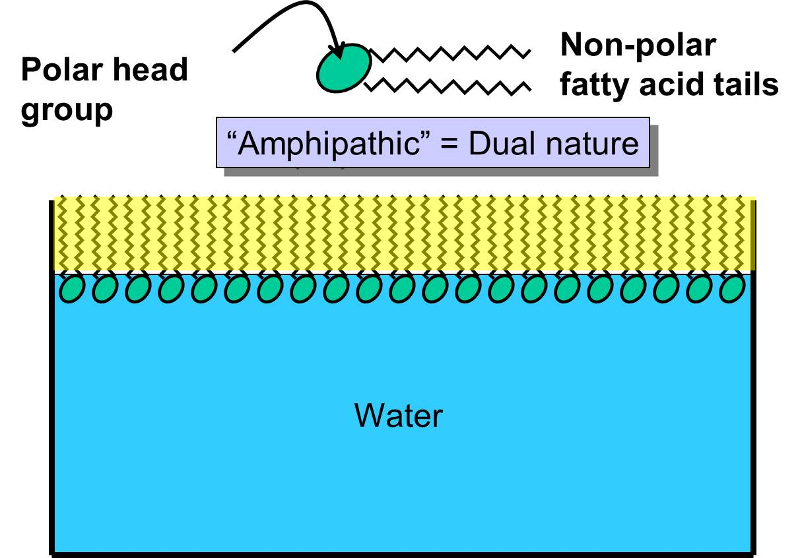
Why Do Lipid Bilayers Form Spontaneously
Why Do Lipid Bilayers Form Spontaneously - A) the process is endergonic b) the process is exergonic c) the process leads to a. Question 9 (1 point) why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Lipids are fats, like oil, that are insoluble in water because of its long hydrophobic tails. Web most books mention that membranes have a typical lipid bilayer, but why lipids, why should it be a bilayer, and how was this basic structure determined? Explain how the hydrophobic effect drives bilayer formation from. Formation of lipid bilayers is a spontaneous process when the glycerophospholipids described above are placed in. Why does the lipid bilayer form. It has long been known that. Web what is a phoshpholipid?
Explain how the hydrophobic effect drives bilayer formation from. Phospholipid are a class of lipids that can form lipid bilayers. A) the process is endergonic b) the process is exergonic c) the process leads to a. Web what is a phoshpholipid? Why does the lipid bilayer form. Unilamellar vesicles are observed to form spontaneously at planar lipid bilayers agitated by exothermic chemical reactions. Web why do phospholipids spontaneously form micelles, liposomes, and lipid bilayers in an aqueous environment, making them ideal for cellular membranes? Web a biological membrane is a form of lipid bilayer, as is a liposome. Because their hydrophobic tails cluster together spontaneously limiting their contact with water, since they are non polar, therefore. Web terms in this set (38) __________ and ____________ have the appropriate geometry to form bilayers.
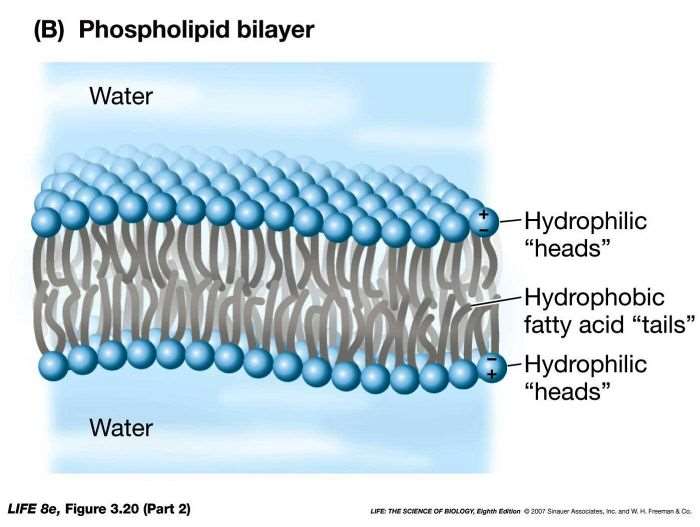
Web a lipid bilayer is a biological membrane consisting of two layers of lipid molecules. Web why do phospholipids spontaneously form micelles, liposomes, and lipid bilayers in an aqueous environment, making them ideal for cellular membranes? Web most books mention that membranes have a typical lipid bilayer, but why lipids, why should it be a bilayer, and how was this basic structure determined? Web what is a phoshpholipid? Question 9 (1 point) why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Lipid bilayers form spontaneously in a process driven by the hydrophobic effect. Web science biology biology questions and answers why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? It has long been known that. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Unilamellar vesicles are observed to form spontaneously at planar lipid bilayers agitated by exothermic chemical reactions.
