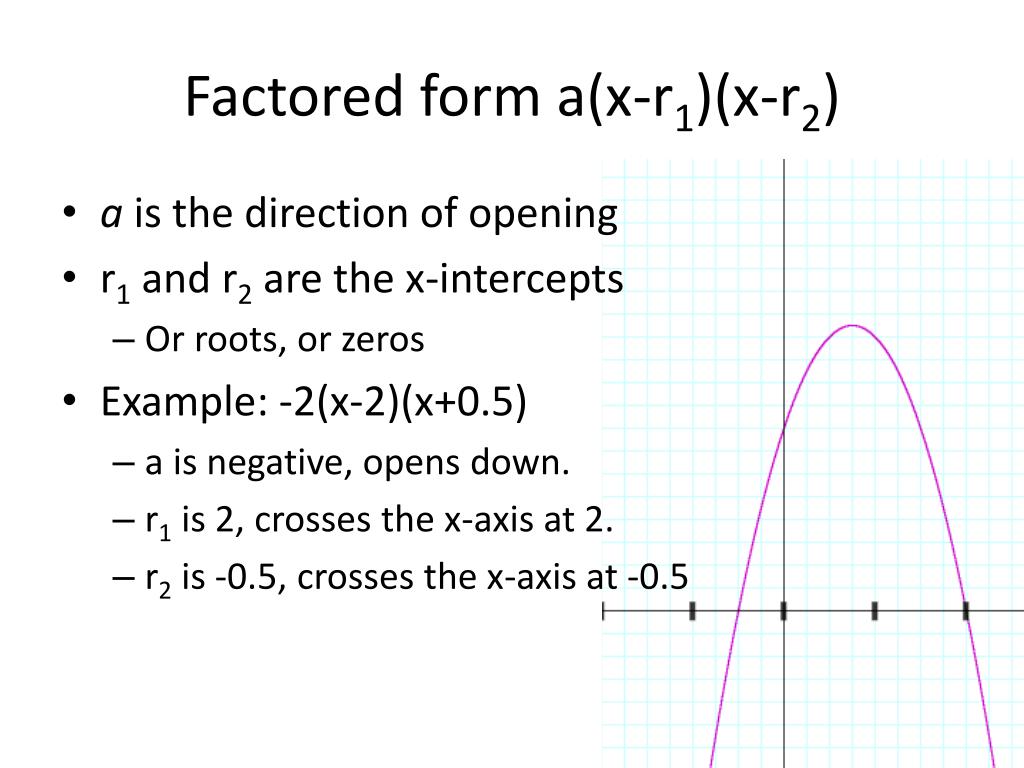
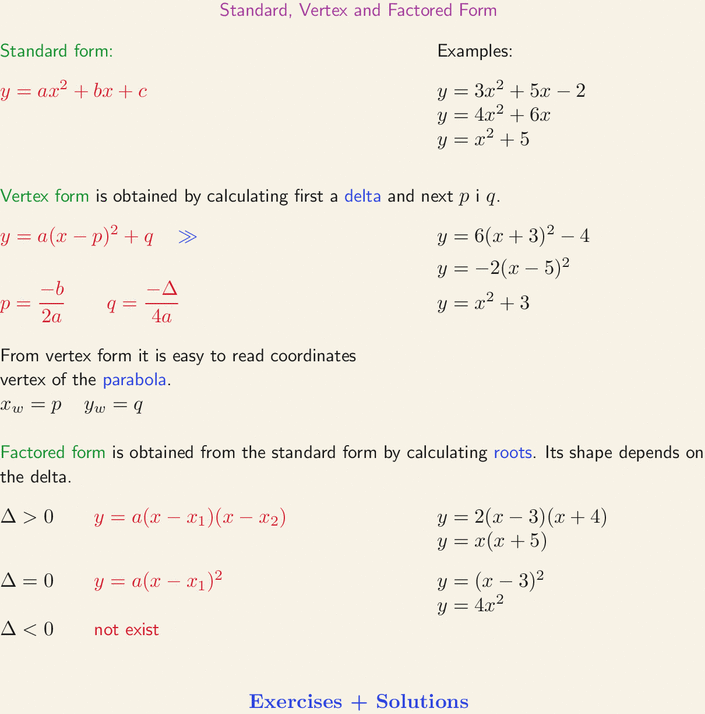
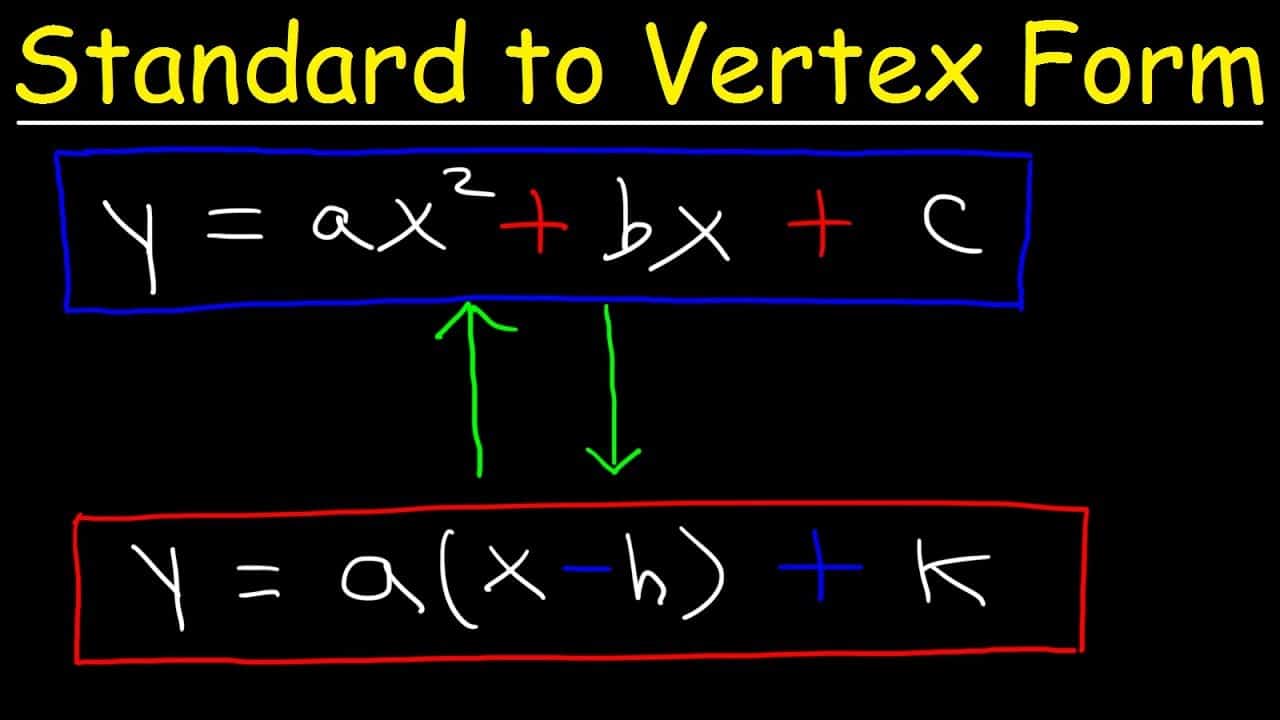
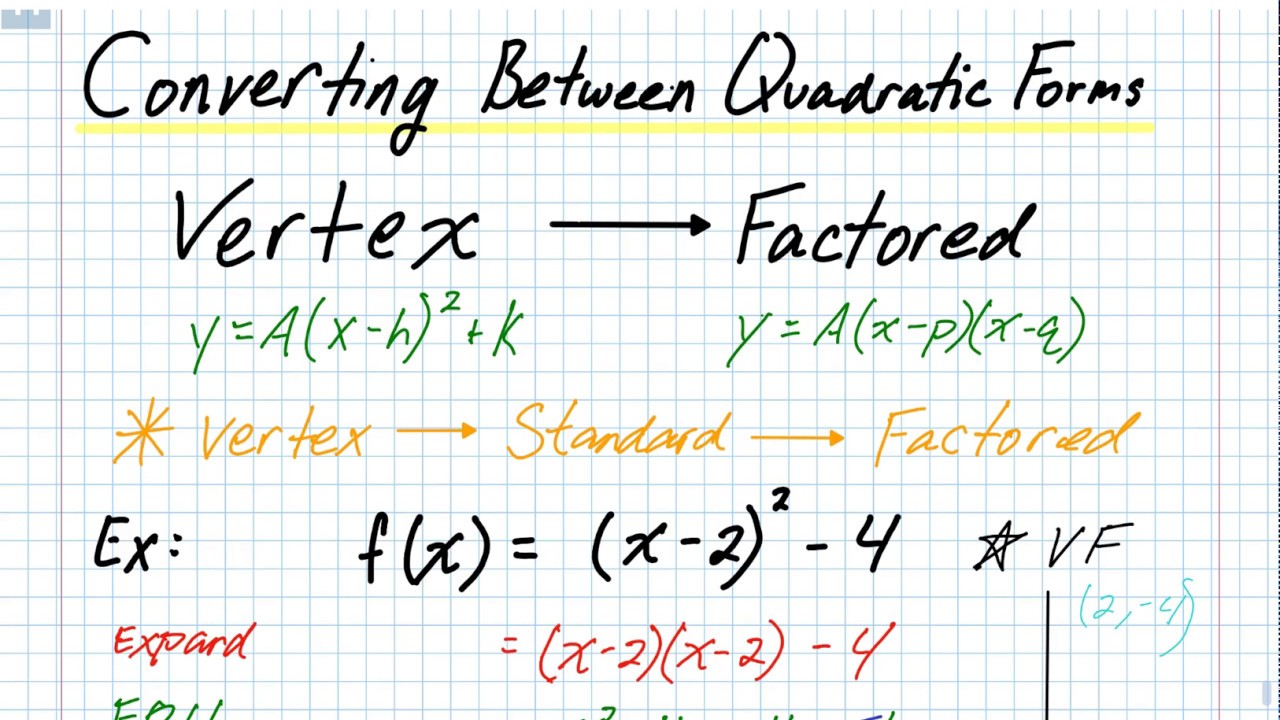
Vertex To Factored Form
Vertex To Factored Form - All resources for big idea 4. Then use the quadratic root formula to determine the roots. = 3(x2 +14x + 49) −2. The vertex form of a quadratic function is expressed as: Change the form of either an equation given in vertex form or an equation given in factored form to make connections between the two forms. As you can see, we need to know three parameters to write a quadratic vertex form. What is the vertex form of a quadratic function? Web vertex form / standard form / factored form. = 3x2 + 42x +145. Y = x2 − 6x − 7 coefficient of x2 is 1.
