a line of high ground with lower elevations on both sides. A low point in the ground or sinkhole. Contour lines depict a u or v shape pointing toward the high ground. Web here are the terrain features that catch my attention: A draw could be considered as. Web spur (minor terrain feature) spur. The area of low ground itself is the draw, and it is defined by the spurs surrounding it. A draw could be considered as. Web i’ll be telling you all about the five major terrain features that every prepper should know in the rest of this article, and we’ll discuss the minor terrain features in a separate article. And one example of each minor terrain.
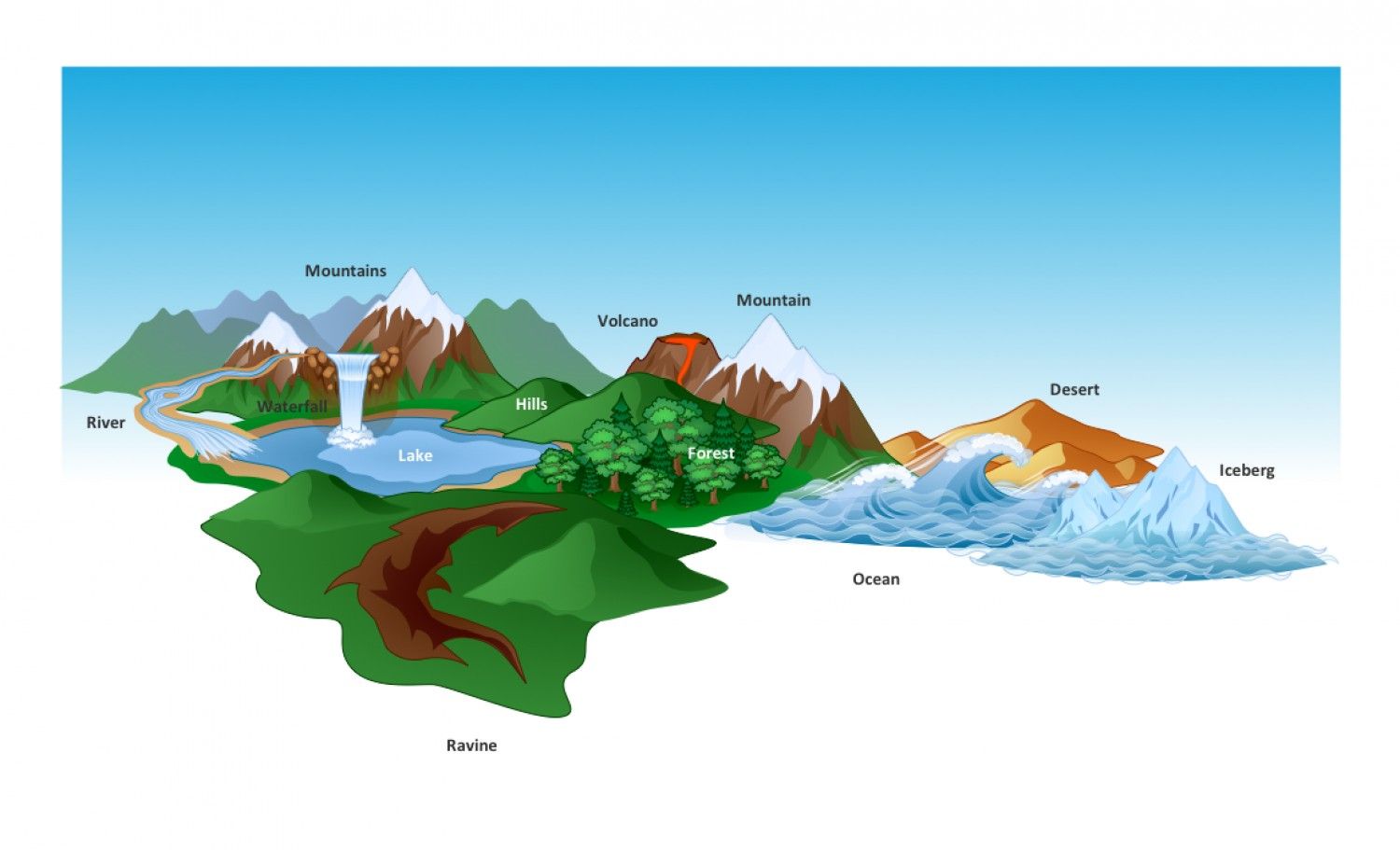
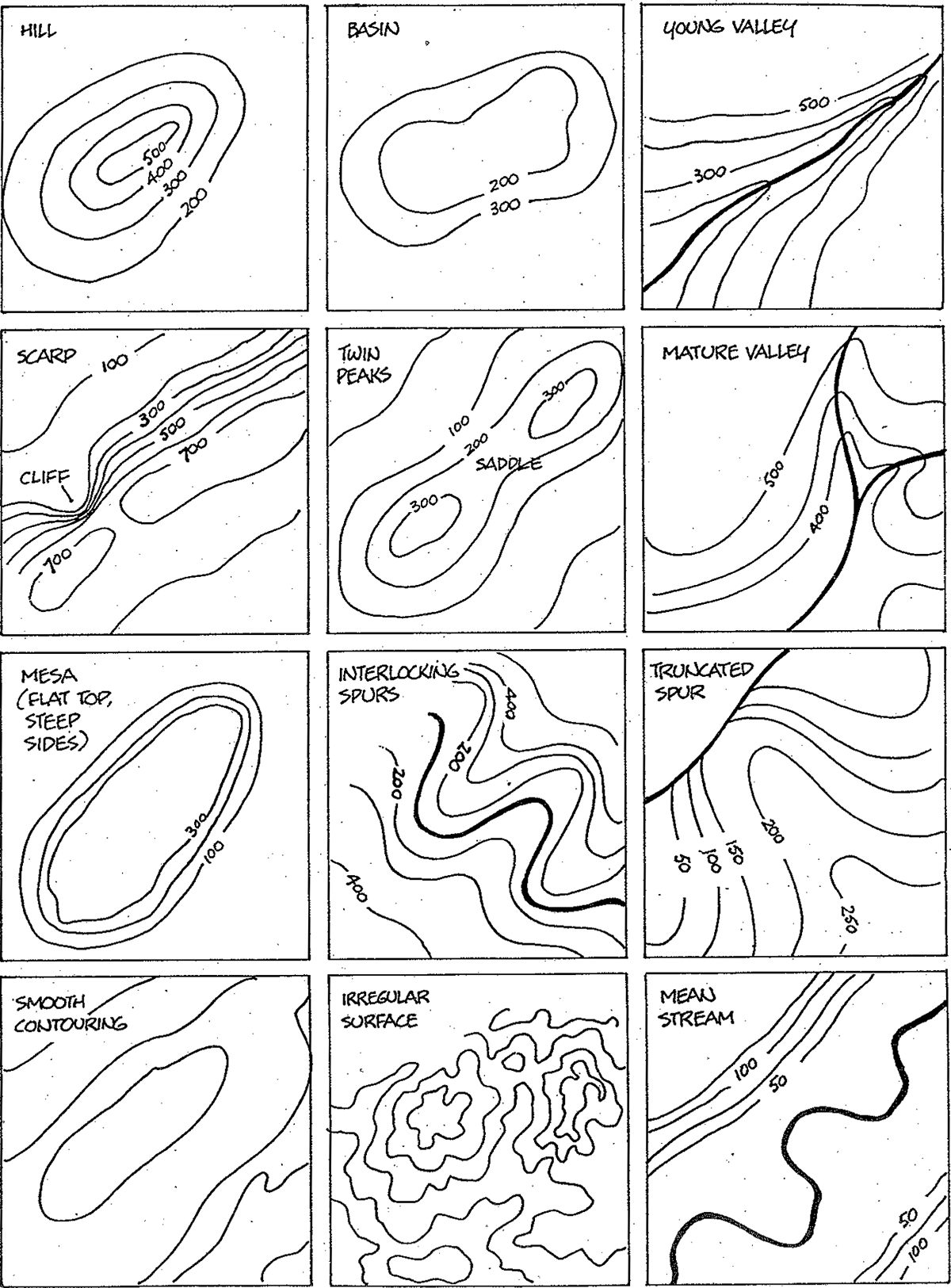
Hills are the most fundamental and instantly recognizable terrain feature, defined as points or areas of high ground. Tectonic plate movement under earth can create landforms by pushing up mountains and hills. Short, continuously sloping line of higher ground normally jutting out from the side of a ridge. If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upward in three directions and downward in the other direction. Web spur (minor terrain feature) spur. Import a surveyor dwg file for a site plan or terrain perimeter. If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upwards in three directions and downward in the other direction. The three minor terrain features are: Web the five major terrain features are: A draw could be considered as.