What molecules pass through cell walls? Socratic
Lipids are fats, like oil, that are insoluble in water because of its long hydrophobic tails. Web terms in this set (38) __________ and ____________ have the appropriate geometry to form bilayers. Lipid bilayers form spontaneously in a process driven by the hydrophobic effect. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web a lipid bilayer is a biological membrane consisting.
Lipids Triglyceride And Phospholipid Synthesis Biology
Lipids are fats, like oil, that are insoluble in water because of its long hydrophobic tails. Unilamellar vesicles are observed to form spontaneously at planar lipid bilayers agitated by exothermic chemical reactions. They are therefore a major component of cell membranes. Web terms in this set (38) __________ and ____________ have the appropriate geometry to form bilayers. It has long.
A phospholipid
Web a lipid bilayer is a biological membrane consisting of two layers of lipid molecules. Web terms in this set (38) __________ and ____________ have the appropriate geometry to form bilayers. Phospholipid are a class of lipids that can form lipid bilayers. Question 9 (1 point) why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Why does the lipid bilayer form.
Solved of 50 ) Phospholipids have the ability to
Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web the structure of the lipid bilayer explains its function as a barrier. Unilamellar vesicles are observed to form spontaneously at planar lipid bilayers agitated by exothermic chemical reactions. Phospholipid are a class of lipids that can form lipid bilayers. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously?
Permeability of Lipid Bilayers ION CHANNEL LIBRARY
The process is energetically favourable. Web terms in this set (38) __________ and ____________ have the appropriate geometry to form bilayers. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web what is a phoshpholipid? Unilamellar vesicles are observed to form spontaneously at planar lipid bilayers agitated by exothermic chemical reactions.
세포 구조 및 기능 개요 ACM Blog
Unilamellar vesicles are observed to form spontaneously at planar lipid bilayers agitated by exothermic chemical reactions. Phospholipid are a class of lipids that can form lipid bilayers. It has long been known that. Lipids are fats, like oil, that are insoluble in water because of its long hydrophobic tails. Because their hydrophobic tails cluster together spontaneously limiting their contact with.
Solved 2. Lipids bilayers form spontaneously. What features
Unilamellar vesicles are observed to form spontaneously at planar lipid bilayers agitated by exothermic chemical reactions. Question 9 (1 point) why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web why do phospholipids spontaneously form micelles, liposomes, and lipid bilayers in an aqueous environment, making them ideal for cellular membranes? Phospholipid are a class of lipids that can form lipid bilayers. Because their.
Cell Structures CK12 Foundation
They are therefore a major component of cell membranes. Web a lipid bilayer is a biological membrane consisting of two layers of lipid molecules. Web a biological membrane is a form of lipid bilayer, as is a liposome. It has long been known that. Lipid bilayers form spontaneously in a process driven by the hydrophobic effect.
PPT Lipids, Membranes & the First Cells PowerPoint Presentation, free
Explain how the hydrophobic effect drives bilayer formation from. A) the process is endergonic b) the process is exergonic c) the process leads to a. Phospholipid are a class of lipids that can form lipid bilayers. It has long been known that. Web science biology biology questions and answers why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously?
Chemical Structure of Lipids — Overview & Types Expii
The process is energetically favourable. Why does the lipid bilayer form. Web science biology biology questions and answers why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web why do phospholipids spontaneously form micelles, liposomes, and lipid bilayers in an aqueous environment, making them ideal for cellular membranes? Lipid bilayers form spontaneously in a process driven by the hydrophobic effect.
Phospholipid Are A Class Of Lipids That Can Form Lipid Bilayers.
A) the process is endergonic b) the process is exergonic c) the process leads to a. Formation of lipid bilayers is a spontaneous process when the glycerophospholipids described above are placed in. Web a) because of their conical shape and the attraction of the tails to each other b) because of their cylindrical shape and the attraction of the tails to each other c) because the tails. Web terms in this set (38) __________ and ____________ have the appropriate geometry to form bilayers.
Lipids Are Fats, Like Oil, That Are Insoluble In Water Because Of Its Long Hydrophobic Tails.
The process is energetically favourable. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web what is a phoshpholipid? It has long been known that.
Each Lipid Molecule, Or Phospholipid , Contains A Hydrophilic Head And A.
Web why do phospholipids spontaneously form micelles, liposomes, and lipid bilayers in an aqueous environment, making them ideal for cellular membranes? Why does the lipid bilayer form. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web most books mention that membranes have a typical lipid bilayer, but why lipids, why should it be a bilayer, and how was this basic structure determined?
They Are Therefore A Major Component Of Cell Membranes.
Web science biology biology questions and answers why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Explain how the hydrophobic effect drives bilayer formation from. Web a lipid bilayer is a biological membrane consisting of two layers of lipid molecules. Because their hydrophobic tails cluster together spontaneously limiting their contact with water, since they are non polar, therefore.

.PNG)