Web vertex form / standard form / factored form. This formula also works if the parabola has only one root. Change the form of either an equation given in vertex form or an equation given in factored form to make connections between the two forms. What is the vertex form of a quadratic function? We can write the vertex form equation as: = 3(x2 +14x + 49) −2. Y = x2 − 6x − 7 coefficient of x2 is 1. Y = 3(x + 7)2 − 2. And, if the vertex isn't spaced exactly between the two zeros, then it wouldn't be symmetrical. Using the formula for determining roots (and a very sharp pencil) −b ± √b2 −4ac 2a.
Web vertex form / standard form / factored form. Then use the quadratic root formula to determine the roots. Web connecting vertex form to factored form. (i) converting into factored form : As you can see, we need to know three parameters to write a quadratic vertex form. This formula also works if the parabola has only one root. Web there are three forms of quadratic functions such as the standard or general form, factored or intercept form, and the vertex form. We can write the vertex form equation as: What is the vertex form of a quadratic function? The structure of a quadratic equation provides insights about its key characteristics.:
Vertex, Standard, and Factored form of a quadratic YouTube
Web connecting vertex form to factored form. Y = x2 − 6x − 7 coefficient of x2 is 1. (i) converting into vertex form : Then use the quadratic root formula to determine the roots. Y = 3(x + 7)2 − 2.