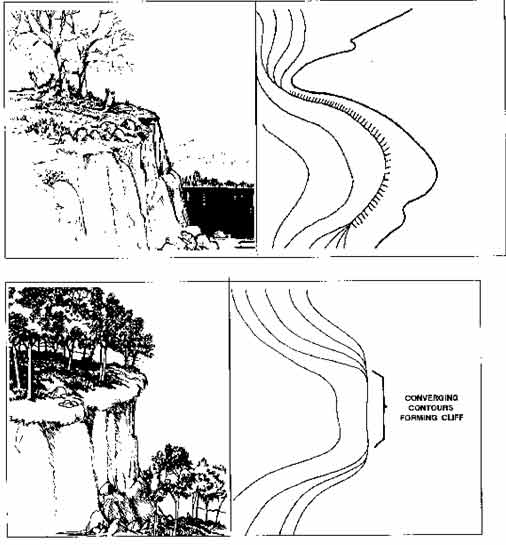
The contour lines depicting a draw are u. Terrain features can be learned using the fist or hand to show what each would look like on the ground. Low ground between two parallel ridges or spurs, with ground sloping upward on either side. A spur is often formed by two rough parallel streams, which cut draws down the side of a ridge. Import a surveyor dwg file for a site plan or terrain perimeter. If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upwards in three directions and downward in the other direction. A low point in the ground or sinkhole. A draw could be considered as. A draw is a less developed stream course than a valley. The serrated shoulder design maximizes.
Landforms Drawing at Explore collection of
A draw could be considered as. A draw is a less developed stream course than a valley. However, while valleys are by nature. The ground sloped down in three directions and up in one direction. A draw could be considered as.
How Terrain Features are Depicted with Contour Lines
If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upwards in three directions and downward in the other direction. Topographic maps use contour lines to express 3d reality in two dimensions, allowing people to visualize rising and falling landscapes, and identify features such as mountains or canyons by height and shape. Web the apple pencil pro carries those advanced.
Map Basics and Identifying Terrain Features
Deer like to walk these ridges, with the mature bucks using less noticeable trails just over the edge of the ridge, allowing them to stay hidden. Erosion by water and wind can wear. The area of low ground itself is the draw, and it is defined by the spurs surrounding it. Hill, ridge, valley, saddle, and depression. Web the basics.
Map Reading Common Terrain Features In A Topographic Map
And one example of each minor terrain. If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upward in three directions and downward in the other direction. A draw could be considered as. The serrated shoulder design maximizes. A draw is a less developed stream course than a valley.
Features of Topographic Maps Bushwalking Leadership SA
Randomly number the circled terrain. Reddit user reveals his retirement account’s “hourly wage” — here’s how much your. Hill, ridge, valley, saddle, and depression. The area of low ground itself is the draw, and it is defined by the spurs surrounding it. If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upward in three directions and downward in the.
PPT Identify Terrain Features on a Map PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web the five major terrain features are: A draw is a less developed stream course than a valley. If standing in a draw, the ground slopes upward in three directions and downward in one. If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upward in three directions and downward in the other direction. Web spur (minor terrain feature) spur.
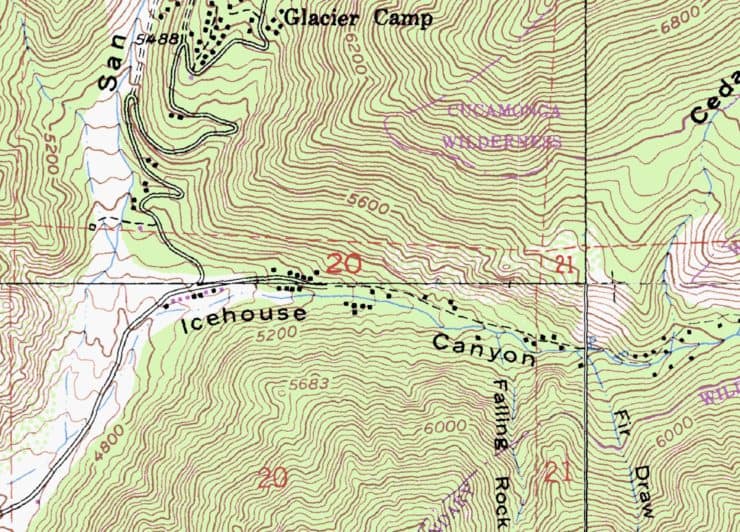
How To Read a Topographic Map
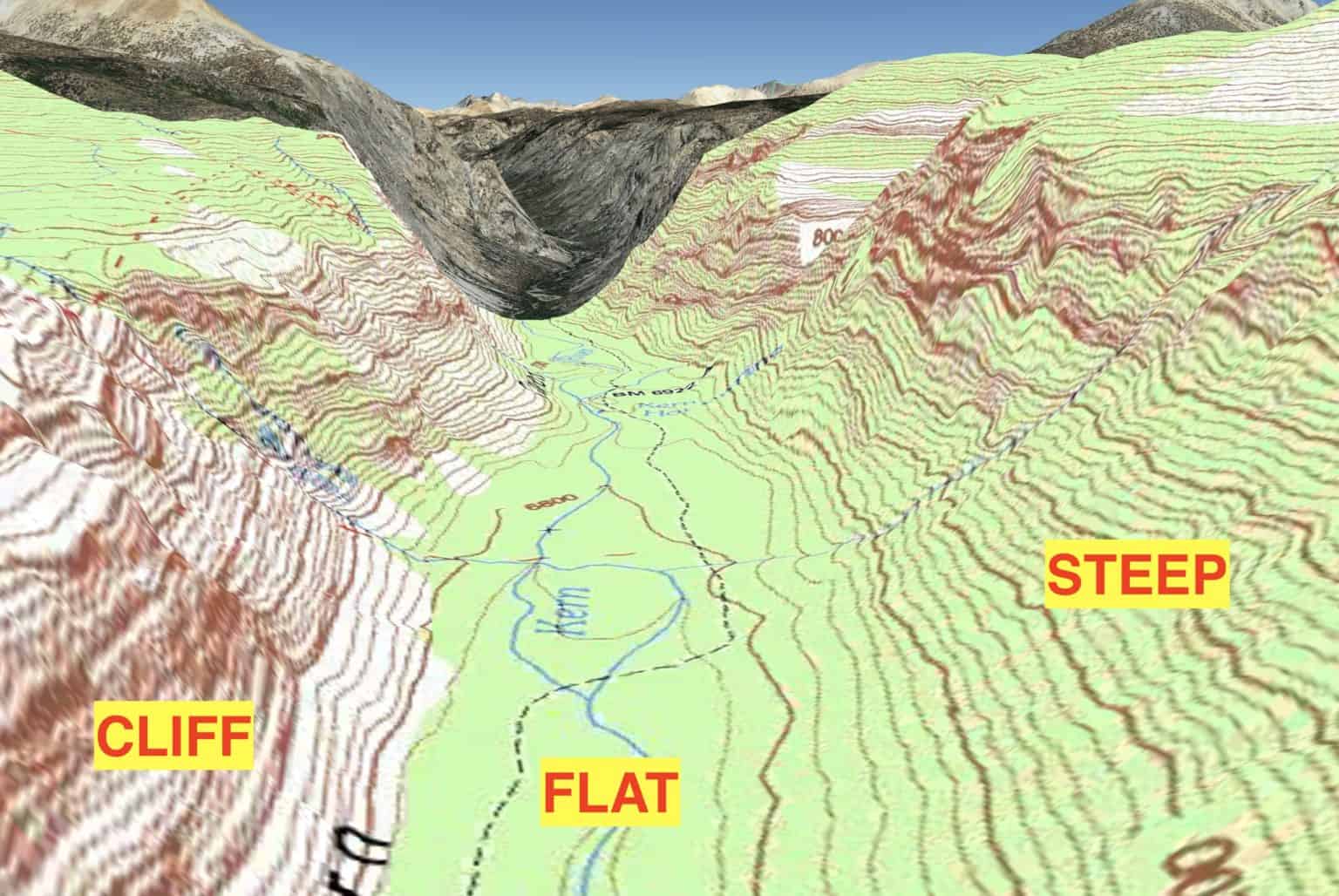
In a draw, there is essentially no level ground and, therefore, little or no maneuver room within its confines. Low ground between two parallel ridges or spurs, with ground sloping upward on either side. Terrain features are identified in the same manner on all maps, regardless of the contour interval, but you must realize that a hill in the rocky.
Topographic Maps and Slopes
Fills are shown on a map when they are at least 10 feet high, and they are drawn with a contour line along the fill line. Hills are the most fundamental and instantly recognizable terrain feature, defined as points or areas of high ground. If you are standing in a draw, the ground slopes upward in three directions and downward.
How To Read a Topographic Map
Reddit user reveals his retirement account’s “hourly wage” — here’s how much your. In a draw, there is essentially no level ground and, therefore, little or no maneuver room within its confines. Short, continuously sloping line of higher ground normally jutting out from the side of a ridge. Web the basics of creating a terrain perimeter, sloping a lot, road.
PPT Identify Terrain Features on a Map PowerPoint Presentation, free
If standing in a draw, the ground slopes upward in three directions and downward in one. Terrain features can be learned using the fist or hand to show what each would look like on the ground. Deer like to walk these ridges, with the mature bucks using less noticeable trails just over the edge of the ridge, allowing them to.