PPT Vertex Form PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2384030
From there, you must complete the square (see above!). The vertex form of a quadratic function is expressed as: Expand the vertex form into standard quadratic form; This formula also works if the parabola has only one root. Y = 3(x + 7)2 − 2.
Standard, Vertex and Factored Form}
= 3x2 + 42x +145. The vertex form of a quadratic function is expressed as: One of them is a, the same as in the standard form. Then use the quadratic root formula to determine the roots. Web intuitively, the vertex form of a parabola is the one that includes the vertex’s details inside.
Vertex from Factored Form YouTube
Y = 3(x + 7)2 − 2. Expand the vertex form into standard quadratic form; Write the coefficient of x as multiple of 2. All resources for big idea 4. Change the form of either an equation given in vertex form or an equation given in factored form to make connections between the two forms.
Standard Form to Vertex Form? With Easy Examples Get Education Bee
The vertex form of a quadratic function is expressed as: One of them is a, the same as in the standard form. To find the vertex from factored form, you must first expand the equation into standard form. Y = 3(x + 7)2 − 2. This formula also works if the parabola has only one root.
A1 Converting Vertex Form to Factored Form YouTube
Y = x2 − 6x − 7 coefficient of x2 is 1. Web intuitively, the vertex form of a parabola is the one that includes the vertex’s details inside. Change the form of either an equation given in vertex form or an equation given in factored form to make connections between the two forms. Y = 3(x + 7)2 −.
Converting Vertex Form to Factored Form YouTube
= 3x2 + 42x +145. From there, you must complete the square (see above!). Expand the vertex form into standard quadratic form; Web intuitively, the vertex form of a parabola is the one that includes the vertex’s details inside. (i) converting into vertex form :
ShowMe find vertex from factored form
Write the coefficient of x as multiple of 2. Web there are three forms of quadratic functions such as the standard or general form, factored or intercept form, and the vertex form. (a will stay the same, h is x, and k is y). Change the form of either an equation given in vertex form or an equation given in.
Quadratic Vertex/Factored Form Exploration GeoGebra
One of them is a, the same as in the standard form. (i) converting into factored form : (a will stay the same, h is x, and k is y). Y = x2 − 6x − 7 coefficient of x2 is 1. This is because the vertex must be on the axis of symmetry.
vertex from factored form YouTube
Web vertex form / standard form / factored form. Y = x2 − 6x − 7 coefficient of x2 is 1. (a will stay the same, h is x, and k is y). Web there are three forms of quadratic functions such as the standard or general form, factored or intercept form, and the vertex form. (i) converting into vertex.
We Can Write The Vertex Form Equation As:
And, if the vertex isn't spaced exactly between the two zeros, then it wouldn't be symmetrical. The structure of a quadratic equation provides insights about its key characteristics.: Y = x2 − 6x − 7 coefficient of x2 is 1. Web connecting vertex form to factored form.
(I) Converting Into Factored Form :
The vertex form of a quadratic function is expressed as: All resources for big idea 4. Using the formula for determining roots (and a very sharp pencil) −b ± √b2 −4ac 2a. This is because the vertex must be on the axis of symmetry.
Web Vertex Form / Standard Form / Factored Form.
From there, you must complete the square (see above!). Y = 3(x + 7)2 − 2. This formula also works if the parabola has only one root. Expand the vertex form into standard quadratic form;
(I) Converting Into Vertex Form :
(a will stay the same, h is x, and k is y). Write the coefficient of x as multiple of 2. Change the form of either an equation given in vertex form or an equation given in factored form to make connections between the two forms. Web intuitively, the vertex form of a parabola is the one that includes the vertex’s details inside.