The Serrated Shoulder Design Maximizes.
One example of each major terrain feature. A spur is a short, continuous sloping line of higher ground, normally jutting out from the side of a ridge. The ground sloped down in three directions and up in one direction. Terrain features can be learned using the fist or hand to show what each would look like on the ground.
If You Are Standing In A Draw, The Ground Slopes Upwards In Three Directions And Downward In The Other Direction.
Contour lines depict a u or v shape pointing toward the high ground. Hill, valley, ridge, saddle, depression. Topographic maps use contour lines to express 3d reality in two dimensions, allowing people to visualize rising and falling landscapes, and identify features such as mountains or canyons by height and shape. A draw could be considered as.
Short, Continuously Sloping Line Of Higher Ground Normally Jutting Out From The Side Of A Ridge.
When you are on a hilltop, the ground slopes down. Web the basics of creating a terrain perimeter, sloping a lot, road tools, building pad height, terrain modifiers, terrain & retaining walls, setbacks and adding a north pointer. And one example of each minor terrain. Low ground between two parallel ridges or spurs, with ground sloping upward on either side.
Web Typical Draw, Little Carpathians.
Trace a terrain lot image to create a site plan or terrain perimeter. The area of low ground itself is the draw, and it is defined by the spurs surrounding it. Minor landforms include buttes, canyons, valleys, and basins. Contour lines on a map depict a spur.